Bovine-derived A-type pasteurella multocida inactivated vaccine as well as preparation method and application thereof
A Pasteurella and inactivated vaccine technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of animal husbandry economic losses, low cross-immunity efficacy, lack of cross-protective vaccines, etc., and achieve the effect of less harm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] The preparation of embodiment 1 bovine type A Pm inactivated vaccine and the establishment of serum antibody ELISA method
[0042] In this example, one Pm (Pm12) strain of type A was selected as the research object according to the research of the previous experiment, and Pm12 (type A) and M6 (type B) were prepared into inactivated vaccines according to the preparation procedure of bacterial inactivated vaccines. The ELISA conditions were screened according to the checkerboard method, and an indirect ELISA method for detecting serum antibodies of different animals was established. The results show that: the prepared inactivated vaccine is qualified through the safety test, and the bacterial content of the Pm12 (type A) inactivated vaccine is 8×10 9 CFU / mL, the bacterial content of M6 (type B) inactivated vaccine is 1.4×10 10 CFU / mL.
[0043] 1. Preparation of seedling oil phase
[0044] Medicinal white oil 94mL, aluminum stearate 2g, first take a small amount of whit...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Example 2 Analysis of changes in antibody levels and immune protection effects of Pm12 inactivated vaccines after immunization of mice and rabbits
[0097] 1. The median lethal dose (LD) 50 ) determination
[0098] Take 30 mice, 10 in each group, and challenge the virus by intraperitoneal injection, each group is challenged with 1×10 6 , 1×10 7 , 1×10 8 CFU, LD was calculated according to the modified Cole's method 50 . The groups of mice are shown in Table 7, and the preparation of the four inactivated vaccines refers to Example 1.
[0099] Table 7 Grouping situation of mouse median lethal dose
[0100]
[0101] Experimental results: According to the modified Cole's method, the median lethal dose of Pm12 is about 3.8×10 1 CFU, the median lethal dose of Pm8 is about 4.2×10 1 CFU, the median lethal dose of Pm122 is about 3.1×10 1 CFU, the median lethal dose of M6 is about 5.6×10 1 CFU.
[0102] 2. Mouse immune antibody assay and challenge protection test
...
Embodiment 3
[0148] Example 3 Determination and Analysis of Serum Antibody Levels of Pm12 Inactivated Vaccine Immunized Different Day-Old Cattle
[0149] 1. Determination of the immune effect and immune antibody of cows in the dry period
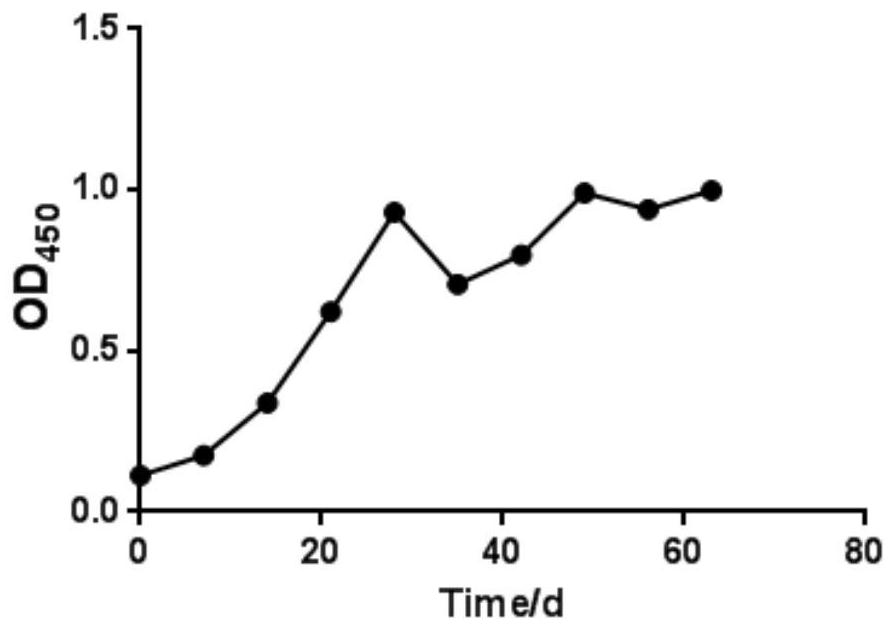
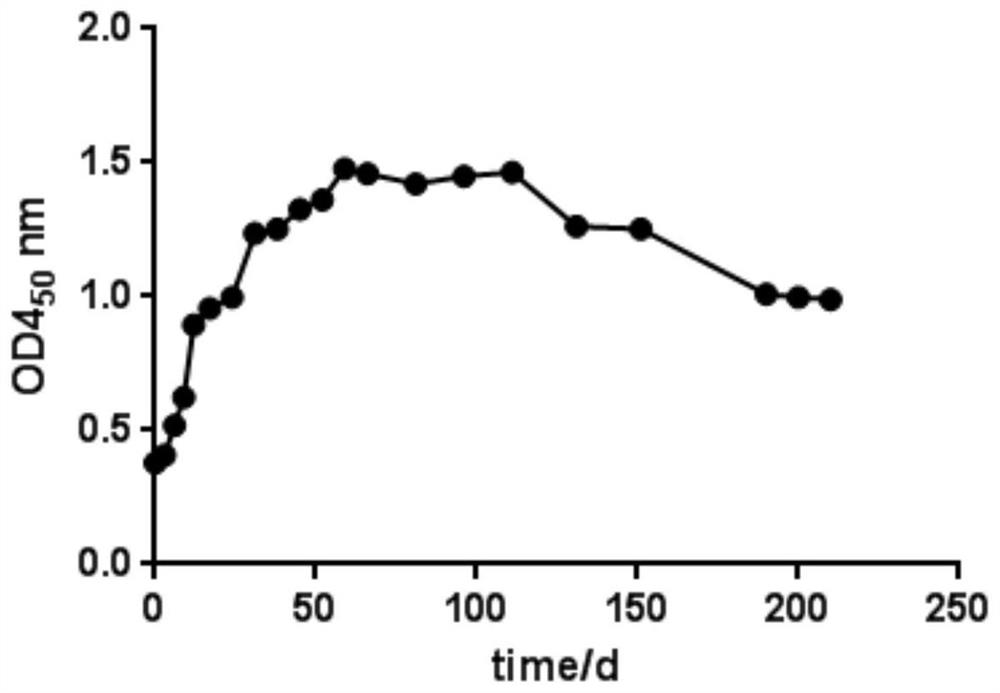
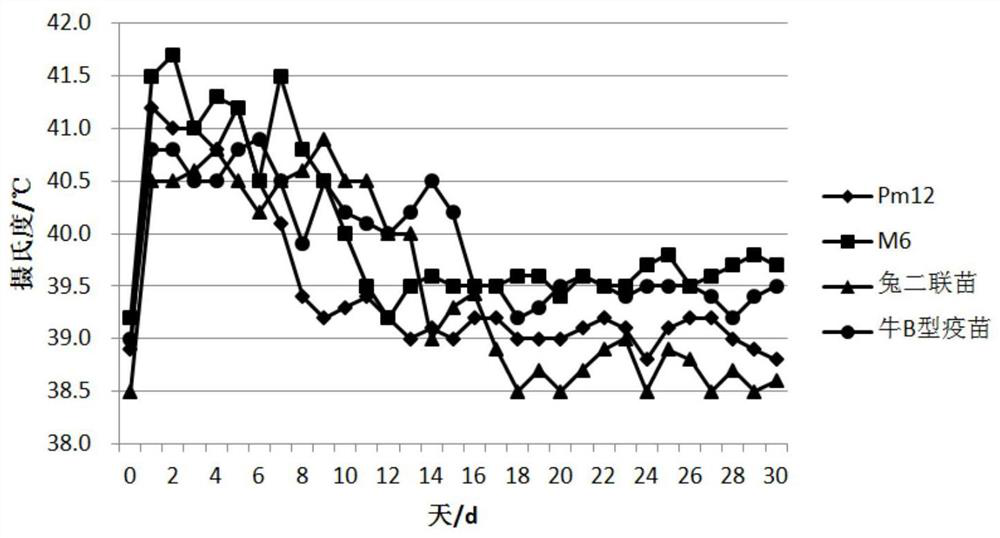
[0150] Select 30 cows in the dry period (the expected delivery date is about 60 days) and divide them into 3 groups, 10 cows in each group, and inoculate Pm12 inactivated vaccine, M6 inactivated vaccine and Pm12-M6 bivalent inactivated vaccine respectively. Each head and neck muscle Inoculate with 2 mL, and perform the second immunization 21 days after the first immunization, and observe the appetite and mental status of the cows during the dry period. Blood was collected before vaccination as a negative control. After the first vaccination, blood was collected every 7 days to separate serum for antibody monitoring. Indirect ELISA was used to detect the regularity of antibody levels produced by inactivated vaccines in cows during the dry period.
[0151...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com