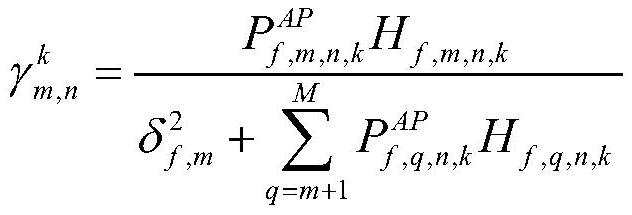Ultra-dense network wireless resource allocation method based on NOMA and beam forming
An ultra-dense network and wireless resource technology, applied in the field of ultra-dense network wireless resource allocation and resource allocation based on NOMA and beamforming, can solve problems such as increased overhead and power consumption, total capacity interference impact, and complex SIC receivers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0110] The present invention will be described in further detail below through examples, and the following examples are explanations of the present invention and the present invention is not limited to the following examples.
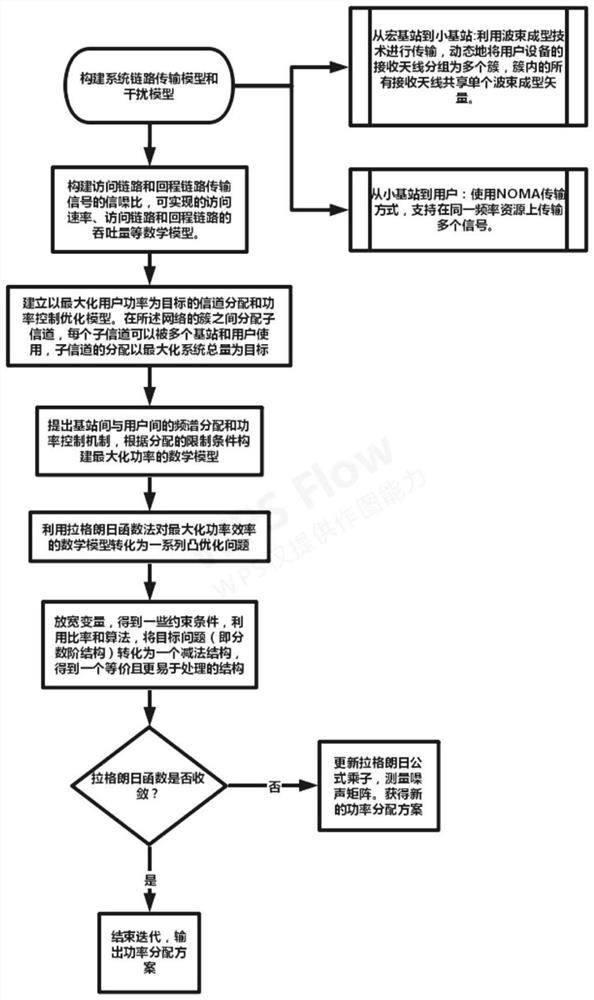
[0111] like figure 1 As shown, the NOMA and beamforming-based ultra-dense network wireless resource allocation method of the present invention includes the following steps:
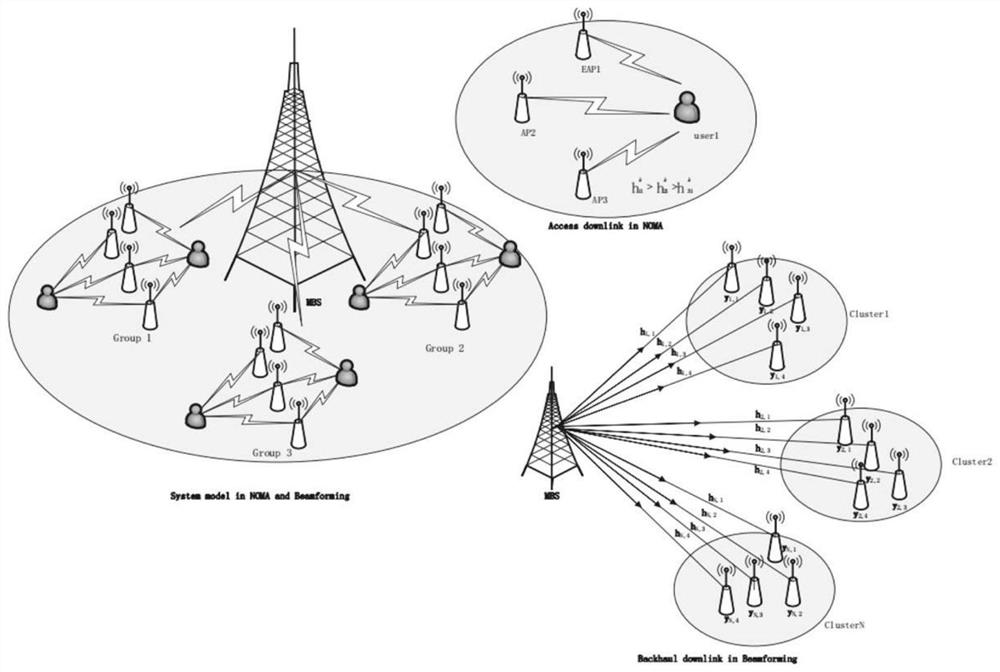
[0112] Step 1: the present invention only considers the downlink, such as figure 2 As shown, a downlink system is constructed, the number of base stations is m, the number of users is n, and k non-orthogonal channels are used, and each channel bandwidth is 10MHz for allocation to any base station and user. Each user forms a link with the accessed base station, which is divided into an access link and a backhaul link. From the macro base station to the small base station (ie, the backhaul link), the present invention will use beamforming technology for transmission, and dynamical...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com