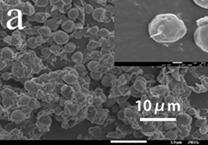
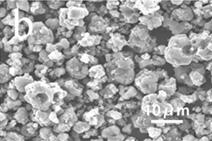
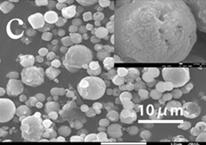
Preparation method of porous hollow calcium carbonate drug-loaded microspheres
A technology of drug-loaded microspheres and calcium carbonate, applied in the field of biomedical engineering, can solve problems such as poor controllability, small holes, and difficulty in entering porous CaCO, and achieve the effects of low cost, simple preparation process, and high drug-loading capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Add the yeast into 5 mL of liquid medium, put it into a constant temperature shaker set at 180 rpm and 37°C for 16 h, and wait for the bacteria to grow to 10 6After cfu / mL concentration, centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 5 min, remove the supernatant, take the precipitate and place it in 0.9% NaCl solution for resuspension; add 20 mL of polydiene dimethyl at a concentration of 1.0 g / mL to the above bacteria solution Ammonium chloride solution (PDDA) solution, shake in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C at 180 rpm for 15 minutes, then centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 5 minutes, then remove the supernatant, add 20 mL of polystyrene sulfonate with a concentration of 1.0 g / mL Shake the acid solution at 180 rpm for 15 min in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C, and then centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 5 min. Repeat this step 4 times. The strain cells treated above were transferred into a beaker, and 100 mL of 0.33 M Ca 2+ The solution was placed in a water bath under magnetic force at 3...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Add the above-mentioned yeasts into 5 mL of liquid medium, put them into a constant temperature shaker set at 180 rpm and 37°C for 16, and wait for the bacteria to grow to 10 6 After cfu / mL concentration, centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 5 min, remove the supernatant, take the precipitate and place it in 0.9% NaCl solution for resuspension; add 20 mL of polydiene dimethyl at a concentration of 2.0 g / mL to the above bacteria solution Ammonium chloride solution (PDDA) solution, shake in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C at 180 rpm for 15 min, then centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 5 min, then remove the supernatant, add 20 mL polystyrene sulfonate with a concentration of 2.0 g / mL Acid PSS solution, shake well and disperse, shake in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C at 180 rpm for 15 min, then centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 5 min, repeat this step 4-6 times. The strain cells treated above were transferred into a beaker, and 100 mL of 0.5 M Ca 2+ The solution was placed in a water...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Add the above-mentioned Escherichia coli to 5 mL of liquid medium, put it into a constant temperature shaker set at 180 rpm and 37 °C for 16 h, and wait for the bacteria to grow to 10 6 After cfu / mL concentration, centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 5 min, remove the supernatant, take the precipitate and place it in 0.9% NaCl solution for resuspension; add 20 mL of polydiene dimethyl at a concentration of 1.0 g / mL to the above bacteria solution Ammonium chloride solution (PDDA) solution, shake in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C at 180 rpm for 15 minutes, then centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 5 minutes, then remove the supernatant, add 20 mL of polystyrene sulfonate with a concentration of 1.0 g / mL Acid PSS solution, shake well and disperse, shake in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C at 180 rpm for 15 min, then centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 5 min, repeat this step 4-6 times. The above-mentioned treated strain cells were transferred to a beaker, and 100 mL of 0.33M Ca 2+ The so...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com