HSV-2-DELTA-gD VACCINES AND METHODS FOR THEIR PRODUCTION AND USE
A technology of HSV-2, hsv-2gd, applied in the field of HSV-2-DELTA-gD vaccine and its production and use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
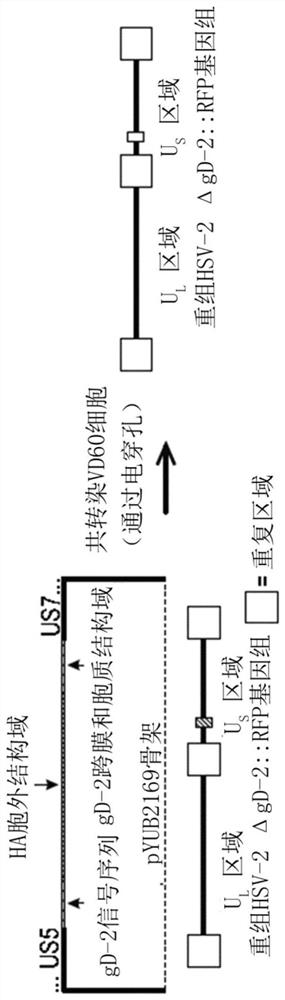
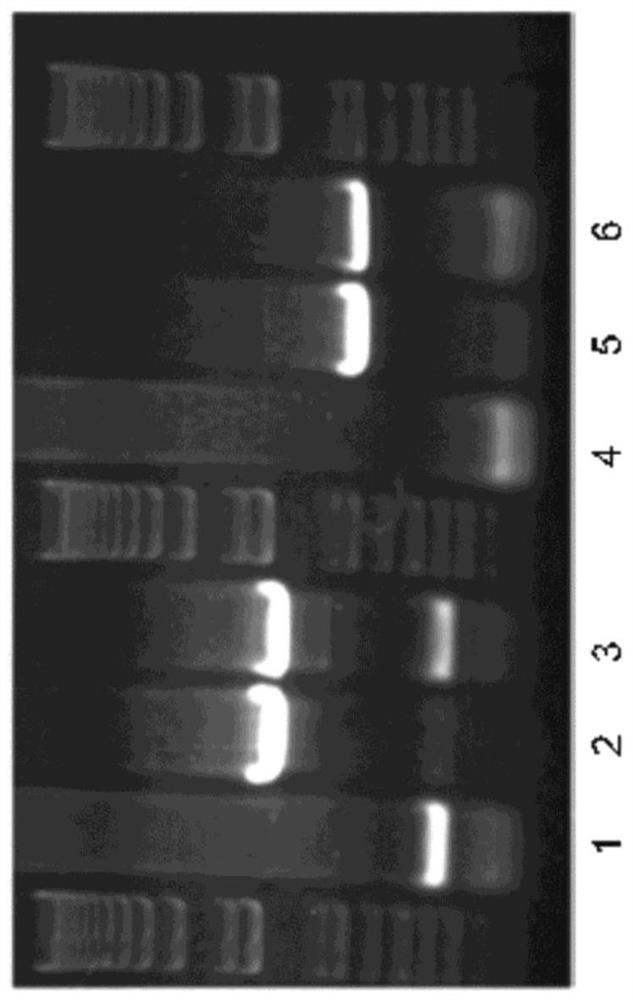
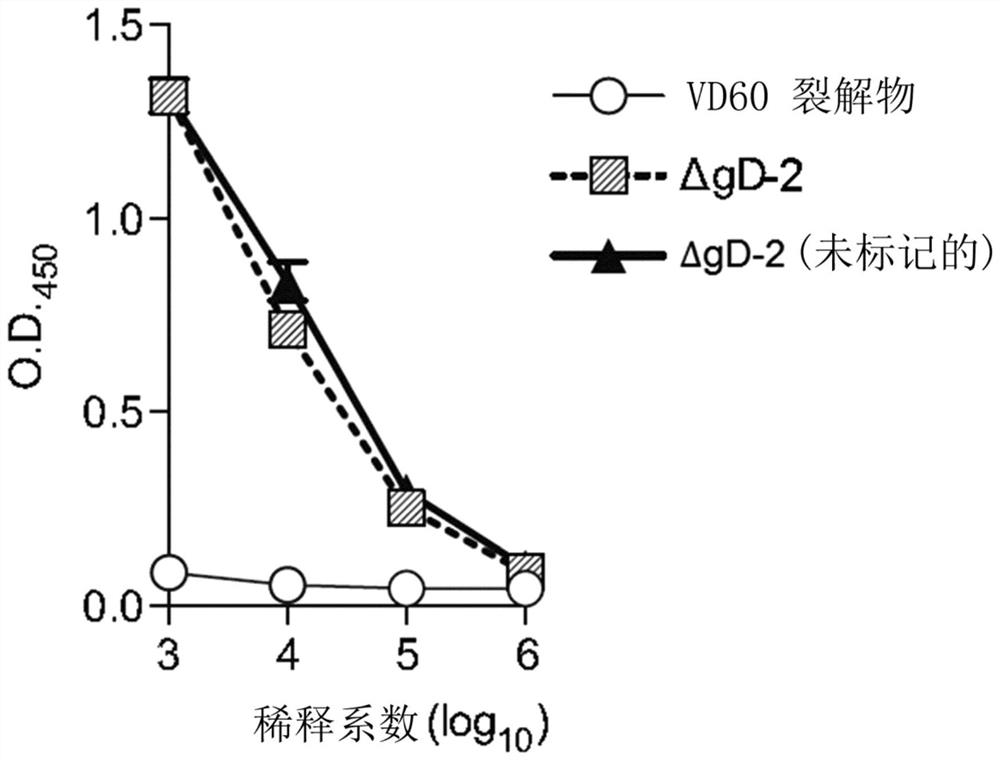
[0152] An engineered HSV-2 virus was constructed that replaced the gD gene (ΔgD-2) with a gene that strongly expresses red fluorescent protein (RFP). Once achieved, this provides an improved screen for the identification and acquisition of novel recombinants. The ΔgD-2::RFP recombinant was made from ΔgD-2 that showed protection. Red fluorescent ΔgD-2:RFP, also referred to herein as B 3 x2.8 or ΔgD-2::P EF1α - RFP, retains the ability of native ΔgD-2 to elicit protective immunity against HSV infection but does not appear to alter replication kinetics in vitro. In addition, ΔgD-2::RFP has obvious advantages over HSV-2ΔgD::GFP virus in preparing recombinants. Since the RFP gene is fused to a highly efficient promoter such as that of the EF1α (elongation factor 1α) gene, its expression can be easily detected using fluorescence microscopy. Furthermore, visualization of red fluorescence in cells infected with AgD-2::RFP was performed without the background that occurs when using...
Embodiment 2
[0202] Design of HIV constructs for expression in HSV-2ΔgD virus: The generation of vaccine vectors in which the glycoprotein antigens of HIV are expressed from ADCC-inducing HSV-2ΔgD vectors was investigated. The rationale for using this vector is that it elicits non-neutralizing, ADCC-inducing IgG antibodies against HSV, and that this immune response is associated with protection in the only HIV vaccine trial to date that has shown any efficacy (Haynes , Gilbert et al. 2012). For glycoprotein antigens, a pass / created clone of Env gp145 lacking the cytoplasmic tail was selected from donor CH505 in the acute HIV-1-infected cohort of CHAVI001 because this well-characterized HIV-1 clade C glycoprotein was considered to be representative of those passing infection bottlenecks in areas of high HIV prevalence (Liao, Lynch et al. 2013). HIV Env is not expressed particularly well in the context of natural infection, and often does not express well exogenously, so steps to enhance an...
Embodiment 3
[0204] Introduction
[0205] Functional in vitro macrophage antibody-dependent cell-mediated killing (ADCK) assay (as done in Example 1) using the HSV-2 ΔgD strain expressing RFP: a single cycle of missing glycoprotein D (ΔgD-2) ( Single-cycle) herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) strains elicit sterilizing anti-HSV immunity by inducing antibodies that bind to and activate Fcγ receptors (FcγR). Murine FcγRIV is highly activated in the presence of sera from vaccinated mice and is expressed on macrophages, monocytes and neutrophils. The exact mechanism of cell killing by FcγRs is not fully understood and additional tools are needed. FcγR-binding antibodies mediate killing of HSV-infected cells by binding to antigens on infected cells and then binding and activating FcγRs on innate leukocytes. This precipitates antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and phagocytosis (ADCC and ADCP), referred to herein as antibody-dependent cell-mediated killing (ADCK). Current assays fac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com