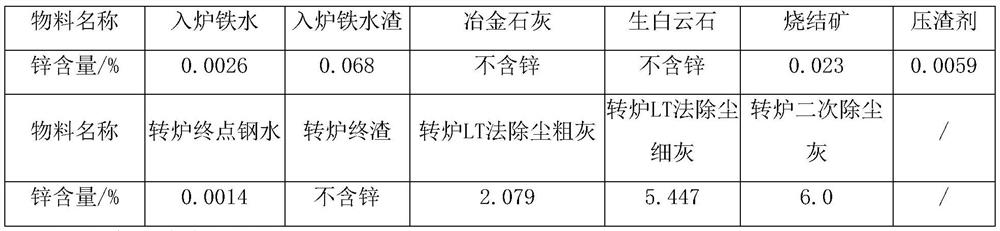
Method for testing zinc content of scrap steel in converter smelting mode
A converter smelting and scrap zinc technology, applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy, can solve the problems of inaccurate testing of scrap zinc content, and achieve the effects of being representative, increasing economic benefits, and reducing steelmaking costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Test scrap material type: cold-rolled automobile sheet punching and briquetting.
[0075] Smelting steel type: SPHC-1R.
[0076] The metal material structure of the furnace: 143 tons of molten iron + 32 tons of test scrap.
[0077] Hot metal weight: 143 tons ± 2 tons; scrap steel weight: 32 tons ± 1 ton.
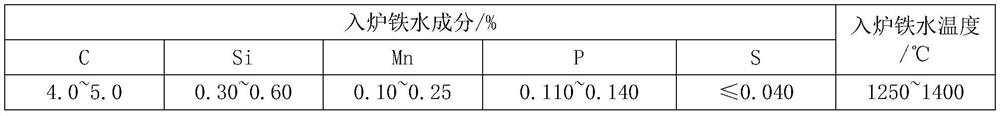
[0078] The composition and temperature of molten iron are shown in Table 1:
[0079] Table 1 Embodiment 1 molten iron composition and temperature table
[0080]
[0081] Types of slagging agents and slagging system: slagging agents are metallurgical lime and raw dolomite, and the binary basicity of the final slag of the converter is 2.5 to 3.5. The amount of slagging agent added and the timing of adding it executes the SPHC-1R blowing model.
[0082] Top and bottom combined blowing process: SPHC-1R blowing model.
[0083] Type and amount of coolant: The coolant is sintered ore, and the amount of coolant added is carried out in the SPHC-1R blowing model.
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Test scrap type: full galvanized scrap briquetting.
[0098] Smelting steel grade: SPHC-1R.
[0099] The metal material structure of the furnace: 143 tons of molten iron + 32 tons of test scrap.
[0100] Hot metal weight: 143 tons ± 2 tons; scrap steel weight: 32 tons ± 1 ton.
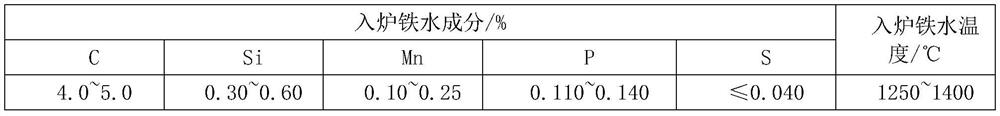
[0101] The composition and temperature of molten iron are shown in Table 3:
[0102] Table 3 Example 2 molten iron composition and temperature table
[0103]
[0104] Types of slagging agents and slagging system: slagging agents are metallurgical lime and raw dolomite, and the binary basicity of the final slag of the converter is 2.5 to 3.5. The amount of slagging agent added and the timing of adding it executes the SPHC-1R blowing model.
[0105] Top and bottom combined blowing process: SPHC-1R blowing model.
[0106] Type and amount of coolant: The coolant is sintered ore, and the amount of coolant added is carried out in the SPHC-1R blowing model.
[0107] End point control target: C: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com