Water treatment method for reducing and degrading halogenated organic matters by using copper-activated thiourea dioxide
A halogenated organic compound and thiourea dioxide technology, which is applied in the reduction water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the harsh reaction conditions of halogenated organic compounds, secondary pollution, and high treatment costs. problem, to achieve the effect of low reaction conditions, stable effect and strong reaction selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
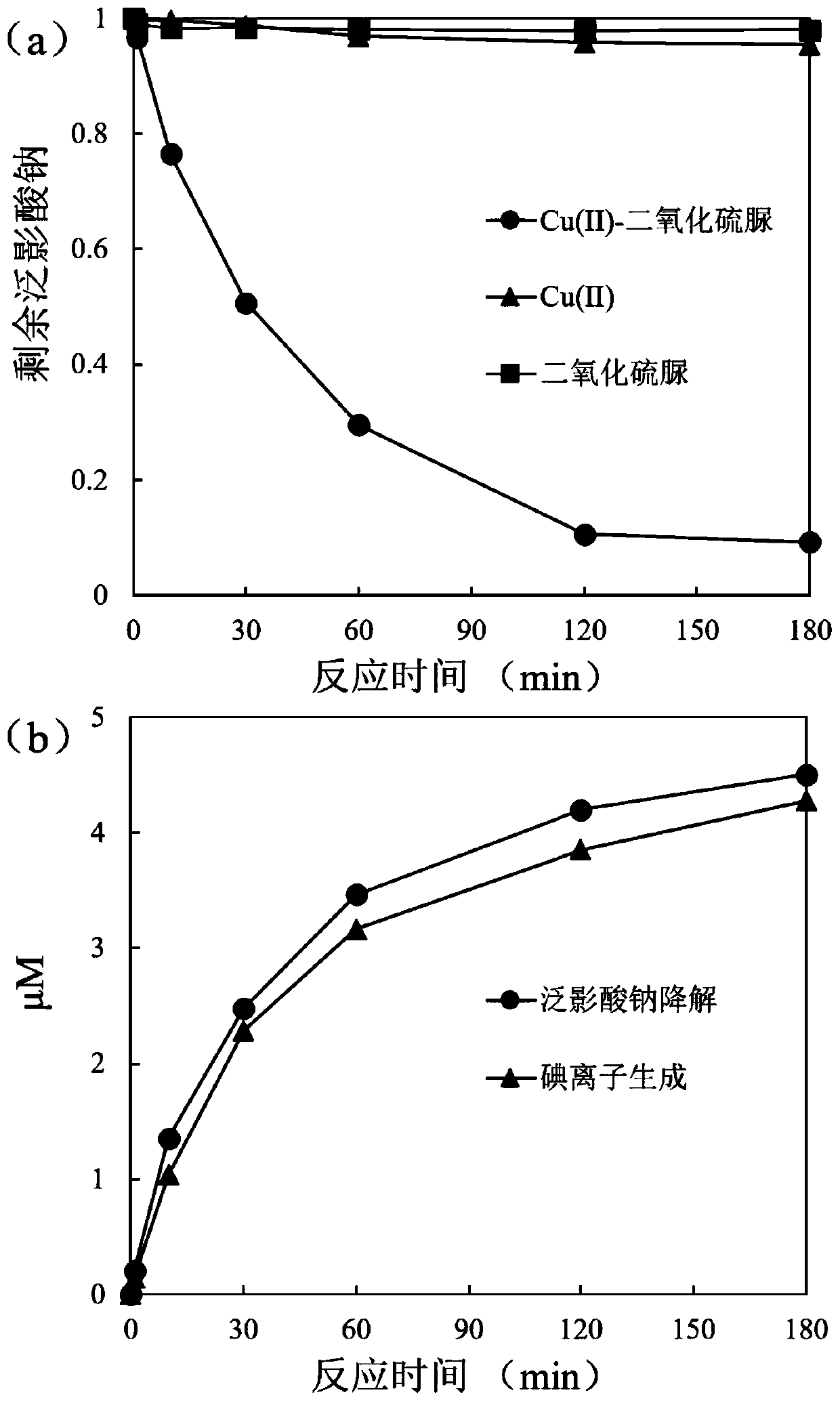
[0039] Prepare a solution of 5 μmol / L sodium diatrizoate, adjust the pH to 7.5 with borate buffer salt, add CuSO 4Stock solution, make the concentration of divalent copper ion reach 10 μmol / L, then add the existing thiourea dioxide stock solution to start the reaction. Do a comparative experiment of adding divalent copper ions and thiourea dioxide alone; the reaction is carried out under magnetic stirring at 25°C, and when the reaction lasts for 1min, 10min, 30min, 60min, 120min, and 180min, samples are taken to determine the concentration of remaining sodium diatrizoate in the solution and the generated iodide ion concentration, the results are as follows figure 1 shown.
[0040] Depend on figure 1 The measurement results show that after 3 hours of reaction, the removal rate of sodium diatrizoate reaches 90%, and the amount of iodide ion generation and the degradation amount of sodium diatrizoate are basically 1:1. In the control experiment, adding divalent copper ions and...
Embodiment 2
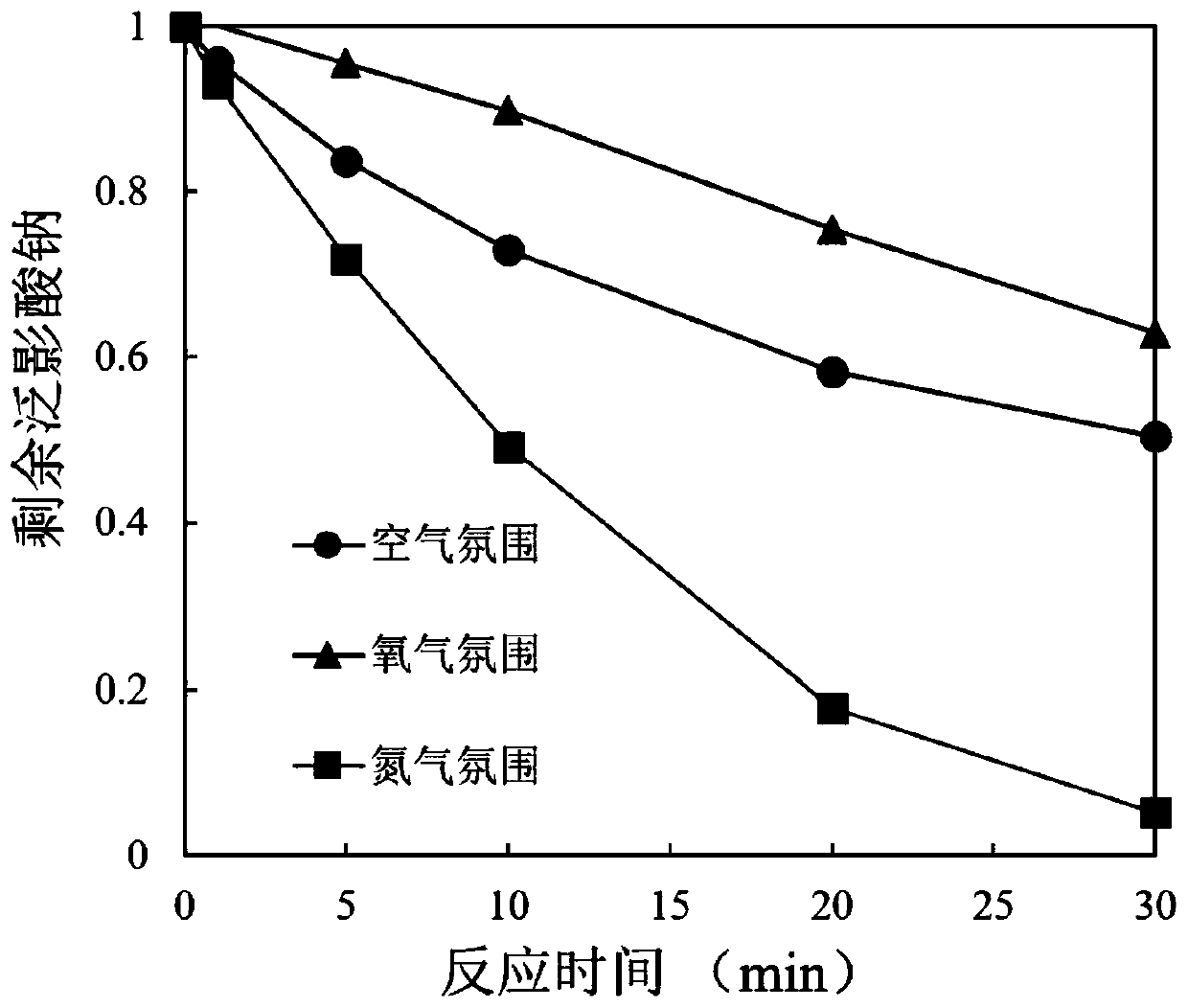
[0042] Prepare a solution of 5 μmol / L sodium diatrizoate, adjust the pH to 7.5 with borate buffer salt, add CuSO 4 Stock solution, so that the concentration of divalent copper ions reaches 10 μmol / L, divide the above mixed solution into three groups, one group is continuously magnetically stirred in the air atmosphere, one group is continuously magnetically stirred into the solution to aerate oxygen, and one group is continuously exposed to the solution Nitrogen was aerated with magnetic stirring; the reaction was started by adding the stock solution of thiourea dioxide that was ready to use, and the initial concentration of thiourea dioxide was 50 μmol / L; In the time of 30min, samples were taken respectively to determine the residual sodium diatrizoate concentration in the solution, and the results were as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0043] Depend on figure 2 According to the measured results, after reacting for 30 minutes, the degradation rate of sodium diatrizoate was 48...
Embodiment 3
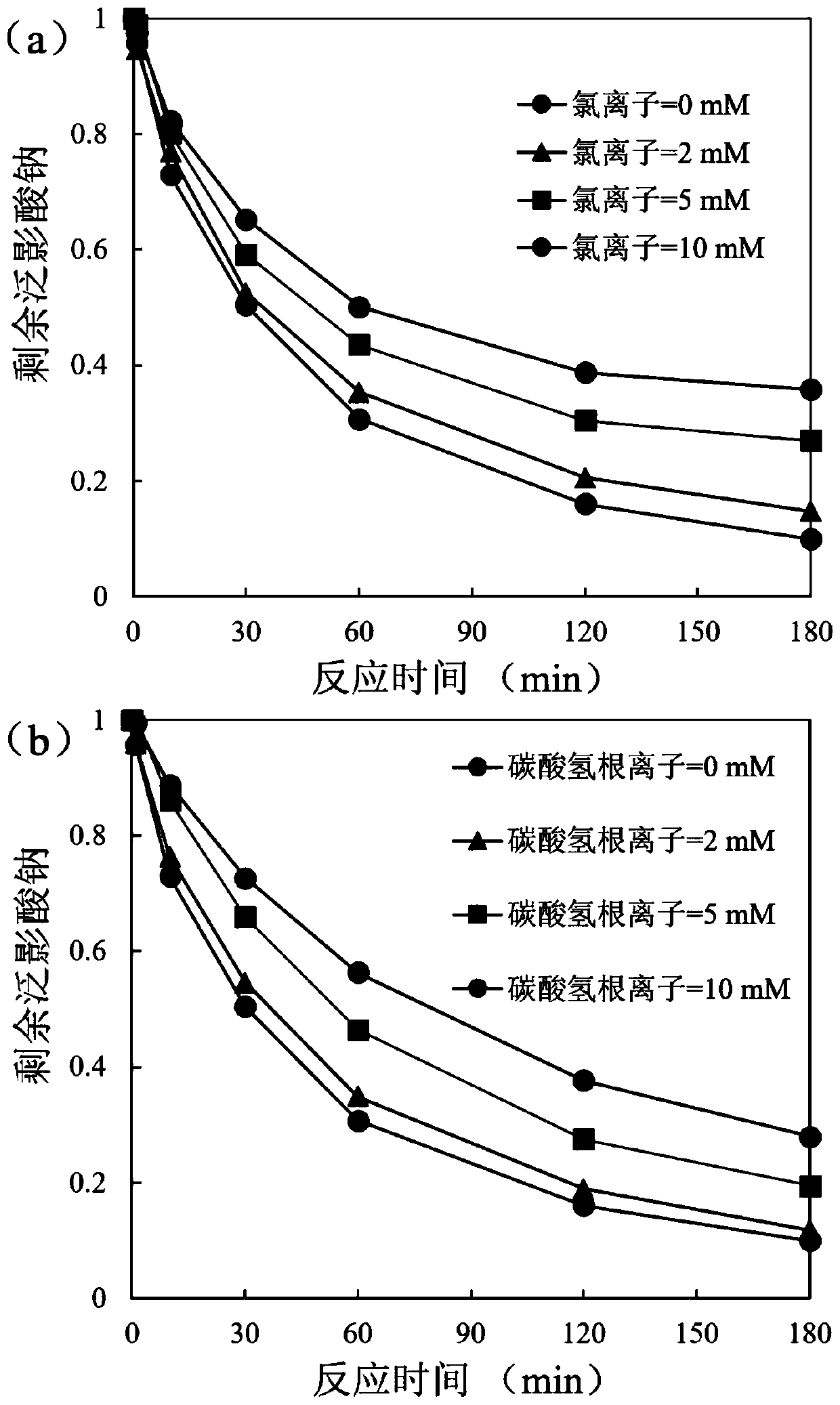
[0045] Prepare a solution of 5 μmol / L sodium diatrizoate, adjust the pH to 7.5 with boric acid buffer salt, divide the above solution into 7 parts, one part is used as a control, and add salt to the other 6 parts of the solution, so that the solutions have the following concentrations Ions: 2mmol / L chloride ion, 5mmol / L chloride ion, 10mmol / L chloride ion, 2mmol / L bicarbonate ion, 5mmol / L bicarbonate ion, 10mmol / L bicarbonate ion-; in 7 solutions Add CuSO 4 stock solution, so that the concentration of divalent copper ions reaches 10 μmol / L, and then add the existing thiourea dioxide stock solution to start the reaction. The initial concentration of thiourea dioxide is 50 μmol / L; When continuing for 1min, 10min, 30min, 60min, 120min, and 180min, samples were taken respectively to determine the remaining sodium diatrizoate concentration and the iodide ion concentration generated in the solution. The results are as follows: image 3 As shown, the unit mM in the figure represents...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com