3D printing mud and preparation method thereof
A 3D printing mud and polysiloxane technology, applied in the direction of additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of being unable to be used again, the product becomes dry and hard, and achieves the effect of safe use, soft hand feeling and light texture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0026] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing 3D printing mud, comprising: mixing filler, polysiloxane, coupling agent, and activator according to a certain ratio; heating and reacting to form 3D printing mud.
[0027] Wherein, the polysiloxane is a polysiloxane containing active groups, which can react with the coupling agent and the filler to enhance the adhesion between the matrix and the filler and prevent the thixotropy of the product. The powder dropping phenomenon of fillers; then by adding an activator, the break and repair of the chemical bond between the coupling agent and polysiloxane can be adjusted, the movement of the molecular segment can be strengthened, and the plasticity of the product can be improved. The printing paste prepared by this method is smooth Slippery and easy to shape, soft, non-sticky, non-sticky, no slag, and long service life, effectively inhibiting bacteria and mold and other excellent characteristics. It is al...
Embodiment 1
[0051] With 40 parts by weight of silica hollow nanospheres (density is 0.2g / cm 3 , particle size is 2μm), 20 parts by weight of (dynamic viscosity is 50mPa s), 10 parts by weight of methyl orthosilicate, and 0.5 parts by weight of citric acid are dropped into the kneader, and the stirring is started to make it fully mixed;
[0052] Raise the temperature of the kneader to 100°C, react for 240 minutes, and then lower the temperature to 50°C to obtain 3D printing paste.
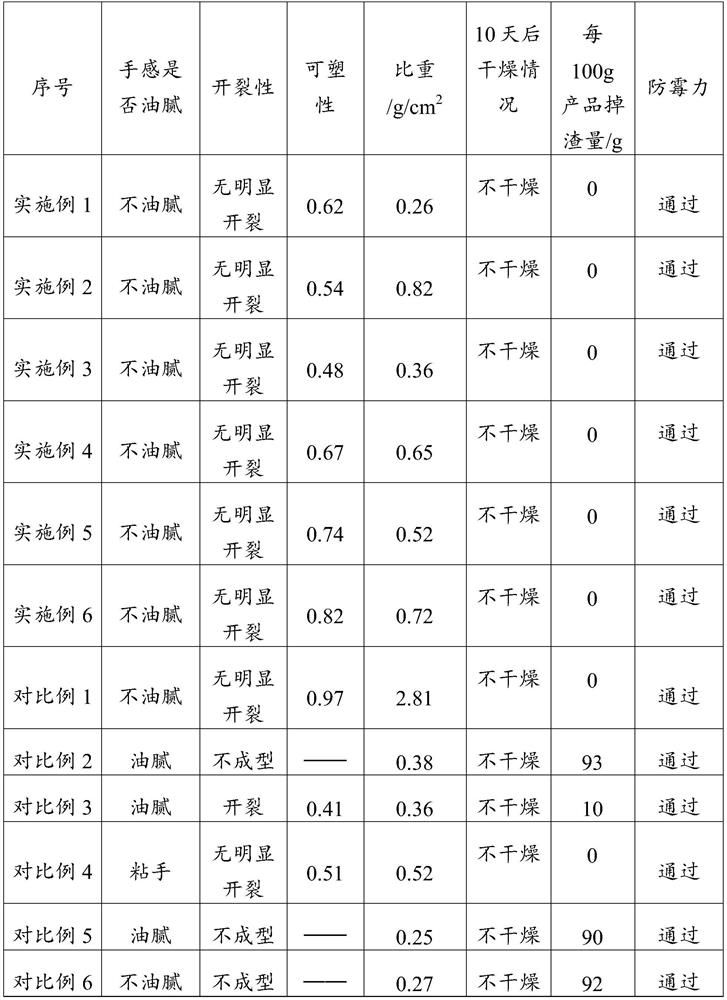
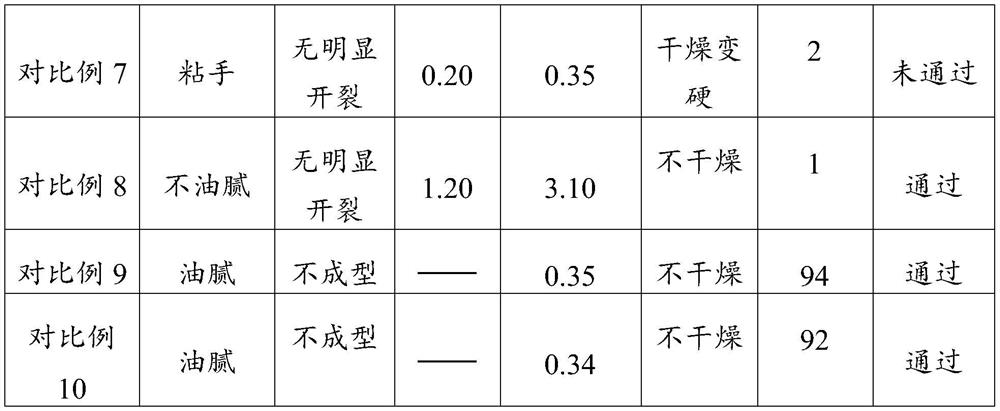
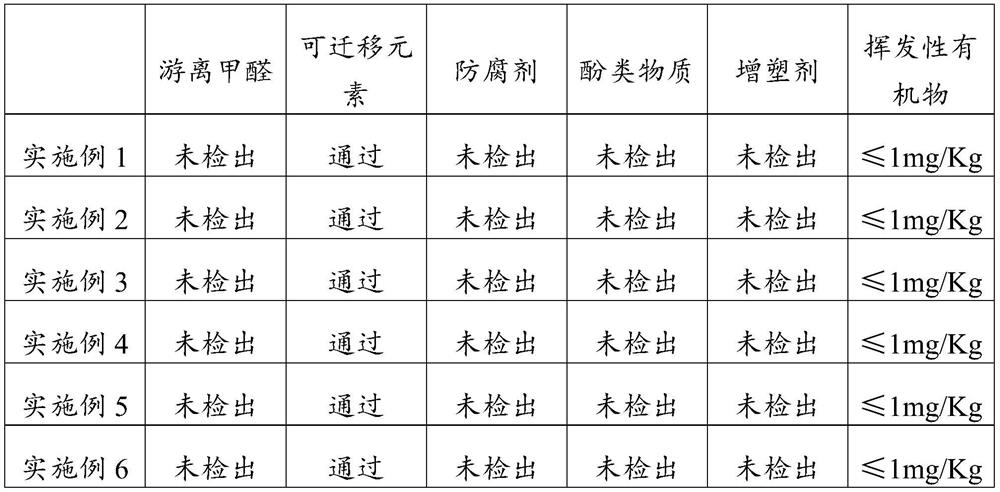
[0053] The 3D printing mud obtained in this embodiment was tested, and its parameters are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
[0054] The parts by weight in this embodiment can be g, kg, etc., and it is g here, and the following examples and comparative examples are also g.
Embodiment 2
[0056] 70 weight parts of hollow glass microspheres (density of 0.6g / cm 3 , particle size is 150μm), 35 parts by weight of (dynamic viscosity is 20000mPa s), the aluminum methoxide of 20 weight parts, the palmitic acid of 8 weight parts drop in the kneader, start stirring, make it fully mix;
[0057] Raise the temperature of the kneader to 300°C, react for 30 minutes, and then lower the temperature to 40°C to obtain 3D printing paste.
[0058] The 3D printing mud obtained in this embodiment was tested, and its parameters are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com