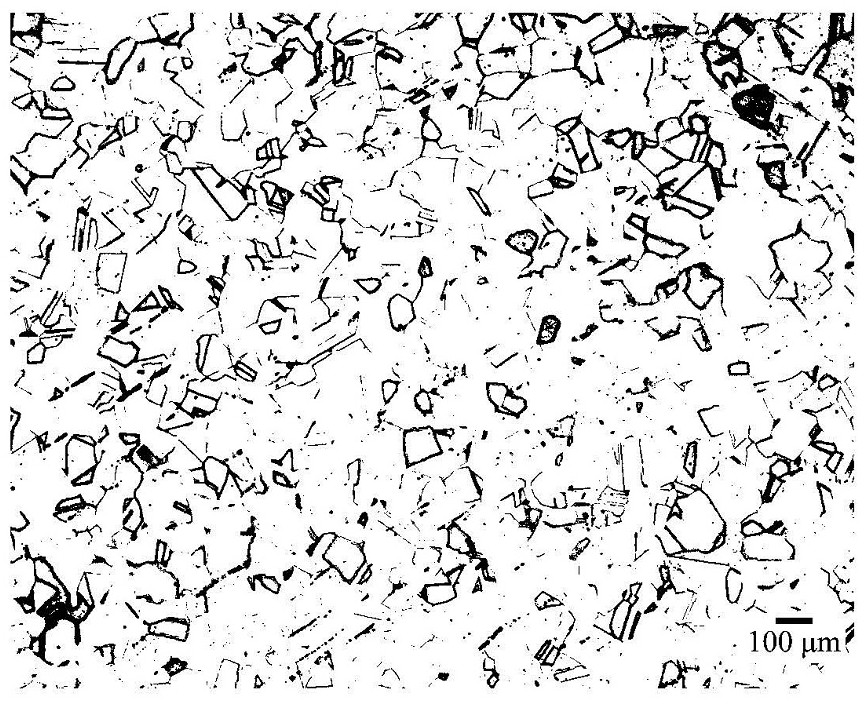
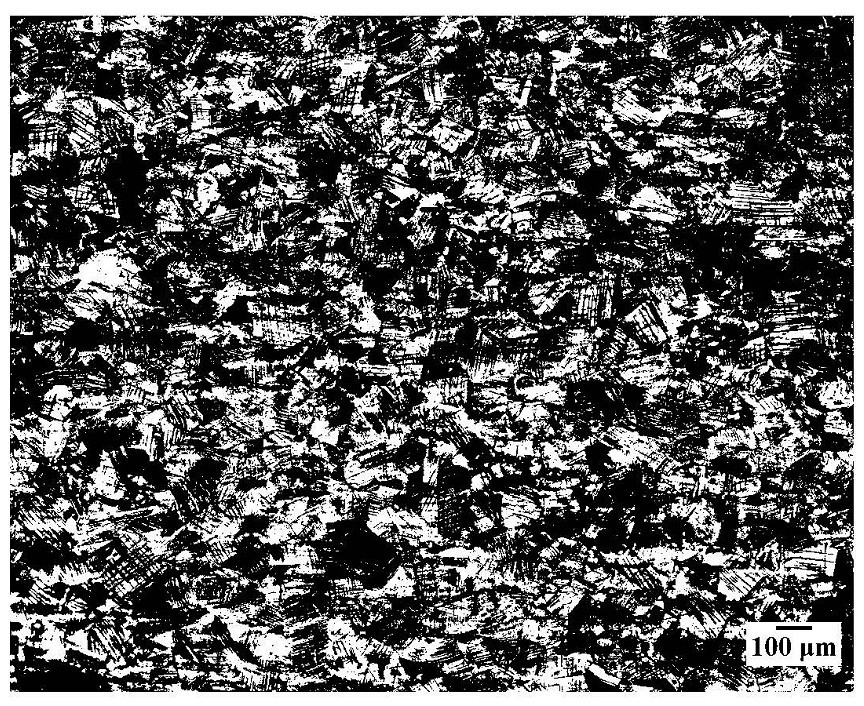
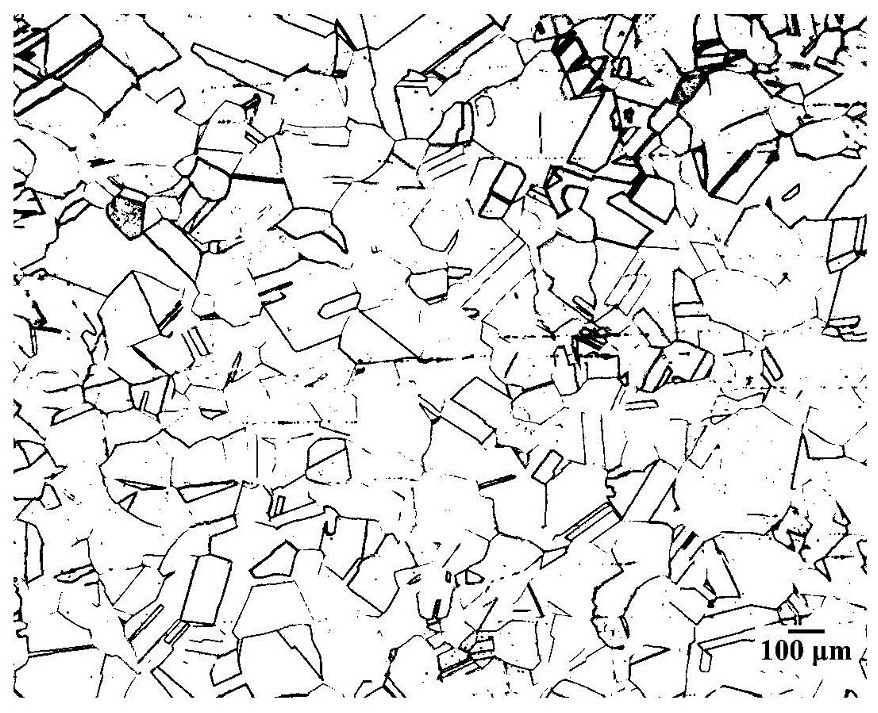
Corrosive agent for metallographic phase of nickel-saving austenitic stainless steel
A technology of austenitic stainless steel and corrosive agent, applied in the field of corrosive agent, can solve the problems of difficulty in grasping the degree of erosion, coarsening and blurring of grain boundaries, low corrosion efficiency, etc. The effect of high corrosion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] (1) Preparation of etchant
[0036] The corrosive agent is prepared from 8-12 parts by weight of oxalic acid, 2-4 parts by volume of hydrochloric acid, and 80-120 parts by volume of distilled water, wherein, when the unit of the parts by weight is gram, the unit of the parts by volume is milliliters ; When the unit of the parts by weight is kilogram, the unit of the parts by volume is liter; the consumption of each component can be enlarged or reduced in equal proportion.
[0037] a) Add 8-12 g of oxalic acid into 80-120 ml of distilled water, and keep stirring to mix evenly.
[0038] b) Pour 2-4ml hydrochloric acid into the prepared oxalic acid solution, stir and mix evenly.
[0039] (2) Metallographic corrosion method
[0040] a) The nickel-free austenitic stainless steel sample is made into a metallographic sample by rough grinding, fine grinding, polishing, cleaning and drying.
[0041] b) Take the prepared sample as the anode, fix it with galvanized tweezers and...
specific Embodiment
[0045] The composition of the J3 stainless steel used in the more specific embodiment 1 and embodiment 2 of the present invention is shown in Table 1; the composition of the J5 stainless steel used in Example 3 is shown in Table 2.
[0046] Table 1: Composition of J3 stainless steel used in the test (wt, %)
[0047] C Si mn Cr Ni Cu P S N Fe 0.12 0.40 9.0 13.8 1.31 0.55 0.04 0.004 0.15 margin
[0048] Table 2: Composition of J5 stainless steel used in the test (wt, %)
[0049] C Si mn Cr Ni Cu P S N Fe 0.08 0.47 7.8 15.9 1.22 / 0.04 0.004 0.20 margin
Embodiment 1
[0051] (1) Preparation of corrosive agent
[0052] First add 10g of oxalic acid into a beaker containing 100ml of distilled water, stir evenly, then add 2ml of hydrochloric acid into the prepared oxalic acid solution, stir evenly to prepare a corrosive agent.
[0053] (2) Sample preparation
[0054] Grind and polish the test surface of the J3-section nickel-type austenitic stainless steel cold-rolled sample with 240#, 360#, 600#, 800#, 1000#, and 1200# water-grinding paper in turn after bright annealing to form a sample to be corroded, and then Rinse with distilled water, spray with alcohol and blow dry.
[0055] (3) Corrosion display
[0056] Fix the sample with tweezers and connect it to a DC power supply. The sample is connected to the positive pole, the aluminum plate is connected to the negative pole, the voltage is 20V, and the time is 50s. After the corrosion is over, cut off the power supply, remove the sample, rinse it with distilled water, then spray it with alco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com