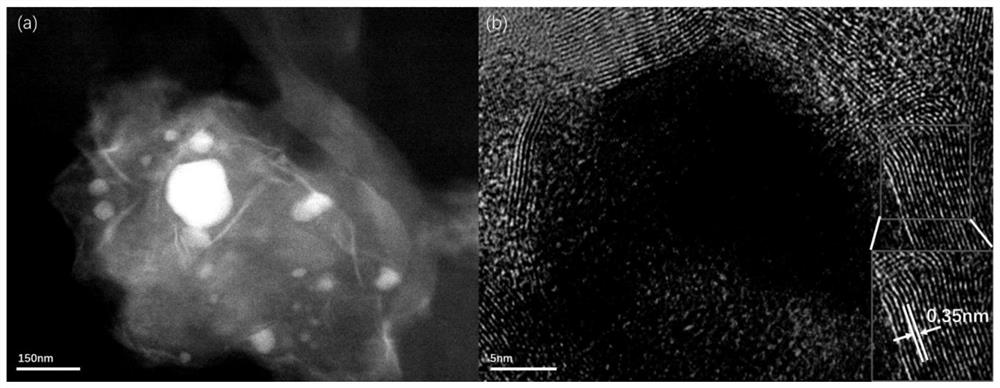
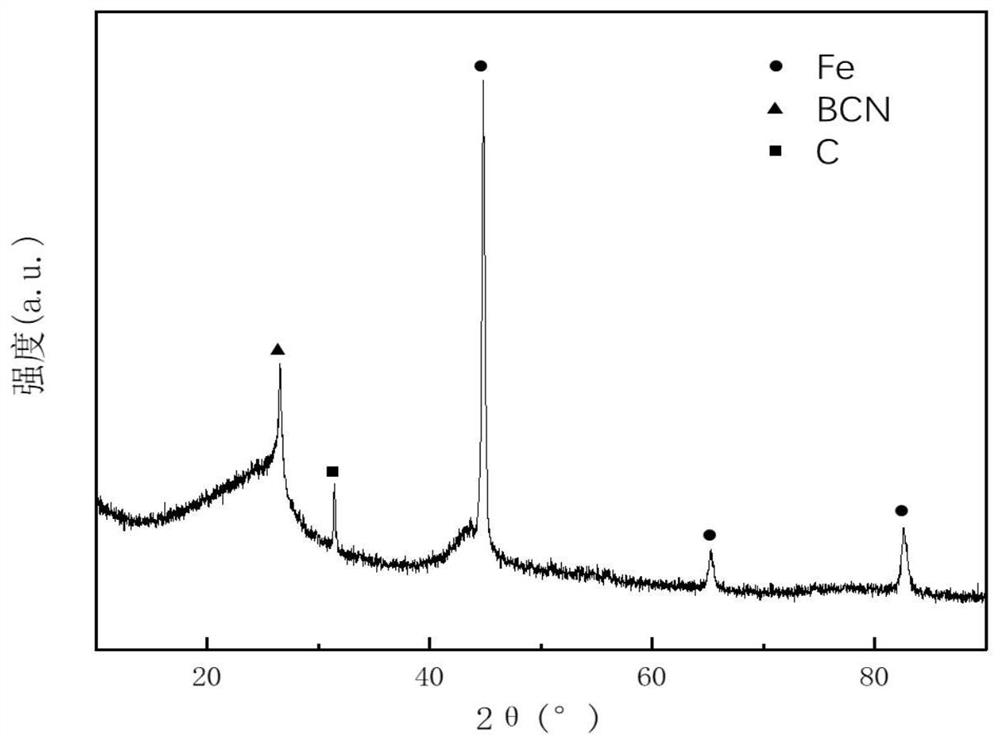
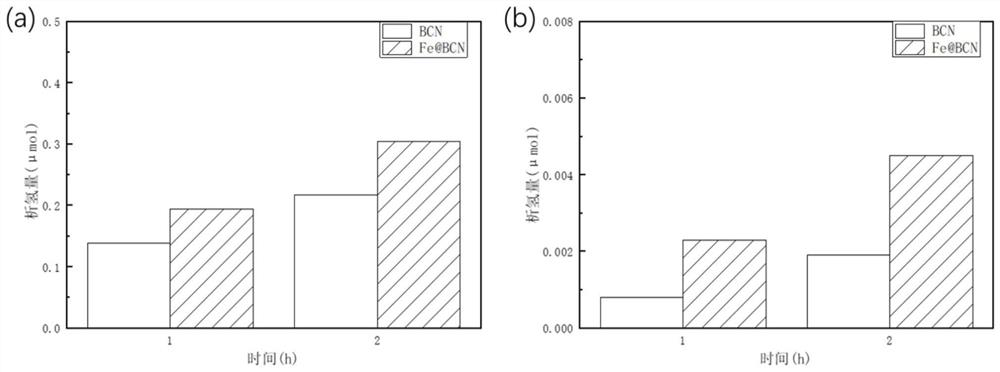
A preparation method of iron@bcn ceramics for photocatalytic hydrogen production
A photocatalytic and ceramic technology, applied in the field of preparation of iron@BCN ceramics for photocatalytic hydrogen production, can solve the problems of material inactivity, low hydrogen evolution efficiency, limited hydrogen evolution efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost and easy processing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Preparation of iron@BCN ceramics with 1:3:1 molar ratio of boric acid, urea and sodium alginate:
[0024] 1. Weigh 3.983g (0.01 mol) of sodium alginate (carbon source) in a beaker, add 30 mL of water, put it into a magnetic stirrer and stir for 12 hours to ensure that sodium alginate is fully dissolved in water, then weigh 0.618 g (0.01 mol) boric acid (boron source) and 1.8 g (0.03 mol) urea (nitrogen source) in a beaker, add 30 mL of water, sonicate for 1 h to fully dissolve it, add it to the sodium alginate solution after dissolving, continue to stir in a magnetic stirrer Stir for 12h to form a homogeneous mixed solution;
[0025] 2. Preparation of ferric chloride solution: prepare iron ion solution, wherein the mass of iron element is 1% of the total mass of boric acid, urea and sodium alginate. Weigh 0.3090g of ferric chloride hexahydrate (containing 0.0640g of iron) in a beaker, add 60mL of water, and sonicate for 30min;
[0026] 3. Add the prepared ferric chlor...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Preparation of iron@BCN ceramics with boric acid, urea and sodium alginate molar ratio of 1:6:1:
[0033]1. Weigh 3.983g (0.01 mol) of sodium alginate (carbon source) in a beaker, add 30 mL of water, put it into a magnetic stirrer and stir for 12 hours to ensure that sodium alginate is fully dissolved in water, then weigh 0.618 g (0.01 mol) boric acid (boron source) and 3.6g (0.06 mol) urea (nitrogen source) in a beaker, add 30 mL of water, sonicate for 1 h to make it fully dissolved, add it to the sodium alginate solution after dissolving, continue to stir in a magnetic stirrer Stir for 12h to form a homogeneous mixed solution.
[0034] 2. Preparation of ferric chloride solution: prepare iron ion solution, wherein the mass of iron element is 1% of the total mass of boric acid, urea and sodium alginate. Weigh 0.3958g of ferric chloride hexahydrate (containing 0.0820g of iron) in a beaker, add 60mL of water, and sonicate for 30min;
[0035] 3. Add the prepared ferric c...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Preparation of iron@BCN ceramics with a molar ratio of boric acid, urea and sodium alginate of 1:9:1:
[0041] 1. Weigh 3.983g (0.01 mol) of sodium alginate (carbon source) in a beaker, add 30 mL of water, put it into a magnetic stirrer and stir for 12 hours to ensure that sodium alginate is fully dissolved in water, then weigh 0.618 g (0.01 mol) boric acid (boron source) and 5.4 g (0.09 mol) urea (nitrogen source) in a beaker, add 30 mL of water, ultrasonicate for 1 h to fully dissolve it, add it to the sodium alginate solution after dissolving, continue to stir in a magnetic stirrer Stir for 12h to form a homogeneous mixed solution.
[0042] 2. Preparation of ferric chloride solution: prepare iron ion solution, wherein the mass of iron element is 1% of the total mass of boric acid, urea and sodium alginate. Weigh 0.4827g of ferric chloride hexahydrate (containing 0.1000g of iron) in a beaker, add 60mL of water, and sonicate for 30min;
[0043] 3. Add the prepared fe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com