Methods of isolating T cells having antigenic specificity for P53 cancer-specific mutation
A specific and antigen-specific technology, applied in the field of isolating T cells with antigen specificity for P53 cancer-specific mutations, can solve the problems of difficult identification and isolation of T cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
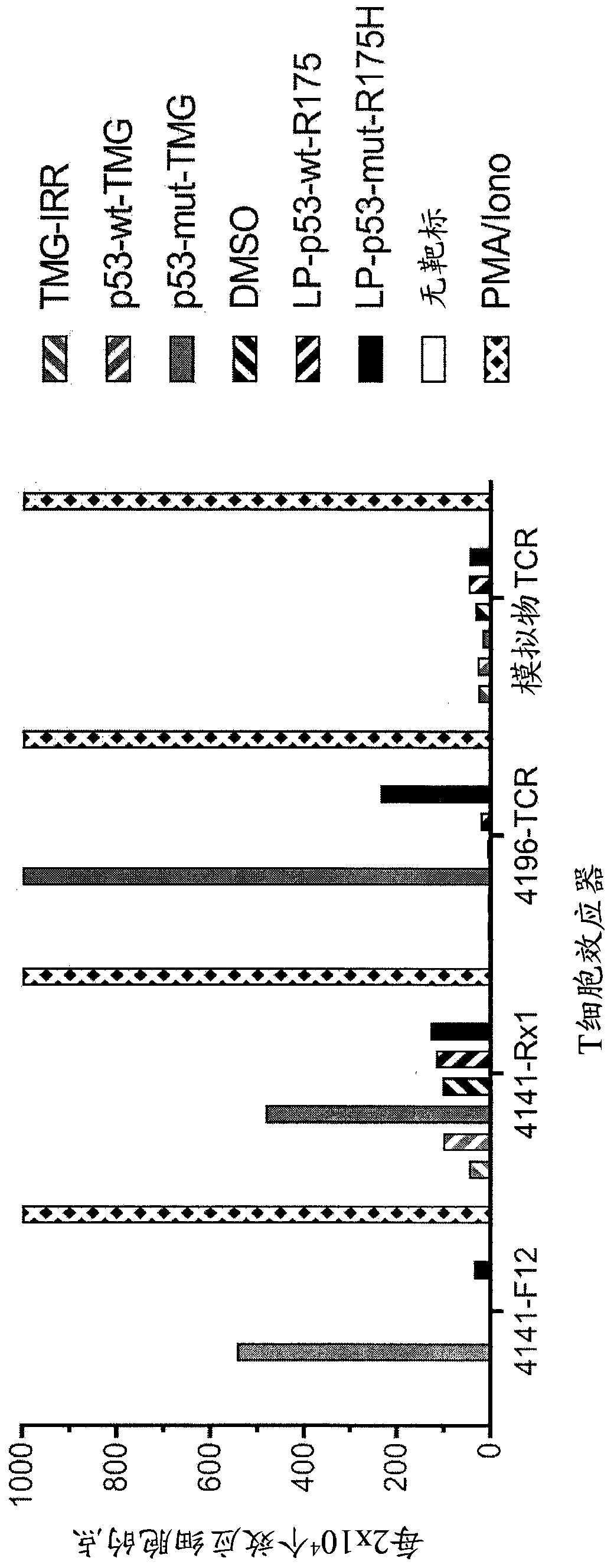
[0139] This example demonstrates the identification of anti-mutant p53 T cells in patient 4141 by co-culturing autologous APCs induced to express mutated p53 within autologous T cells ("p53 hotspot mutation universal screen"). This example also demonstrates the isolation and specific reactivity of the TCR from patient 4141.
[0140] Such as figure 1 and 45 -48 Experiments were performed as described for patient 4141. TIL fragment F12 and infusion bag TIL (Rx1 ) from patient 4141 and p53-R175H-specific TCR or mock-transduced T cells from patient 4196 were used as effectors. Co-cultures of T cell effectors with HLA-A*02:01APCs (autologous for patient 4141) were (1) electroporated with TMG consisting of irrelevant, WT p53, or mutated p53 sequences, or (2) with a peptide vehicle (DMSO) or a purified (>95% by HPLC) 25 amino acid peptide pulse consisting of the WT p53-R175 sequence or the mutated p53-R175H sequence. T cells only (no target) are negative controls, and PMA and Ion...
Embodiment 2
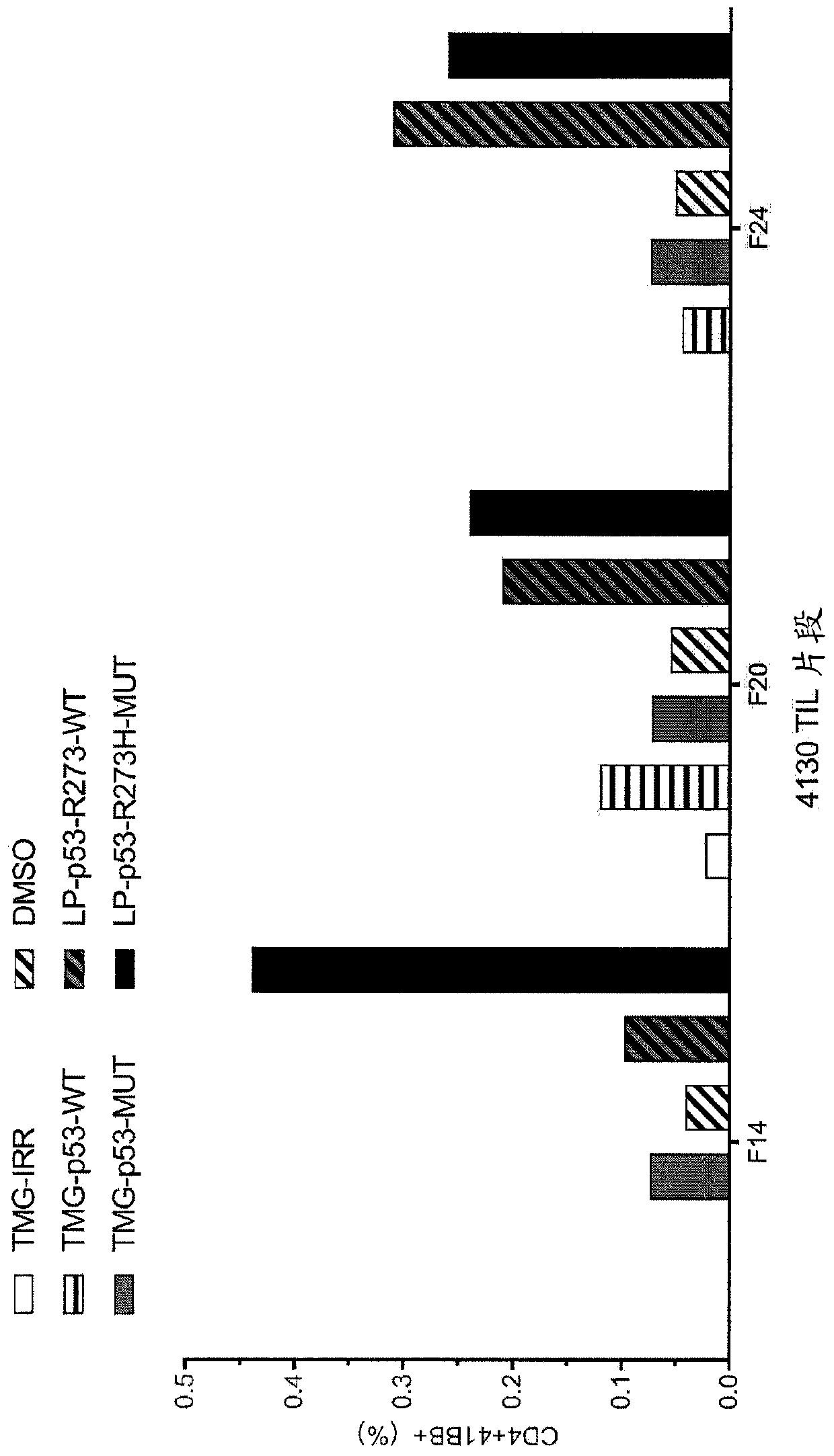
[0159] This example demonstrates the identification of anti-mutant p53 T cells in patient 4130 by co-culturing autologous APCs induced to express mutated p53 within autologous T cells ("p53 hotspot mutation universal screen").
[0160] Such as figure 2 Experiments were performed as described for patient 4130. TIL fragments (F14, F20 and F24) from patient 4130 were co-cultured with autologous APCs (1) electroporated with TMG consisting of irrelevant, WT p53 or mutated p53 sequences, or (2) Pulse with peptide vehicle (DMSO) or purified (>95% by HPLC) 25 amino acid peptide consisting of WT p53-R273 sequence or mutated p53-R273H sequence. Co-cultivation was performed overnight at 37°C. Expression of 4-1BB was assessed by flow cytometry after gating on lymphocytes→viable cells (PI negative)→CD3+ (T cells). The results are shown in figure 2 middle.
Embodiment 3
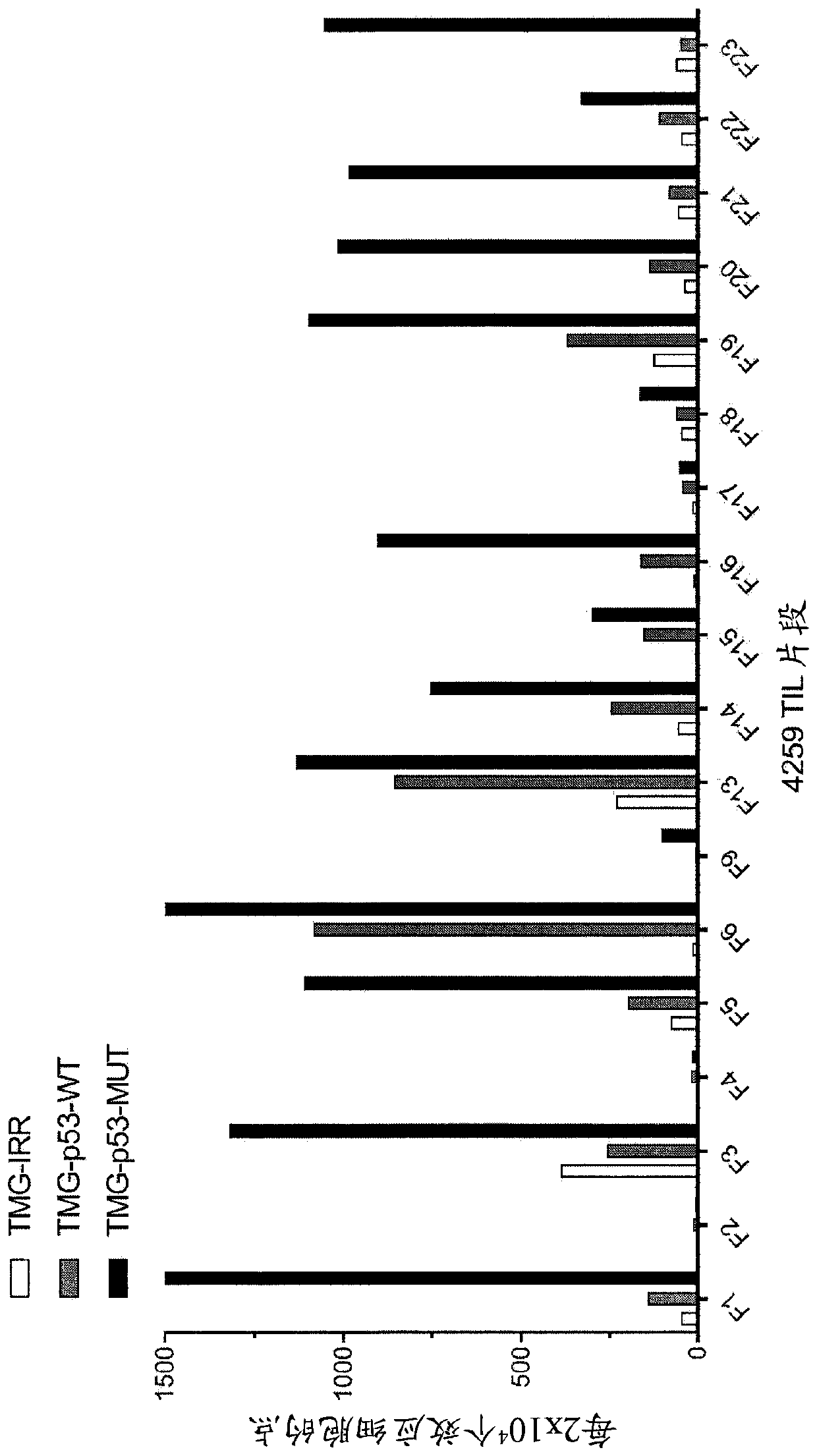
[0162] This example demonstrates the identification of anti-mutant p53 T cells in patient 4259 by co-culturing autologous APCs induced to express mutated p53 within autologous T cells ("p53 hotspot mutation universal screen"). This example also demonstrates the isolation and specific reactivity of the TCR isolated from patient 4259.
[0163] Such as Figure 3-8 and 49-53 were performed as described for patient 4259. TIL fragments (n=18) from patient 4259 were co-cultured with autologous APCs electroporated with TMG consisting of irrelevant, WT p53 or mutated p53 sequences. Co-cultivation was performed overnight at 37°C. IFN-γ secretion was assessed using an ELISPOT assay. The results are shown in image 3 middle. Expression of 4-1BB was assessed by flow cytometry after gating on lymphocytes→viable cells (PI negative)→CD3+ (T cells). The results are shown in Figure 4-5 middle.
[0164] TIL fragments (n=18) from patient 4259 were combined with a purified (>95% by HPLC) 25...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com