Genetically engineered high-producing strain Streptomyces diastatochromogenes and method for increasing yield of epsilon-polylysine
A technology of Streptomyces chromogenes and high-yielding strains is applied in the biological field, which can solve the problems of increasing ε-polylysine and the like, and achieve the effect of improving the fermentation level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
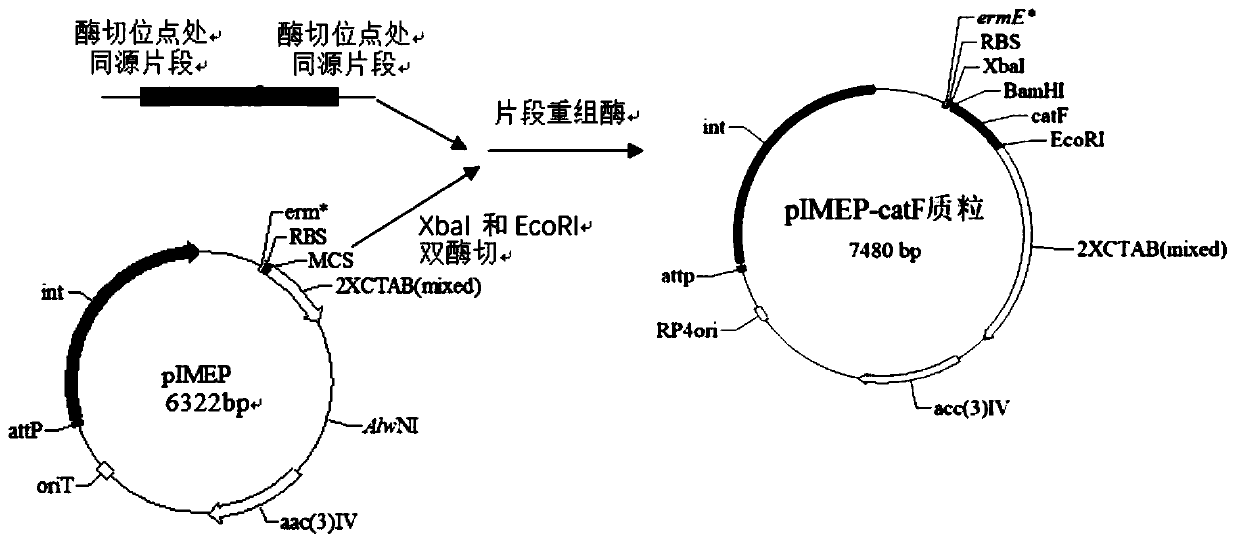
[0070] Obtaining the target catF gene: design the primer sequence according to the catF gene, introduce EcoRI and XbaI enzyme cutting sites at both ends of the gene catF, and add 6 nucleotides to the upstream 5' end of the catF nucleotide sequence to form a restriction The site of the sex endonuclease XbaI, add 6 nucleotides at the downstream 5' end of the catF nucleotide sequence to form the site of the restriction endonuclease EcoRI to extract the amylase Streptomyces chromogenes TUST genomic DNA As a template, use the sequence table SEQ ID No.2 and SEQ ID No.3 as the upstream and downstream primers respectively to carry out PCR reaction to amplify the catF gene in the amylase Streptomyces chromogenes TUST, the full length is 1158bp, see the sequence table SEQ ID No .1.
[0071] PCR reaction system: 2×phanta max buffer 25 μL, dNTP mixture (10mM) 1 μL, template (20ng / ul) 1 μL, upstream and downstream primers ((10 μM)) 2 μL each, DMSO 2 μL, phanta max×Super-Fidelity DNA Polyme...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Construction of recombinant plasmid pIMEP-catF containing catF gene:
[0074] The catF gene fragment amplified by PCR was double-digested with XbaI and EcoRI, and the erythromycin promoter PermE* plasmid pIMEP was double-digested with XbaI and EcorI, and then the catF gene fragment was connected to the double-digested pIMEP plasmid. The corresponding XbaI and EcoRI restriction sites were used to obtain the recombinant plasmid pIMEP-catF of the ligation product. Such as figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0076] Transformation of recombinant plasmid pIMEP-catF:
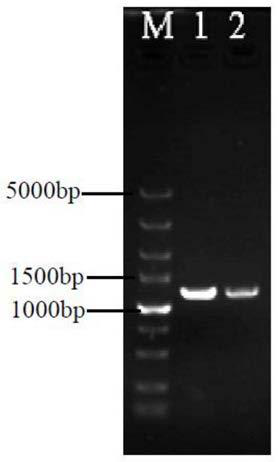
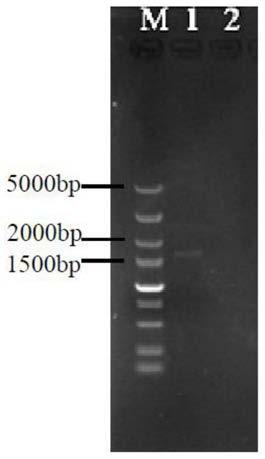
[0077] Take the recombinant plasmid pIMEP-catF of the ligation product and add it to the centrifuge tube containing Escherichia coli JM109 competent cells that have been melted in the ice bath, flick the tube wall, mix well, and put it in the ice bath for 30 minutes. Heat shock at 42°C for 90s, then immediately ice bath for 5min (do not move during this process). Under sterile conditions, add 900 μL of LB medium to the centrifuge tube, mix by pipetting, and incubate with shaking at 37°C and 200 r / min for 45 minutes. Centrifuge the centrifuge tube at 12000r / min for 1min, remove 900μL of supernatant, blow and mix the remaining liquid with a pipette, and spread it on the LB solid plate containing apramycin resistance. Incubate the LB plate upside down at 37°C overnight until a single colony is clearly identifiable, pick positive transformants for colony PCR verification, and the results are as follows figure 2 As shown...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com