Method for removing organic arsenic in water through synchronous oxidation and in-situ adsorption
A technology for organic arsenic and water removal, applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc. Large specific surface area, efficient adsorption and removal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0043] Specific embodiment one: a kind of synchronous oxidation and in-situ adsorption method of removing organic arsenic in the present embodiment, it is carried out according to the following steps:
[0044] Add ferrous salt and persulfate to arsenic-containing water to realize simultaneous oxidation degradation and in-situ adsorption to remove organic arsenic in water, wherein the molar ratio of ferrous salt and persulfate is: 1:0.8-4.
[0045] In this embodiment, the total arsenic concentration can be detected by an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) or an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS), and the separation and determination of organic arsenic and inorganic arsenic can be performed by high performance liquid chromatography. Combined with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LC-ICP-MS) detection.
[0046] This embodiment adopts divalent iron salt (Fe 2+ ) activating the persulfate to treat the organic arsenic in...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0047] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that the arsenic-containing water is organic arsenic and / or inorganic arsenic. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0048] The method in this embodiment is mainly aimed at organic arsenic, but the method is also applicable to inorganic arsenic or a mixture of the two, and can still achieve the technical effect described in the present invention.
[0049] Verify the beneficial effects of the present invention through the following examples:
Embodiment 1
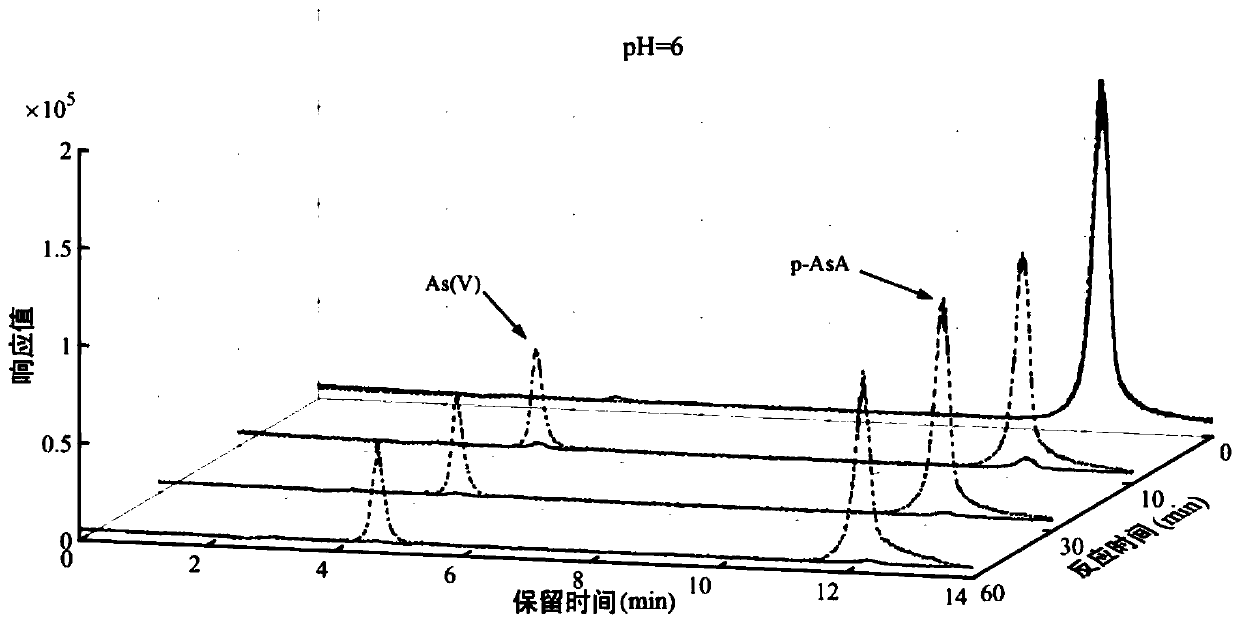
[0051] A method for removing organic arsenic in water by synchronous oxidation and in-situ adsorption of the present embodiment comprises the following steps: adding 100 μmol of ferrous sulfate and 75 μmol of potassium peroxodisulfate to 1 L of water containing p-aminophenylarsine, The concentration of aminophenylarsine is 5 μmol / L, the pH is 3, and the temperature is 25°C. After stirring for 30 minutes, adjust the pH to 6, and filter through a 0.22 μm cellulose acetate membrane to complete the removal of arsenic in water. After testing, 90.3% of p-aminophenylarsine was oxidatively degraded, the removal rate of total arsenic was 99.4%, and the content of remaining total arsenic was 2.25 μg / L, which was lower than that specified in the Hygienic Standard for Drinking Water (GB5749-2006). The specified limit of arsenic concentration in water (10μg / L).
[0052] Compared with CN 109942070A patent, the condition of pH=3 in this embodiment, and the minimum pH of CN 109942070A patent ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com