Method for optimizing optical Isin machine system
An optical and optical circuit technology, applied in optics, nonlinear optics, optical computing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of mapping deviation and inability to obtain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
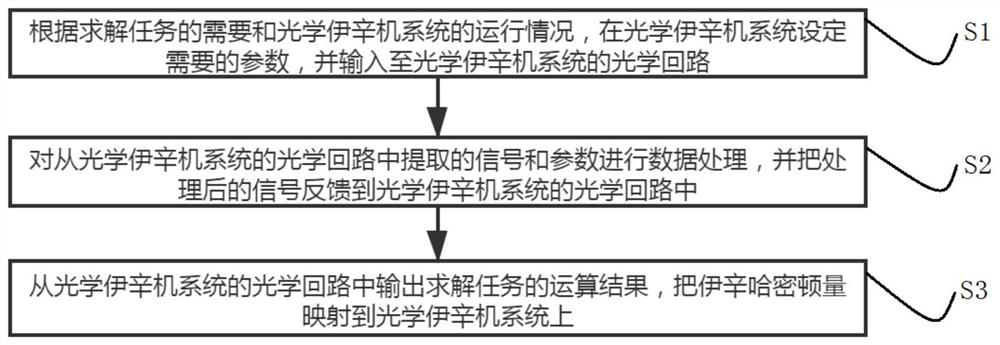
[0047] Such as figure 1 figure 2 and image 3 As shown, a method for optimizing an optical Ising machine system includes the following steps:
[0048] S1: According to the needs of solving tasks and the operation of the optical Ising machine system, set the required parameters in the optical Ising machine system and input them into the optical circuit of the optical Ising machine system;
[0049] S2: Perform data processing on the signal and parameters extracted from the optical circuit of the optical Ising machine system, and feed back the processed signal to the optical circuit of the optical Ising machine system;
[0050] S3: Output the calculation result of the solving task from the optical circuit of the optical Ising machine system, and map the Ising Hamiltonian to the optical Ising machine system.
[0051] In the above scheme, the optical circuit of the optical Ising machine system is used to realize the coupling between nodes and the gain of the node itself through...
Embodiment 2
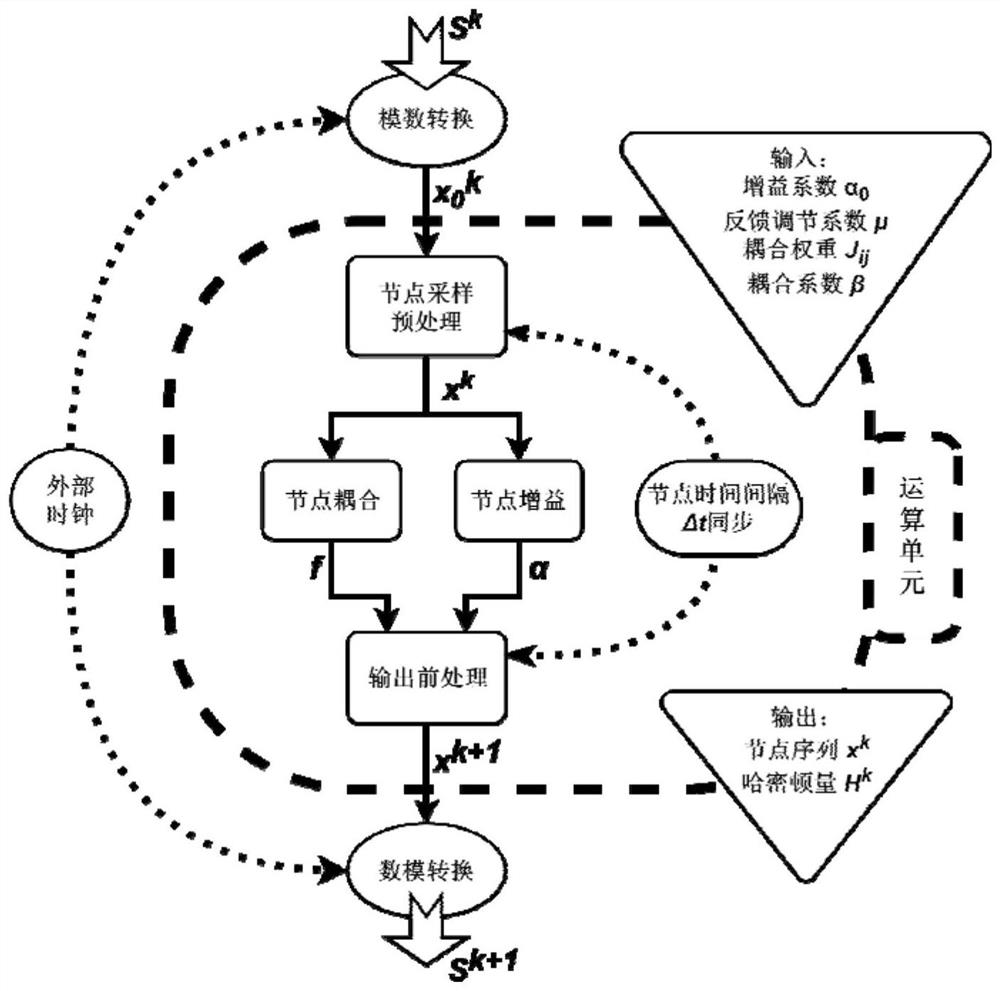
[0076] Such as Figure 4 and Figure 5 As shown, the node status based on this embodiment refers to such as Figure 4 As shown, under ideal or non-ideal conditions, the continuous light is modulated by the electro-optic modulator to form successively arranged small segments that are sequentially divided by a certain time interval Δt in the time domain and have different amplitudes. Among them, the node state x in the ideal node sequence i = a·σ i , where σ i =x i / |x i |∈{-1,+1}, then for all x i , with mean and variance of absolute values, respectively:
[0077]
[0078]
[0079] Therefore, the mapping to the Ising Hamiltonian can have:
[0080] H(x)=-∑ 1≤iπj≤N J ij x i x j =-a 2 ∑ 1≤iπj≤N J ij σ i σ j αH(σ)
[0081] In fact, the variance in the non-ideal node sequence each node x i = a·σ i +δ i , where δ i Indicates the degree to which the node deviates from the average value, and the mapped Hamiltonian at this time:
[0082] H(x)=-∑ 1≤iπj≤N J...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com