A chemically defined medium for in vitro differentiation of muscle stem cells
A technology of stem cell differentiation and cell differentiation, applied in the direction of cell culture active agent, embryonic cells, culture process, etc., can solve the problems of low differentiation efficiency, pollution, hindering the process of cell culture meat industrialization, etc., to achieve improved differentiation efficiency, high The effect of differentiation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Example 1 Induced differentiation of porcine muscle stem cells:
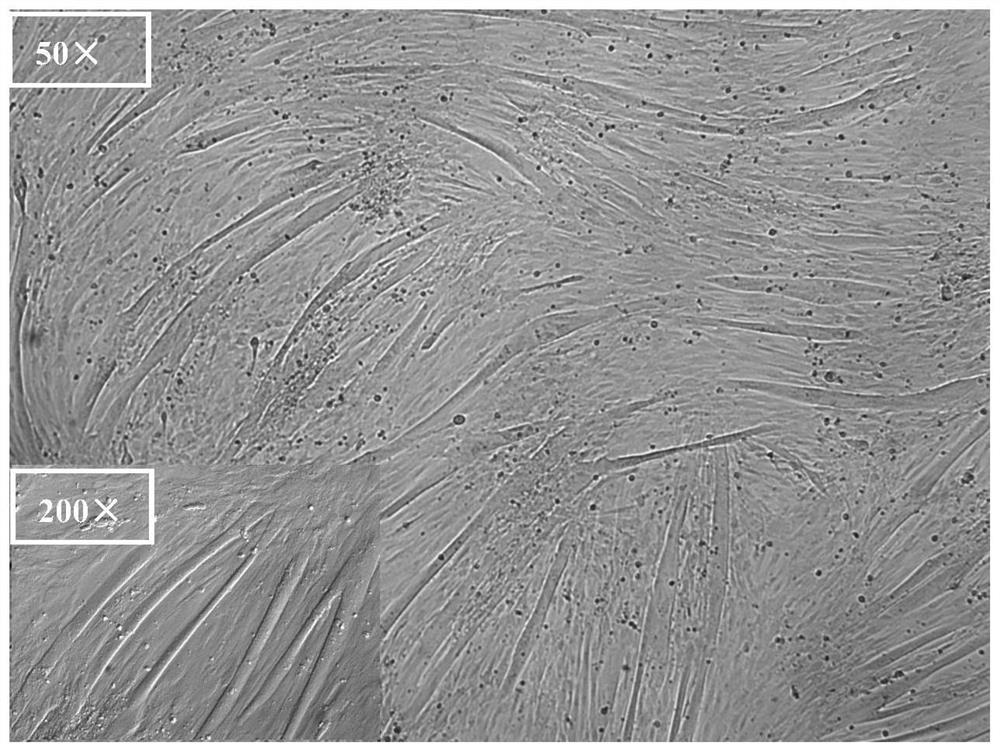
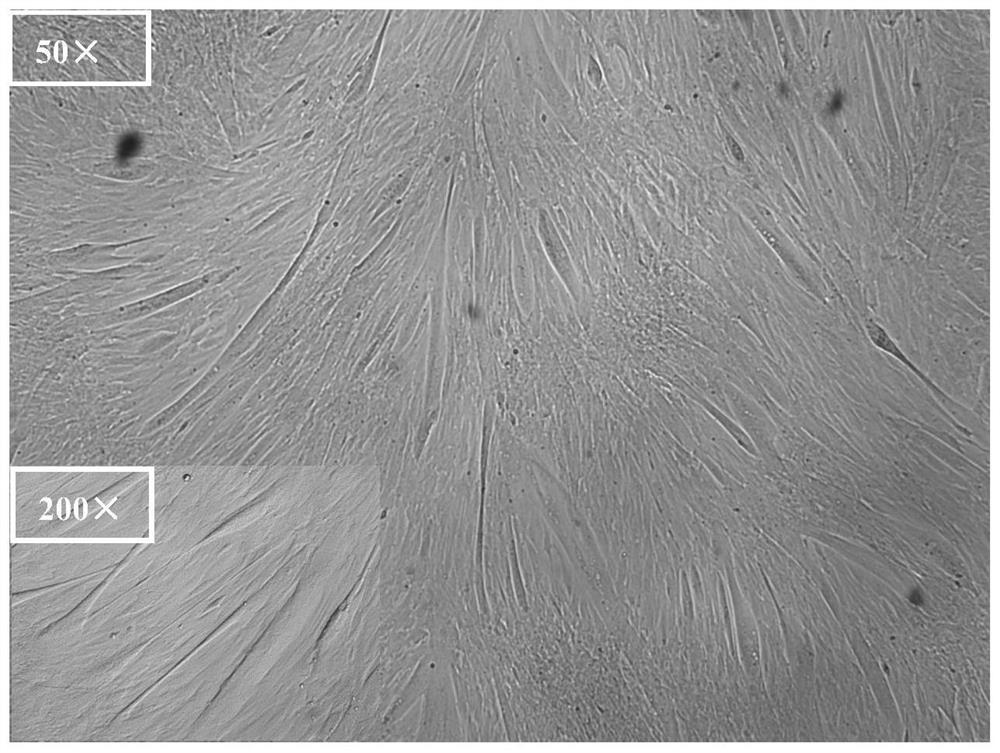
[0063] This experiment is divided into two groups, namely, the existing cell differentiation medium treatment group (positive control) and the improved cell differentiation medium treatment group with definite chemical components, and the specific treatment methods are as follows:
[0064] 1) laying the board with matrix glue: prepare a solution of matrix glue: PBS = 1: 50 (val), add it to a 3.5cm culture dish in the amount of 1mL / board, and place it in CO. 2 Incubate in an incubator for 1-6 hours, take it out, suck up the liquid, wash it with PBS twice, and then suck it up.
[0065] 2) Cell inoculation: High-purity porcine muscle stem cells before P6 generation were inoculated into a 3.5cm culture dish coated with matrix glue at a density of 60,000-120,000 cells per plate, cultured in a proliferation medium supplemented with 5ng / ml recombinant human fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), and changed for two days....
Embodiment 2
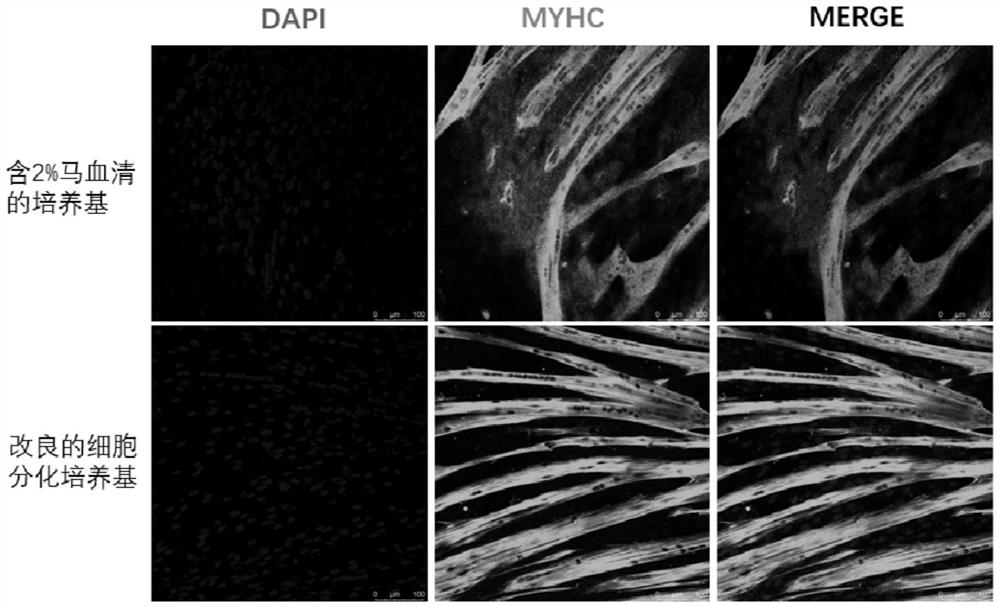
[0068] Example 2 Immunofluorescence detection of induced differentiation of porcine muscle stem cells
[0069] 1) Sample collection: after 5 days of induced differentiation by the existing muscle stem cell differentiation medium treatment group (positive control) and the modified muscle stem cell differentiation medium treatment group with clear chemical composition of the present invention in Example 1, the mature cells in the muscle tube are respectively sucked off, washed once with PBS, and 4% (m / v) paraformaldehyde is added and fixed overnight at 4℃.
[0070] 2) immunofluorescence staining of MYHC protein with DAPI: suck off 4% paraformaldehyde, wash it with PBS for 3 times, shake it with a shaking table for 5 minutes each time, draw a circle with immunohistochemistry, add about 50uL of 0.5%trizol to each circle, shake it for 15min minutes, wash it with PBS for 3 times, add Myhc antibody (1: 800) diluted with 1% BSA, and incubate at 4℃ for 16 hours. Add the second antibody dil...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3 Detection of gene and protein levels of induced differentiation of porcine muscle stem cells
[0074] 1) gene level detection:
[0075] According to the treatment method of Example 1, samples were taken on the 2nd, 4th and 6th day of induced differentiation in step 3), and the gene expression levels of MYOG, MYHC and CAV-3 in the existing muscle stem cell differentiation medium (positive control) and the modified cell differentiation medium with definite chemical composition of the present invention were detected by real-time quantitative PCR ( Figure 4 、 Figure 5 、 Figure 6 )。 Among them, MYOG gene is generally highly expressed in the prophase of differentiation, which indicates the differentiation ability of muscle stem cells, and the expression of MYHC is constantly increasing in the differentiation process, which indicates the differentiation level of muscle stem cells.
[0076] The results show that compared with the existing muscle stem cell differentiation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com