Extraction method of oak bark volatile oil as well as detection method and application of oak bark volatile oil
A technology of extraction method and detection method, which is applied in the field of extraction of volatile oil from oak bark, can solve problems such as bleeding, large side effects, and accelerated cardiovascular diseases, and achieve high anticoagulant effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A kind of extraction method of eucalyptus bark volatile oil, the steps are as follows:
[0034] Take 100g of eucalyptus bark and crush it, add distilled water, stir, soak, carry out steam distillation extraction with a volatile oil extraction device, select the optimal extraction conditions: the ratio of material to liquid is 1:5 (g / mL), and the extraction time is 5h to obtain eucalyptus bark The extraction rate of volatile oil is 0.08%±0.03%, and the extraction rate is 30% higher than other solid-liquid ratios (1:4~7) and extraction time (4~6h). The oil and water are separated to obtain a sample, and before gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis, the volatile oil is stored in a sealed bottle and placed in the freezing layer of the refrigerator.
Embodiment 2
[0036] A method for identifying and analyzing the eucalyptus bark volatile oil prepared by the above-mentioned extraction method, the steps are as follows:
[0037]The detection of volatile oil includes: the volatile oil of the species to be tested is analyzed and detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The flow rate is that the initial temperature is 60°C, keep it for 6 minutes, raise the temperature to 300°C at 3°C / min, and keep it for 10 minutes. The ion source temperature is 230°C, the electron bombardment ion source (EI) energy is 70eV, the transfer line temperature is 280°C, the scanning range (m / z): 40-450, and the mass spectrum search library: Nist05.
[0038] By comparison with the standard alkane series (C 8 -C 40 ) and compare its mass spectrum with the reference data in the equipment database (NIST 05) and literature to determine the characteristics of each component. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0039] Table 1 GC-MS analysis results of ...
Embodiment 3
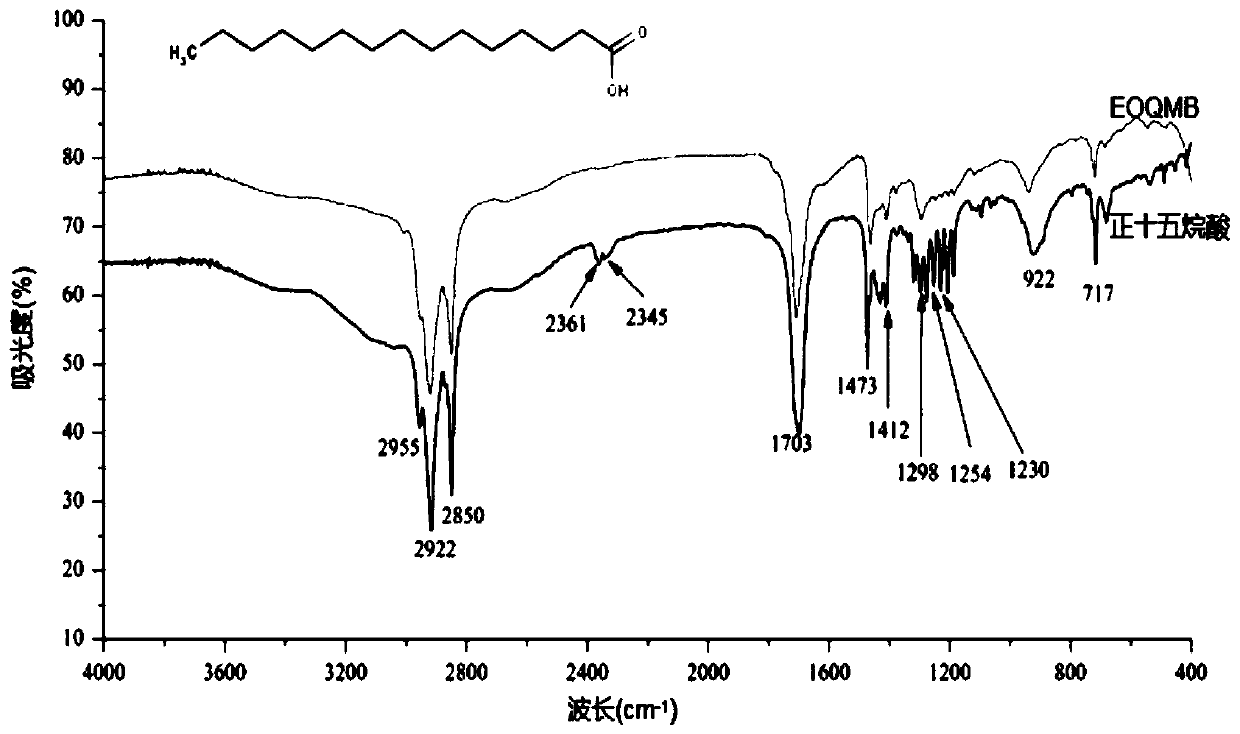
[0063] Adopt Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy to proofread the main components detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, and detect the chemical composition of the eucalyptus bark volatile oil and its main component (pentadecanoic acid), the steps are as follows:
[0064] Mix n-pentadecanoic acid and potassium bromide, grind them at a ratio of 1:100, press them into tablets, apply the volatile oil of oak bark evenly on the KBr solid window, scan the blank spectrum respectively, and use FT-IR spectrophotometry Measured at 4000cm -1 to 400cm -1 The detection was performed 20 times in between, and repeated every 3 minutes.
[0065] As attached to the manual figure 1 The infrared spectrum shown shows that the functional group absorption peak characteristic peaks of oak bark volatile oil and n-pentadecanoic acid are partially similar, and their infrared spectra are mostly consistent, and the GC-MS detection is scientific and reasonable.
[0066] In the attached f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com