Compound, solid electrolyte, electrochemical cell, method for preparing compound, and protected positive electrode active material
A compound, oxidation number technology, applied in the field of solid ion conductors, can solve the problem of low lithium ion conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0234] Embodiment 1: (Li 5.69 Cu 0.06 )P(S 4.70 (SO 4 ) 0.05 ) Cl 1.25 preparation of
[0235] In a glove box with an Ar atmosphere, the Li 2 S, P as a precursor of phosphorus (P) 2 S 5 , LiCl as a chlorine (Cl) precursor, Cu as a copper (Cu) precursor 2 S, and as SO 4 Precursor Li 2 SO 4 to obtain (Li 5.69 Cu 0.06 )P(S 4.70 (SO 4 ) 0.05 ) Cl 1.25 The stoichiometric ratio of the desired composition was mixed, and the resultant was pulverized and mixed in an Ar atmosphere at 100 rpm for 1 hour in a planetary ball mill including zirconia (YSZ) balls, and then pulverized and mixed at 800 rpm for 30 minutes to obtain a mixture. The obtained mixture was pressed by uniaxial pressure to prepare a disc having a thickness of about 10 mm and a diameter of about 13 mm. The wafer thus obtained was covered with a gold film and placed in a carbon furnace, and the carbon furnace was vacuum-sealed by using a quartz glass tube. The temperature of the vacuum-sealed wafer was ...
Embodiment 2
[0237] Embodiment 2: ((Li 5.69+b Cu 0.06 )P(S 4.75+b-a (SO 4 ) a )(Cl 1.25-b (SO 4 ) b ), (SO 4 ) a+b =(SO 4 ) 0.15 , (where 0.05
[0238] A solid ion conductor compound was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the stoichiometric ratio of the starting materials was changed to satisfy (Li 5.69+b Cu 0.06 )P(S 4.75+b-a (SO 4 ) a )(Cl 1.25-b (SO 4 ) b ) composition.
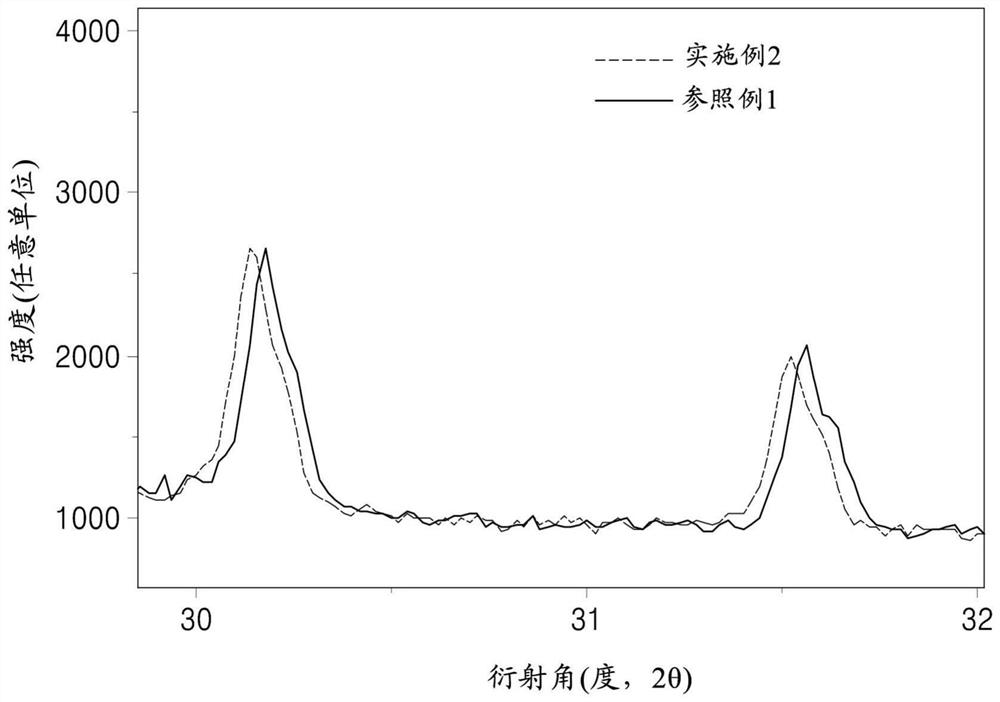
[0239] Such as Figure 1B As shown in , due to the re-precipitation of some Cl of the composition in the form of LiCl, a solid ion conductor compound of the following composition was obtained.
[0240] The composition of the obtained solid ion conductor compound is (Li 5.69+b Cu 0.06 )P(S 4.75+b-a (SO 4 ) a )(Cl1.25-b (SO 4 ) b ), (SO 4 ) a+b =(SO 4 ) 0.15 , (0.05
Embodiment 3
[0241] Embodiment 3: (Li 5.72 Cu 0.03 )P(S 4.725 (SO 4 ) 0.025 ) Cl 1.25 preparation of
[0242] A solid ion conductor compound was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the stoichiometric ratio of the starting materials was changed to satisfy (Li 5.72 Cu 0.03 )P(S 4.725 (SO 4 ) 0.025 ) Cl 1.25 expected composition.
[0243] The composition of described solid ion conductor compound is (Li 5.72 Cu 0.03 )PS 4.725 (SO 4 ) 0.025 Cl 1.25 (where the ratio of the substituted cation (Cu) is 0.005, and the substituted anion (SO 4 ) with a ratio of 0.005).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| ionic conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com