Novel stapled peptides serving as KRASG12C/SOS1 inhibitor and application of novel stapled peptide
A technology of A0B0C0D0E0F0G0A1B1C1D1, stapled peptides, applied in the direction of animal/human peptides, peptides, peptide sources, etc., can solve problems such as inability, reduced solubility, and poor stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] Example 1: Preparation and Characterization of Stapled Peptides:
[0111] 1.1. Synthesis of stapled peptide
[0112] Synthesis of stapled peptides was artificially carried out by SPPS method; the synthesis scale was 0.1 mmol, 40-RAM amphiphilic Rink amide resin was loaded at 0.4 mmol / g, and an excess of 5 equivalents was used for protected amino acids; all protected amino acids and even The joint agent HATU was pre-dissolved in DMF to prepare a stock solution with a concentration of 0.5M; under vortex stirring, the resin was first swelled in 6mlDMF for 15 minutes, and after the DMF was removed by filtration, the solution was added by adding 20% piperidine / DMF solution ( 6ml) and vortexed for 1 minute to deprotect the Fmoc group; the above steps were carried out twice; finally, the resin was washed 3 times with DMF, and then the required amino acid (1ml, 0.5mmol), N, N-diisopropyl Diethylamine (DIEA) (0.164ml, 1mmol) and HATU coupling reagent (1ml, 0.5mmol) and stirre...
Embodiment 2
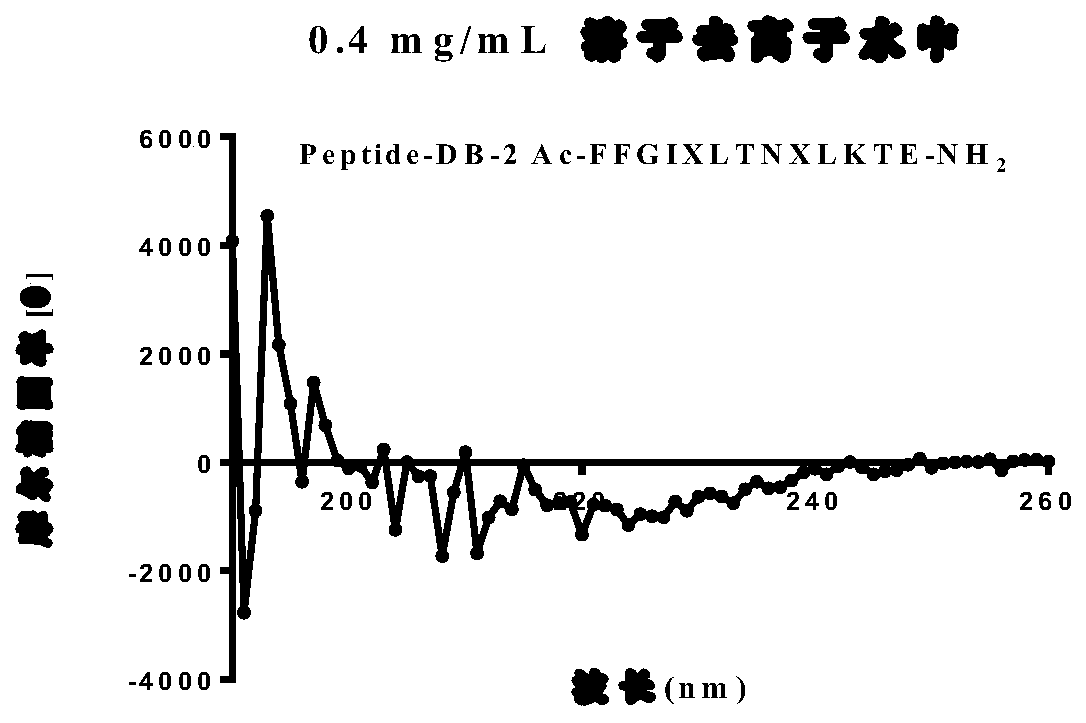
[0120] Example 2: Evaluation of whether stapled peptides maintain α-helical structure:
[0121] In order to further understand the effect of shortening the length of the polypeptide on the α-helical structure, and using trifluoroethanol to promote the formation of the α-helical secondary structure, a circular dichroism test was performed on the stapled peptide; on the CD spectrum The typical secondary structure of polypeptides in the far ultraviolet region (185–245nm) has its own characteristic absorption peaks; among them, the α-helix has double negative peaks at 208nm and 222nm, and a positive peak at 195nm; A weaker negative peak appears; random curl has a negative peak at 200nm, and a small and broad positive peak at 220nm.
[0122] Determination of the secondary structure of stapled peptides by circular dichroism spectroscopy, CD spectra were measured using a J-810 spectrometer at 25 °C using a quartz cell with an optical path length of 1.0 mm and recorded by scanning in th...
Embodiment 3
[0131] Example 3: Evaluation of stapled peptides and KRAS G12C Protein binding affinity:
[0132] For detection of SAH-SOS1A and Peptide-DB-1 with KRAS G12C For direct protein binding, real-time binding assays were performed using label-free biomolecules combined with the ForteBio Octet Red 96 system and biolayer interferometry (BLI) technology; biomolecules bind to the sensor surface to form biofilms; biofilms interfere with the light transmitted through the sensor; Interference phenomena are detected by phase shifts and thus changes in the number of molecules bound to the sensor surface; binding affinity is typically assessed using the Kd (equilibrium dissociation constant), which is used to assess the strength of bimolecular interactions.
[0133] Assessment of stapled peptides and KRAS by biofilm interferometry (BLI) G12C Binding affinity of protein; KRAS assessed using biolayer interferometric biosensor in OctetRed 96 instrument G12C Binding affinity between proteins a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com