Smearing type biodegradable extravascular stent and preparation method thereof
A technology for external stents and blood vessels, which is applied in the fields of extravascular stents and their preparation, smear-type biodegradable extravascular stents and their preparations, and can solve the problems of single form of extravascular stents and complicated preparation process, and achieve biocompatibility Excellent, high viscosity, antithrombotic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Embodiment 1, preparation of extravascular stent hydrogel composite solution
[0055] (1) The raw materials used in the hydrogel composite solution in this embodiment are composed of the following, in terms of mass percentage: gelatin 10.0%, bacterial cellulose 0.6%, endothelial hyperplasia inhibitor rapamycin 1.0%, glutamine transaminase 16.7% , 71.7% sterile PBS solution.
[0056] (2) The preparation steps are as follows:
[0057] 1) Add gelatin, bacterial cellulose, and rapamycin, a drug for inhibiting endothelial hyperplasia, into a square petri dish in sequence, and irradiate with ultraviolet light for 12-24 hours.
[0058] 2) Add the irradiated gelatin, bacterial cellulose, anti-endothelial hyperplasia drug rapamycin and sterile PBS solution in 1) into the Shu Niu bottle, and then heat it with magnetic stirring at 30-35°C for 1 hour to make the components All dissolved to form a mixture (hydrogel solution).
[0059] 3) Add transglutaminase to the suspension.
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2, preparation of extravascular stent hydrogel composite solution
[0061] (1) The raw materials used in the hydrogel composite solution in this embodiment are composed of the following, in terms of mass percentage: gelatin 15.0%, bacterial cellulose 0.6%, endothelial hyperplasia inhibitor rapamycin 1.0%, glutamine transaminase 16.7% , sterile PBS solution 66.7%.
[0062] (2) The preparation steps are as follows:
[0063] 1) Add gelatin, bacterial cellulose, and rapamycin, a drug for inhibiting endothelial hyperplasia, into a square petri dish in sequence, and irradiate with ultraviolet light for 12-24 hours.
[0064] 2) Add the irradiated gelatin, bacterial cellulose, anti-endothelial hyperplasia drug rapamycin and sterile PBS solution in 1) into the Shu Niu bottle, and then heat it with magnetic stirring at 30-35°C for 1 hour to make the components All dissolved to form a mixture (hydrogel solution).
[0065] 3) Add transglutaminase to the suspension.
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3, preparation of extravascular stent hydrogel composite solution
[0067] (1) The raw materials used in the hydrogel composite solution in this embodiment are composed of the following, in terms of mass percentage: 20.0% gelatin, 0.6% bacterial cellulose, 1.0% anti-endothelial hyperplasia drug rapamycin, and 16.7% transglutaminase , sterile PBS solution 61.7%.
[0068] (2) The preparation steps are as follows:
[0069] 1) Add gelatin, bacterial cellulose, and anti-endothelial hyperplasia drugs to a square petri dish in sequence, and irradiate with ultraviolet light for 12-24 hours.
[0070] 2) Add the irradiated gelatin, bacterial cellulose, anti-endothelial hyperplasia drug rapamycin and sterile PBS solution in 1) into the Shu Niu bottle, and then heat it with magnetic stirring at 30-35°C for 1 hour to make the components All dissolved to form a mixture (hydrogel solution).
[0071] 3) Add transglutaminase to the suspension.
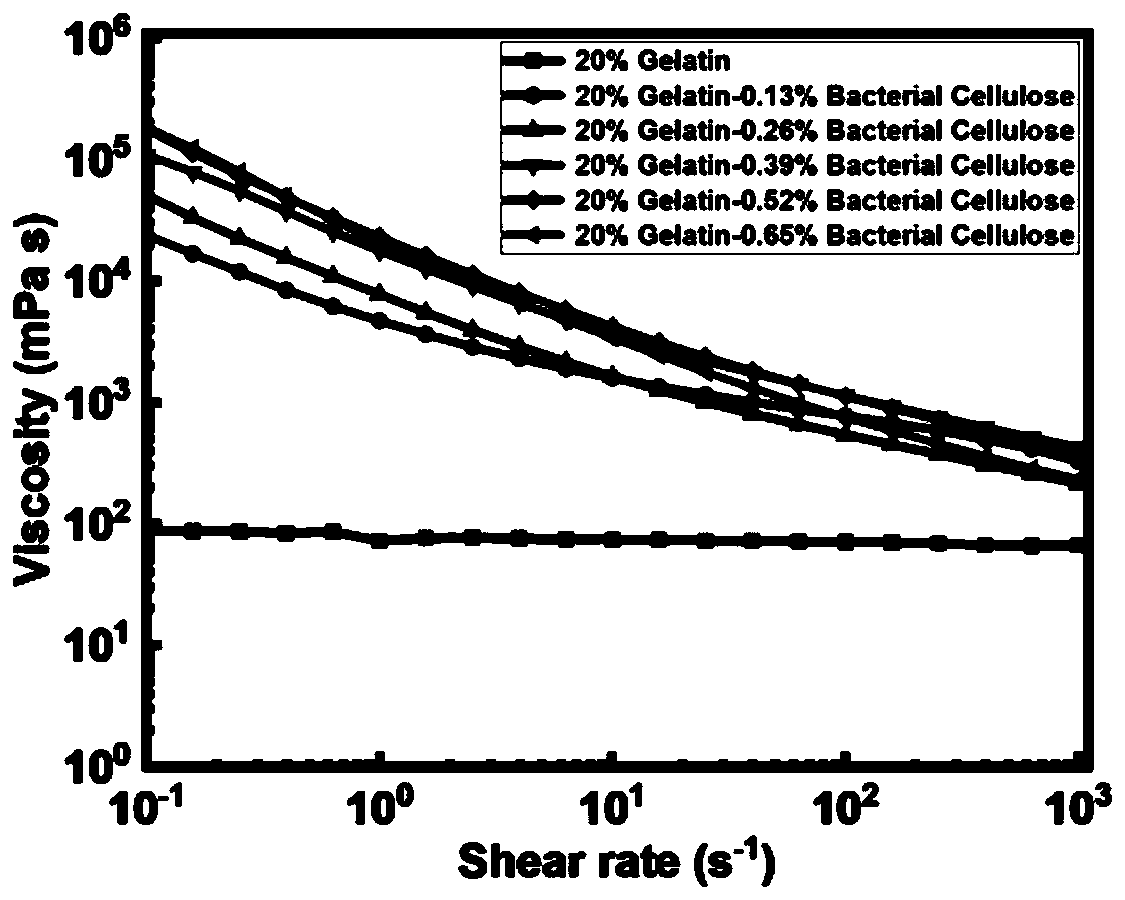
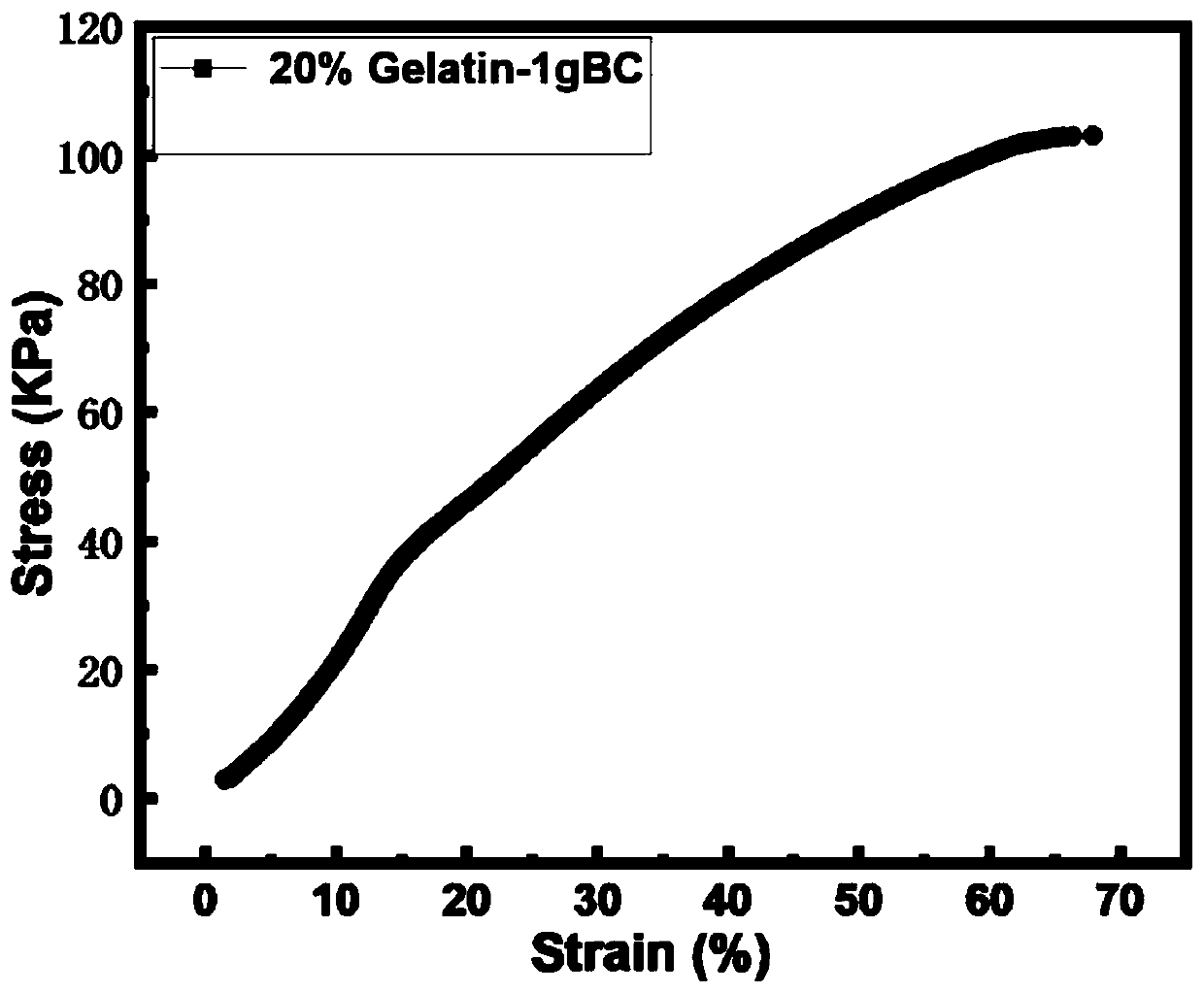
[0072] The shear thinning ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com