Motor winding equivalent model, establishment method and motor temperature field analysis method
An equivalent model, motor winding technology, applied in computer-aided design, special data processing applications, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve the problems of increased difficulty in modeling, low calculation accuracy, and difficulty in solid modeling, etc., to reduce effect of complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
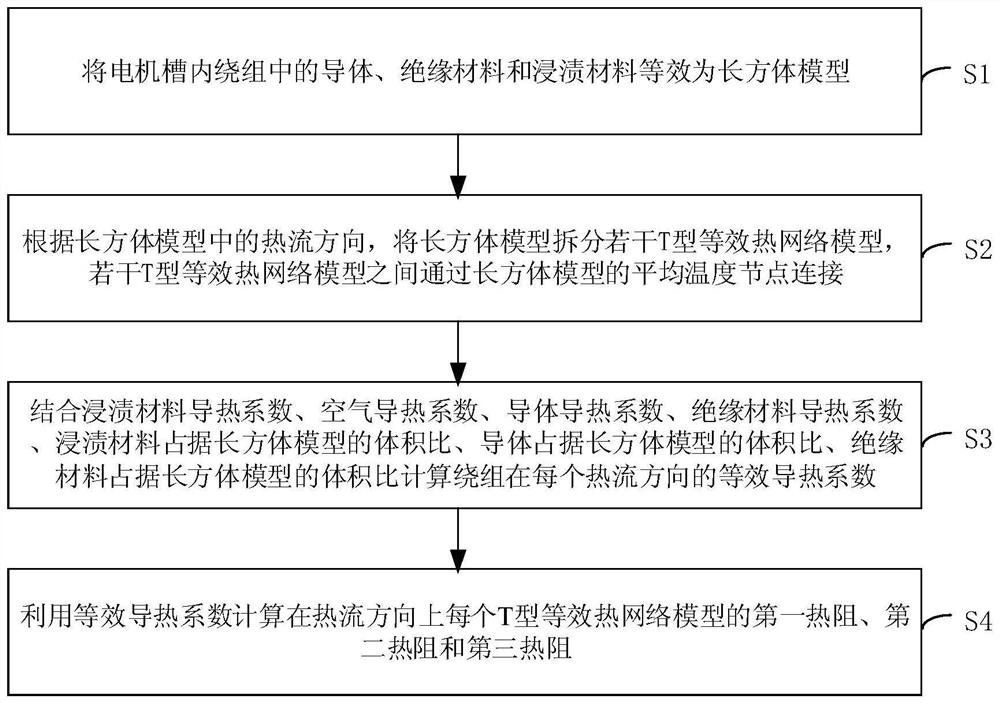
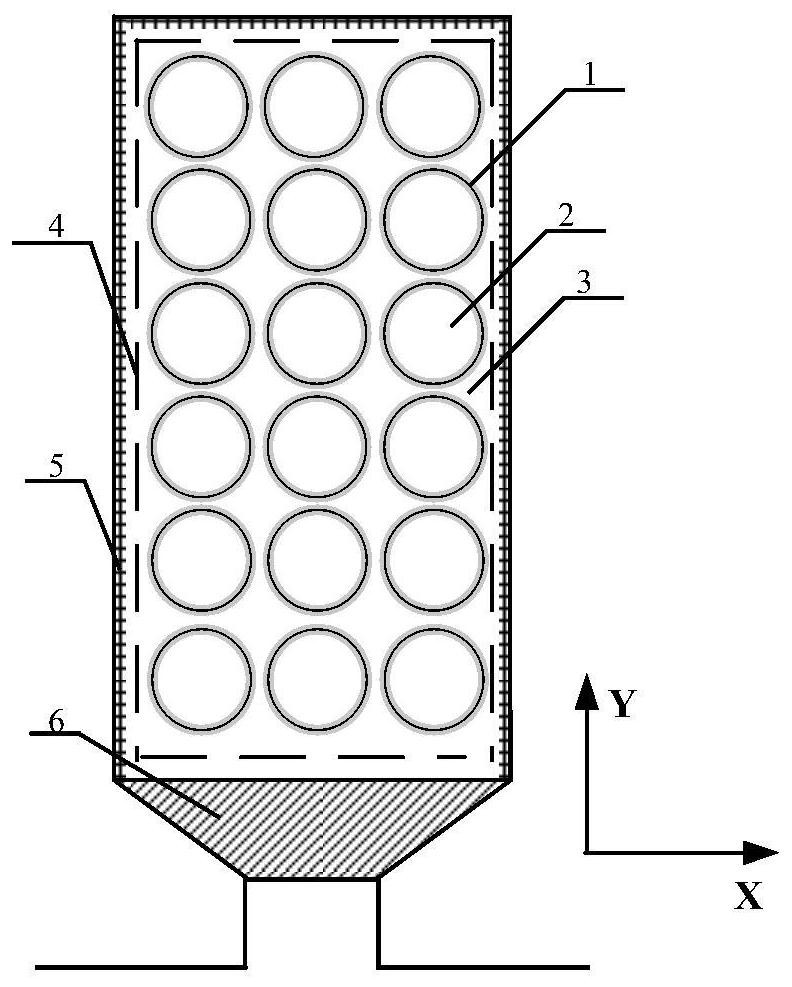
[0060] In the process of analyzing and calculating the temperature field of the motor using the lumped parameter thermal network method, the most critical factor is the calculation of the thermal resistance between each node, which is directly related to the accuracy of the entire calculation result. However, in the actual motor model, the winding placement in the slot is random and discrete, and it is difficult and computationally intensive to perform solid modeling on it. Therefore, in order to reduce the complexity of the winding model and accurately evaluate the temperature of the winding, this embodiment provides a method for establishing an equivalent thermal model of the motor winding, please refer to figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic flowchart of a method for establishing an equivalent model of a motor winding provided by an embodiment of the present invention. The method for establishing the equivalent model of the motor winding includes steps:
[0061] S1. The ...
Embodiment 2
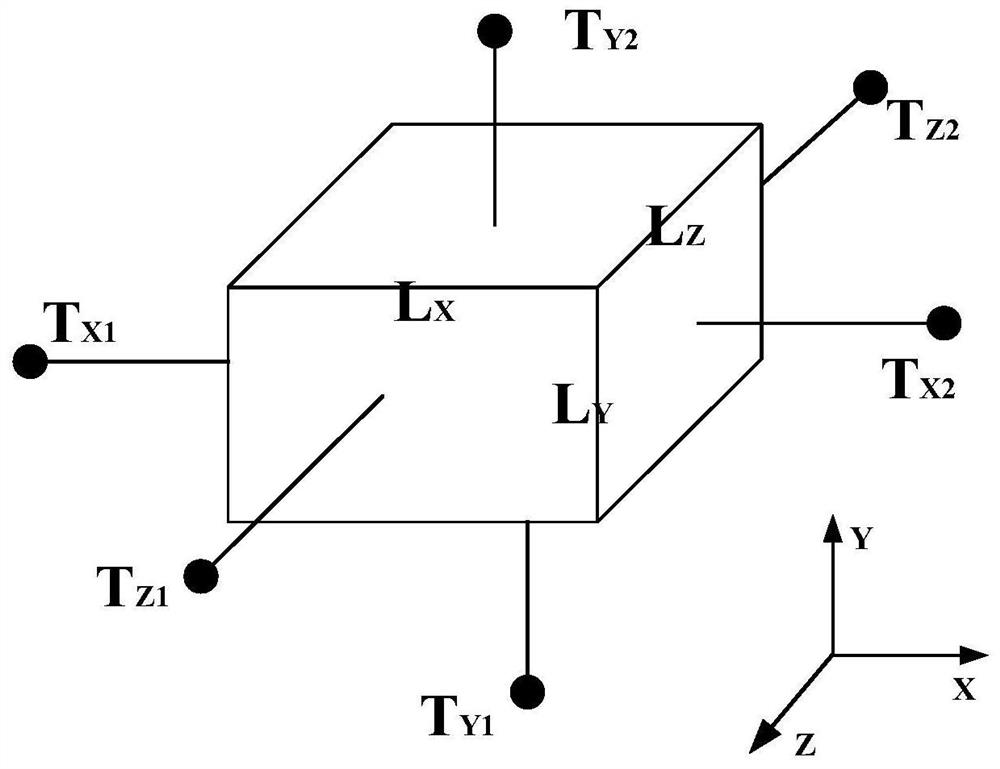
[0106] On the basis of the first embodiment, this embodiment provides an equivalent model of a motor winding, which is obtained by the establishment method of the first embodiment. The equivalent model of the motor winding is a cuboid model including conductors, insulating materials and impregnating materials. Several T-type equivalent thermal network models are set along several heat flow directions in the cuboid model. Several T-type equivalent thermal network models pass through Mean temperature nodal connection for the cuboid model. Each T-type equivalent thermal network model has a first thermal resistance along a first direction, a second thermal resistance along a second direction and a third thermal resistance along a third direction, the first thermal resistance, the second thermal resistance The thermal resistance and the third thermal resistance are calculated from the equivalent thermal conductivity of the winding in the direction of heat flow. Further, the equiva...
Embodiment 3
[0109] Calculation of motor temperature rise is an important part of motor design. It is related to the service life of the motor and the maximum continuous output power; increase computation time. Therefore, on the basis of the first and second embodiments, this embodiment provides a motor temperature field analysis method, which mainly optimizes and improves the entity modeling of the motor winding during the motor temperature field analysis process.
[0110] See Image 6 , Image 6 It is a schematic flowchart of a motor temperature field analysis method provided by an embodiment of the present invention. The analysis method includes steps:
[0111] S1. The conductor, insulating material and impregnated material in the winding in the motor slot are equivalent to a cuboid model.
[0112] S2. According to the heat flow direction in the cuboid model, the cuboid model is split into several T-shaped equivalent heat network models, and several T-shaped equivalent heat network m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com