Improved culture medium for short-term proliferation of cultured meat seed cells
A technology of proliferation medium and seed cells, which is applied in the field of improved medium for cultivating meat seed cells in vitro for short-term proliferation, can solve problems such as environmental pollution, difficulty in meeting human meat needs, animal welfare, etc., and achieve faster proliferation and better Differentiation potential, effect of enhancing differentiation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
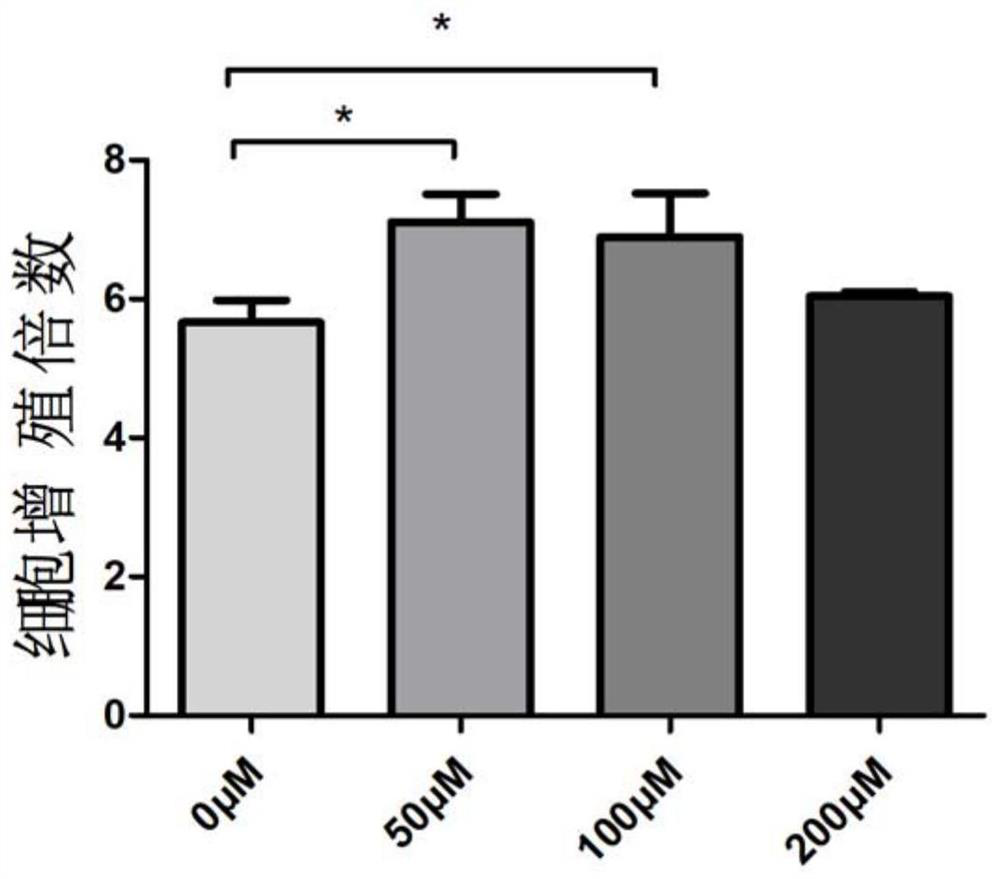
[0053] Example 1 Porcine muscle stem cells proliferative ability detection in vitro short-term culture:
[0054] 1) Short-term culture of muscle stem cells: this embodiment is divided into 4 groups, which are respectively the conventional proliferation medium control group and the experimental group of the improved proliferation medium group with a water-soluble vitamin E concentration of 50 μmol / L, and a water-soluble vitamin E concentration of 100 μmol / L. The experimental group of the modified proliferation medium group of L, the experimental group of the modified proliferation medium group with the concentration of water-soluble vitamin E at 200 μmol / L. Porcine muscle stem cells were divided into 1.5×10 5 / dish was inoculated into 10cm culture dishes of conventional proliferation medium and improved proliferation medium, and the medium was changed for two days, digested with 0.25% trypsin for three days, and counted with a hemocytometer.
[0055] 2) The results show that t...
Embodiment 2
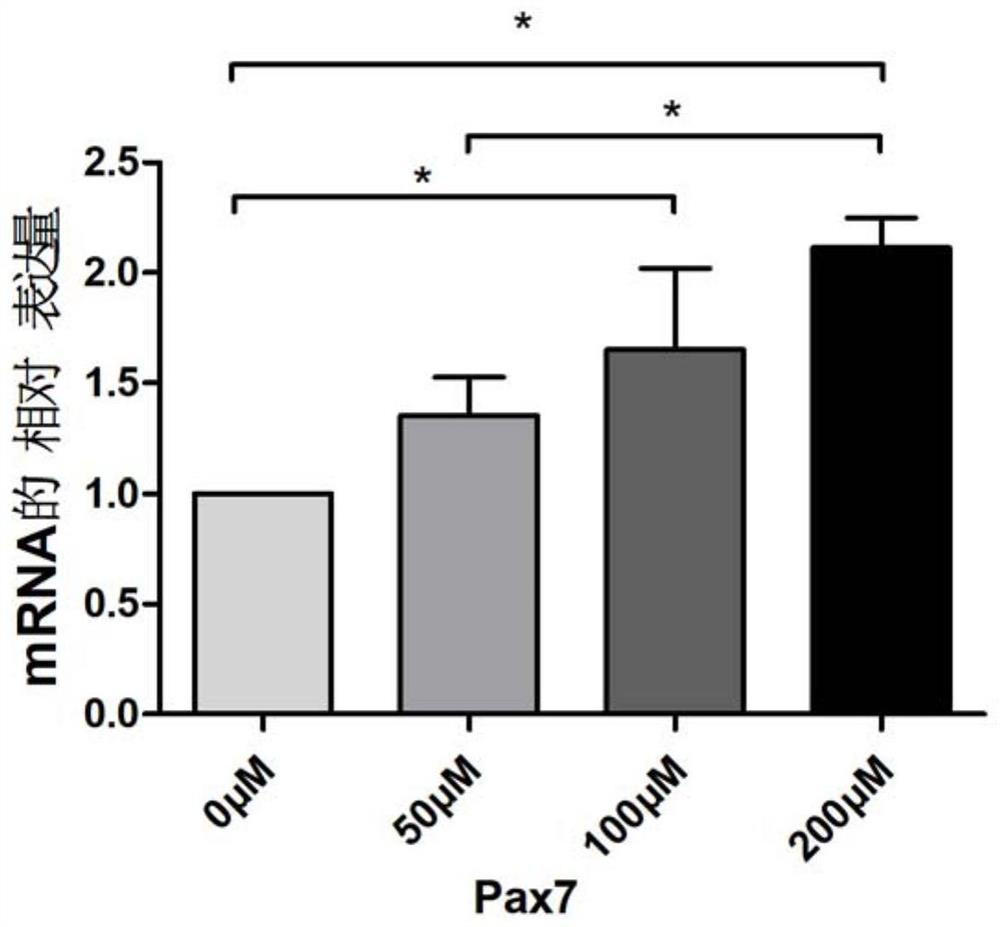
[0056] Example 2 Detection of Muscle Stem Cell Differentiation Potential
[0057] Get the conventional proliferation medium control group in Example 1, the improved proliferation medium group experimental group whose water-soluble vitamin E concentration is 50 μmol / L, the water-soluble vitamin E concentration is 100 μmol / L, and the water-soluble vitamin E concentration is 200 μmol / L. The cells cultured in the proliferation medium group and the experimental group were extracted from the RNA, and the gene expression of the stemness gene "Pax7" that characterizes the differentiation potential of the cells cultured in the improved proliferation medium and the conventional proliferation medium was detected by q-PCR technology.
[0058] The results showed that the short-term culture of the muscle stem cells in the improved proliferation medium added with water-soluble vitamin E could maintain its differentiation potential. When the concentration of water-soluble vitamin E was 50 μmol...
Embodiment 3
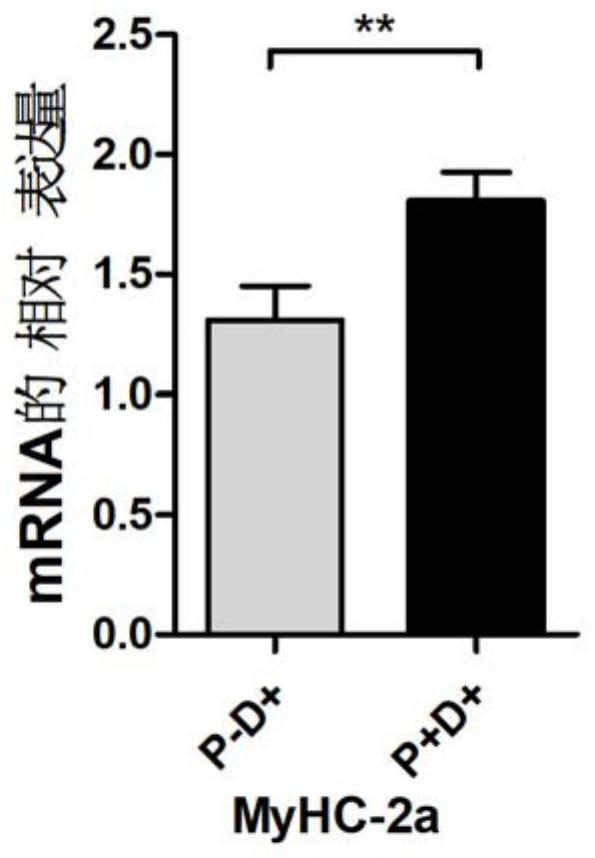
[0059] Example 3 Detection of Muscle Stem Cell Differentiation Level
[0060] Take the muscle stem cells obtained from the modified proliferation medium and conventional proliferation medium in Example 1 where the water-soluble vitamin E is 100 μmol / L, and then induce differentiation: the process of muscle stem cell differentiation in vitro includes two stages, the first stage is muscle stem cells In the proliferation stage of stem cells, the cells are propagated in a differentiation culture dish containing improved proliferation medium and conventional proliferation medium added with water-soluble vitamin E, and the proliferation reaches the pre-differentiation stage after 5 days.
[0061] The cells in the pre-differentiation stage cultured with the improved proliferation medium and conventional proliferation medium supplemented with water-soluble vitamin E were induced to differentiate, and the medium was changed every two days, that is, half of the differentiation medium was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com