Three-layer pixel structure of micro-bolometer
A microbolometer, pixel structure technology, applied in optical radiometry, electrical radiation detectors, radiation pyrometry, etc., can solve problems such as limiting device integration, affecting thermal sensitivity, and limiting device infrared absorptivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
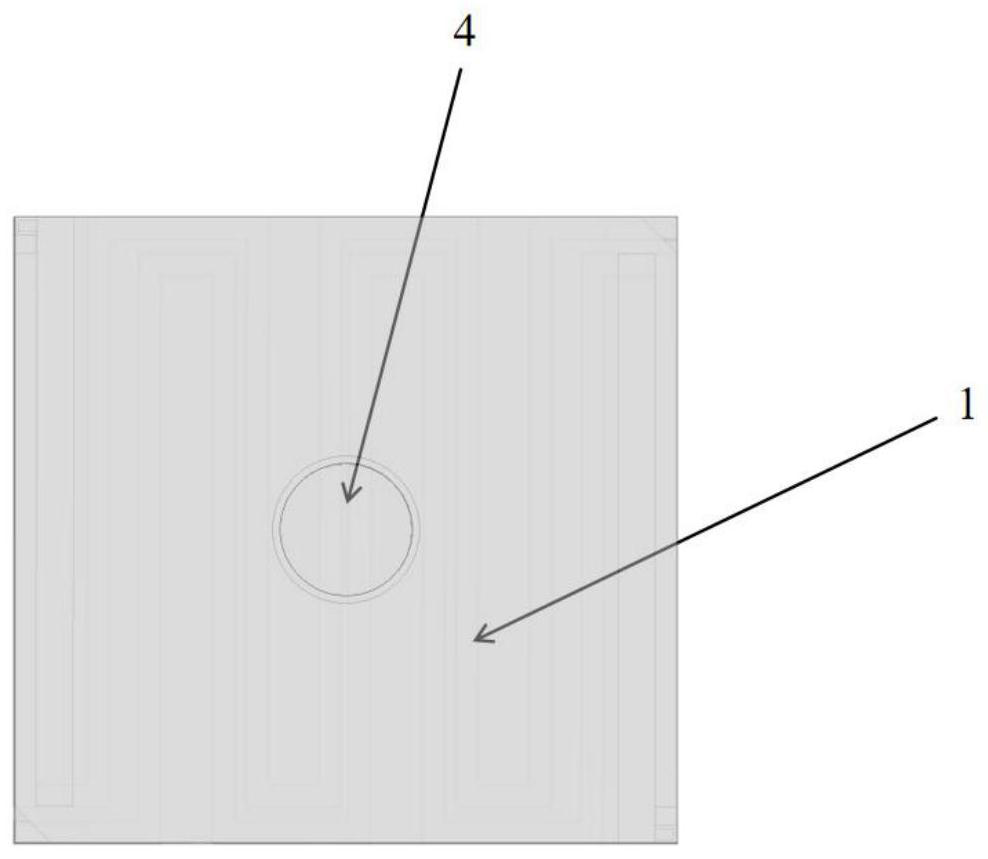
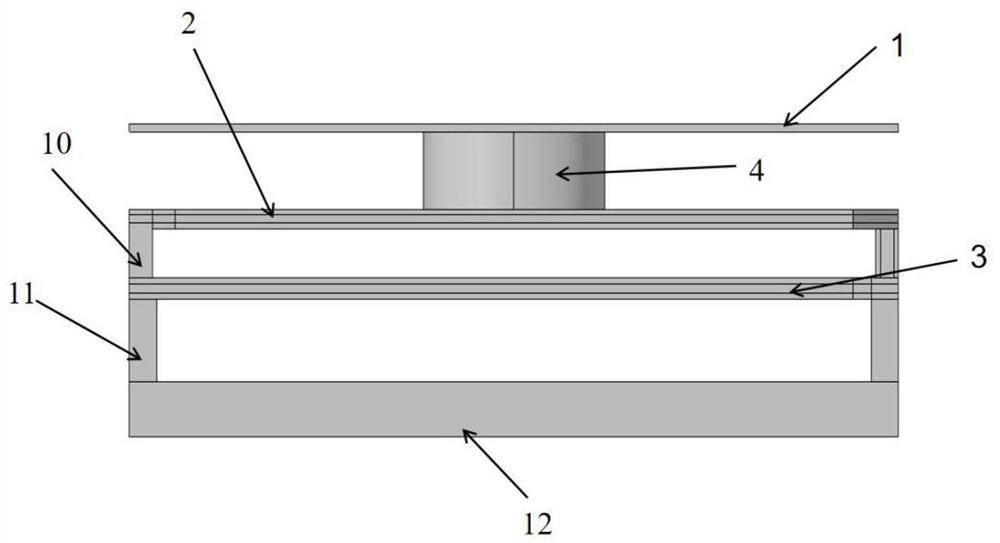
[0023] Specific Embodiment 1: This embodiment describes a three-layer pixel structure of a microbolometer. The three-layer pixel structure is a light-absorbing layer 1, a heat-sensitive layer 2, and an electrode layer from top to bottom. 3. The light-absorbing layer 1 and the heat-sensitive layer 2 are connected through hollow bridges 4, an optical resonant cavity is formed between the light-absorbing layer 1 and the heat-sensitive layer 2, and two electrodes 5 are embedded in the heat-sensitive layer 2, The two electrodes 5 are located on two opposite sides of the thermosensitive layer 2, and the electrode layer 3 includes an electrode layer bridge surface and two rows of bridge legs 6 in a centrally symmetrical triple folded detour structure that are not in contact with each other on the upper surface. and bridge leg two 7, the head end and tail end of each said triple folded circuitous structure are respectively provided with hole one 8 and hole two 9, and the two diagonal s...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: In the three-layer pixel structure of a microbolometer described in Embodiment 1, the light-absorbing layer 1 has a thickness of 0.1um-0.2um and is located on the top of the microbridge. Make the light absorbing layer 1 equal to the pixel area. An optical resonant cavity is formed with the thermosensitive layer 2 . Debugging by the matlab program shows that when the thickness of the light absorbing layer 1 is 0.1um-0.2um, the infrared absorption rate can reach more than 90%.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0025] Specific embodiment three: the three-layer pixel structure of a microbolometer described in specific embodiment one, the height of the hollow bridge column 4 is 2um-2.5um, the thickness is 0.2um-0.5um, and the radius is 2um-3um. The upper surface is a light absorbing layer 1 and the lower surface is a thermosensitive layer 2 . According to the theory of optical resonant cavity, the hollow bridge column 4 has the highest light absorption efficiency when the cavity height is λ / 4. Since the infrared light absorption rate of the pixel is the highest for 8um-10um, the selected height is 2um-2.5um. In consideration of its mechanical stability, the area of the top and bottom of the cylinder should not be too low, and in consideration of the light absorbing layer 1 and the heat sensitive layer 2, the area of the top and bottom of the cylinder should not be too high. Considering the reduction of heat capacity, the thickness of the side wall of the cylinder should not be too...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com