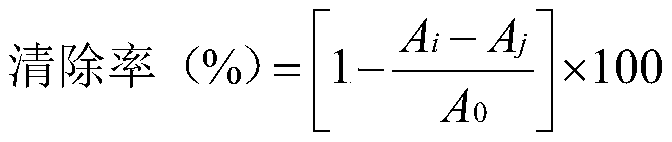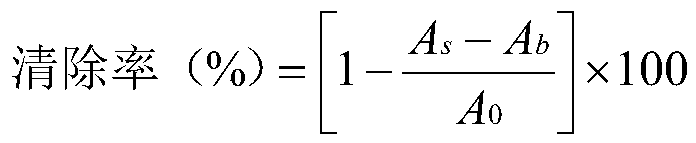Extraction method of lotus leaf polysaccharide
An extraction method and polysaccharide extraction technology are applied in the field of extraction of lotus leaf polysaccharides, which can solve the problems of backward development, high energy consumption, and low yield of lotus leaf polysaccharides, and achieve high yields, increased yields, and high immune activity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0040](2) Preparation of sheep erythrocyte suspension: take appropriate amount of sheep blood, wash with appropriate amount of Hank's solution 3 times (same as before). Discard the supernatant, add an appropriate amount of Hank's solution to dilute and count, so that the final concentration is 8-10 times the concentration of the de-E recipient thymic T cell suspension.
[0041] (3) Preparation of the test solution: take the test sample and prepare a solution containing 1 mg per 1 ml with Hank's solution.
[0042] (4) Determination method: Take 6 small test tubes, 3 of which are added with 0.1ml of Hank's solution as a control tube, and each of the other 3 tubes is added with 0.1ml of the test solution as a test tube, and each tube is added with E receptor thymus T cell suspension 0.2ml. After incubating at 37°C for 1 hour, add 0.2ml of sheep red blood cell suspension, shake well, centrifuge at 500 rpm for 3 minutes, put it in a refrigerator at 4°C overnight, take it out the n...
Embodiment 1
[0072] Embodiment 1: the extraction method of lotus leaf polysaccharide of the present invention
[0073] Step 1: Pretreatment and water extraction of lotus leaf raw materials:
[0074] ①Dry high-quality lotus leaves in an electric heating constant temperature blast drying oven at 40°C for 48 hours, pulverize them with a pulverizer, and pass through a 200-mesh sieve for later use;
[0075] ② Weigh 1 kg of lotus leaf powder, add purified water at a liquid-solid ratio of 20:1, and extract at 75°C for 1.5 hours;
[0076] Step 2: Enzyme Extraction
[0077] Add compound enzyme to the water extraction solution obtained in step 1, control the temperature at 45°C, react for 3 hours while stirring, then raise the temperature to 90-95°C to inactivate the enzyme for 15 minutes, filter with suction, collect the filtrate, concentrate to obtain a concentrated polysaccharide extract ;
[0078] Step 3: alcohol precipitation, deproteinization and decolorization
[0079] Add 3 times the vol...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Embodiment 2: the extraction method of lotus leaf polysaccharide of the present invention
[0086] Step 1: Pretreatment and water extraction of lotus leaf raw materials:
[0087] ①Dry high-quality lotus leaves in an electric heating constant temperature blast drying oven at 40°C for 48 hours, pulverize them with a pulverizer, and pass through a 200-mesh sieve for later use;
[0088] ② Weigh 1 kg of lotus leaf powder, add purified water at a liquid-solid ratio of 30:1, and extract at 75°C for 2 hours;
[0089] Step 2: Enzyme Extraction
[0090] Add compound enzyme to the water extraction solution obtained in step 1, control the temperature at 50°C, react for 3.5 hours while stirring, then raise the temperature to 90-95°C to inactivate the enzyme for 15 minutes, filter with suction, collect the filtrate, concentrate to obtain a concentrated polysaccharide extract ;
[0091] Step 3: alcohol precipitation, deproteinization and decolorization
[0092] Add 4 times the vol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com