Method of removing iron impurities from trivalent chromium compound
A compound, trivalent chromium technology, applied in the field of iron impurity removal, can solve the problems that have not been seen yet, the iron impurity removal effect is not good, and achieve the effect of good application prospect, good iron removal effect and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
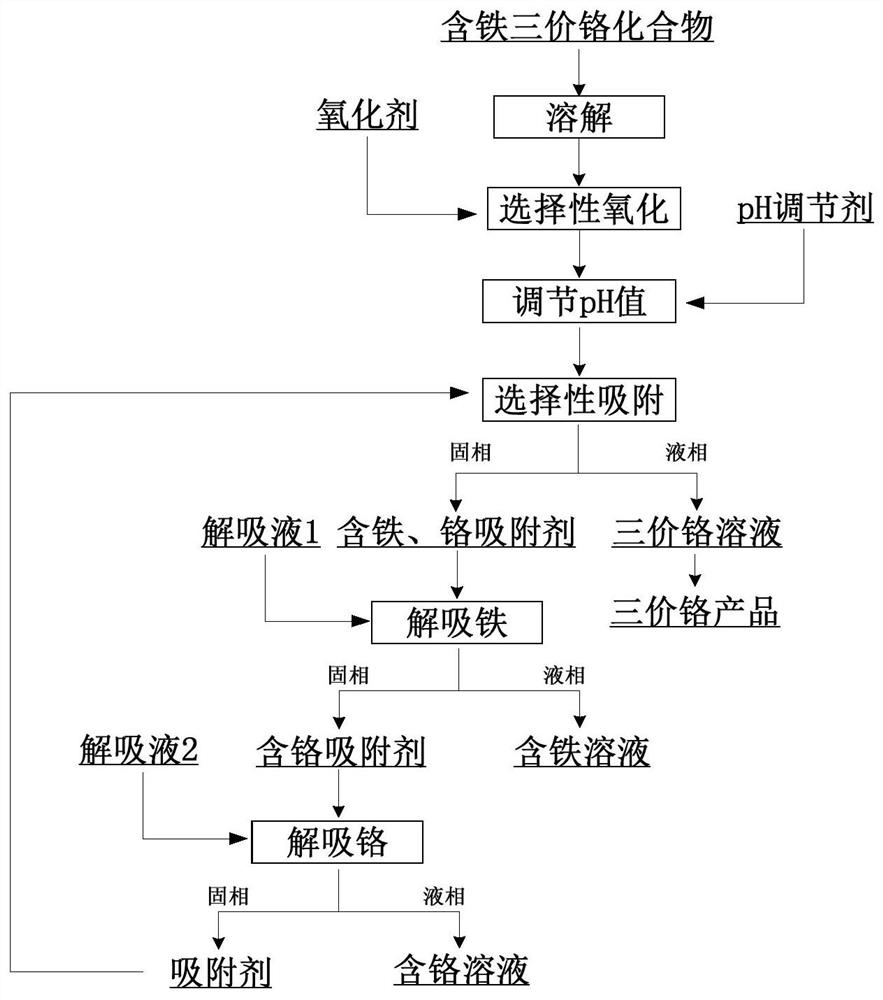
[0050] in 30gL -1 In the basic chromium sulfate solution, quantitatively add 15 times of theoretical amount of hydrogen peroxide according to the content of iron impurities to selectively oxidize the ferrous ions in the solution; add a certain amount of sulfuric acid to adjust the pH value of the solution to 2, Add iron ion imprinting polymer containing phosphonic acid functional groups, the amount added is 0.003g mL -1 , after shaking and adsorbing at 30° C. for 3 hours, the solution was filtered to obtain the adsorbent after adsorption and the basic chromium sulfate solution after iron removal.
[0051] After analysis and calculation, the content of iron impurities in the solution after iron removal is 0.076mg L -1 , The removal rate of iron impurities is 97.60%.
Embodiment 2
[0053] in 30gL -1 In the basic chromium sulfate solution, quantitatively add 1 times the theoretical amount of hydrogen peroxide according to the content of iron impurities, and selectively oxidize the ferrous ions in the solution; add a certain amount of sulfuric acid to adjust the pH value of the solution to 2, Add iron ion imprinting polymer containing phosphonic acid functional groups, the amount added is 0.003g mL -1 , after shaking and adsorbing at 30°C for 3 hours, the solution was filtered to obtain the adsorbent after adsorption and the basic chromium sulfate solution after iron removal. After the solvent in the solution was removed by spray drying, the basic formula after iron removal was obtained. Chromium sulfate.
[0054] After analysis, detection and calculation, the content of iron impurities in the solution after iron removal is 0.298mg L -1 , The removal rate of iron impurities is 90.59%.
Embodiment 3
[0056] in 30gL -1 In the basic chromium sulfate solution, quantitatively add 3 times the theoretical amount of hydrogen peroxide according to the content of iron impurities to selectively oxidize the ferrous ions in the solution; add a certain amount of sulfuric acid to adjust the pH value of the solution to 2, Add iron ion imprinting polymer containing phosphonic acid functional groups, the amount added is 0.003g mL -1 , after shaking and adsorbing at 30° C. for 3 hours, the solution was filtered to obtain the adsorbent after adsorption and the basic chromium sulfate solution after iron removal.
[0057] After analysis, detection and calculation, the content of iron impurities in the solution after iron removal is 0.198mg L -1 , The removal rate of iron impurities is 93.75%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com