Composite magnetic nanoparticle and its preparation method and application
A technology of magnetic nanoparticles and magnetic materials, which can be used in pharmaceutical formulations, preparation of X-ray contrast agents, preparations for in vivo experiments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to achieve operation or drug delivery, cell death, and cytotoxicity, and achieve cost-effective Low, good compatibility, high safety effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Take 10 mL of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) and 50 mL of 0.12M Na 2 SO 4 solution, added to 15 mL of ZnSO 4 ·H 2 In the O solution, after stirring for 20min, 30mL of 0.27M Na was added dropwise 2 CO 3 , producing [Zn 5 (CO3) 2 (OH) 6 ] colloidal precipitation; then take 50 mL of FeSO with a concentration of 0.4 M 4 ·7H 2 Mix O and 0.2g Vc, adjust the pH of the solution to 11.0 with NaOH, then add [Zn 5 (CO 3 ) 2 (OH) 6 ] The colloidal precipitation was thoroughly mixed, and after centrifugation, it was dispersed into an ethanol solution of the same volume, and then transferred to a polytetrafluoroethylene liner in an autoclave. Standby.
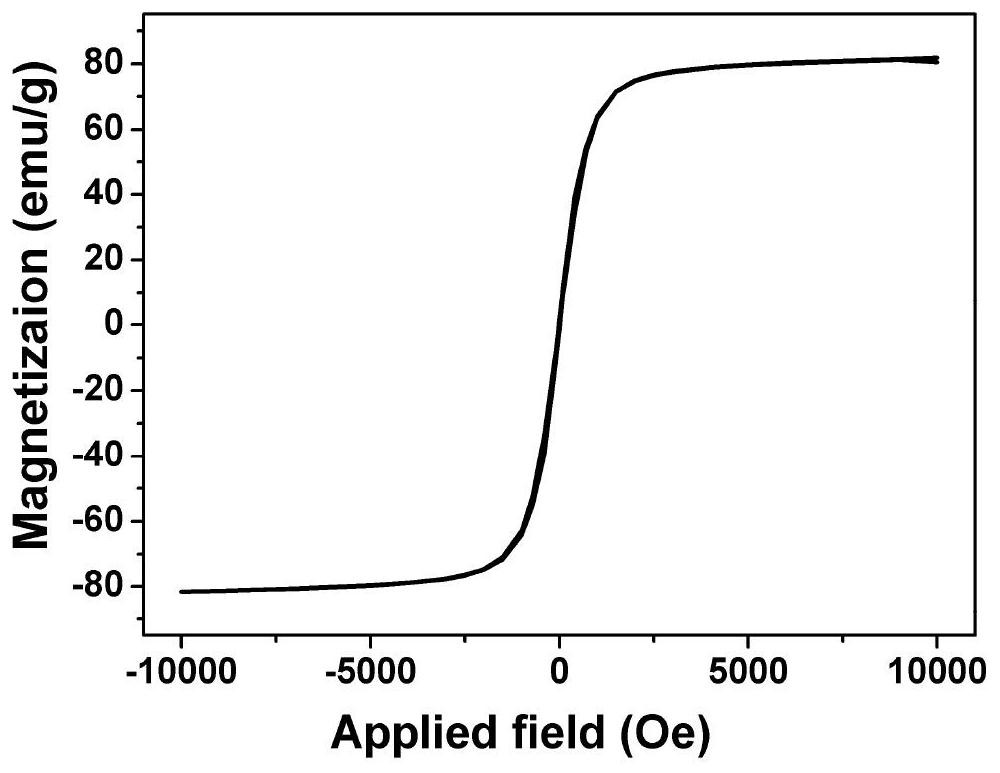
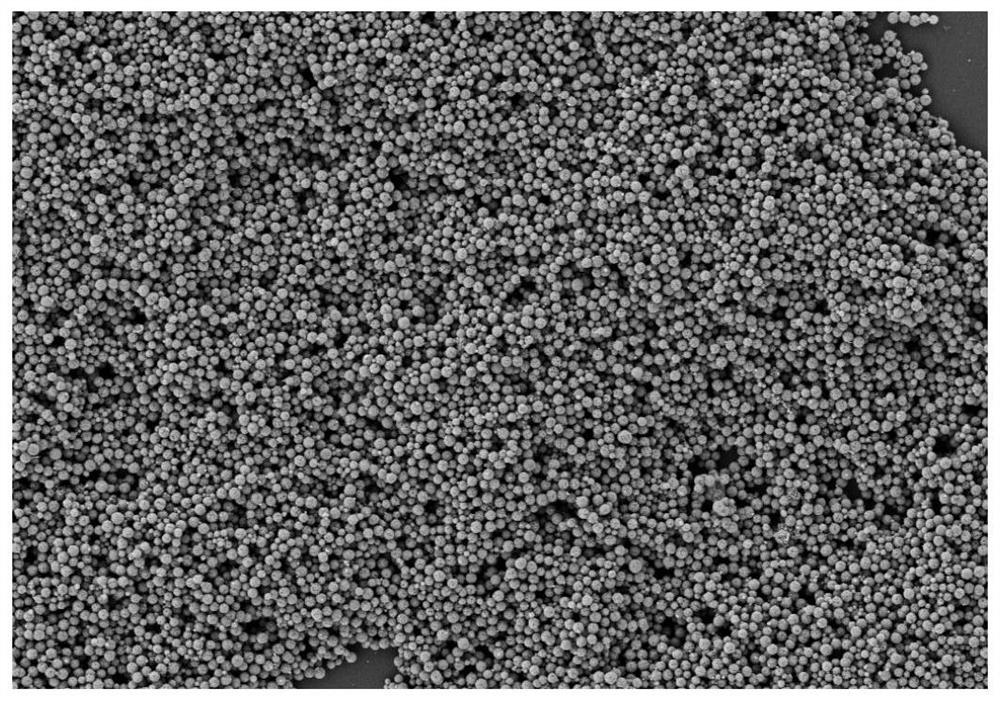
[0046] Saturation magnetization test of the resulting magnetic nanoparticles (see figure 1 ) and SEM morphology characterization (see figure 2 ). The test results show that the saturation magnetization of the nanoparticles can reach 80 emu / g, the particle size is uniform, and the diameter is about...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The cytotoxicity of magnetic nanoparticles was tested by CCK8 method. Different concentrations of magnetic particles were added to a 96-well plate to inoculate rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) and fibroblasts, respectively. Each well was inoculated with a cell suspension (100 μl / well) to make the cell volume about 1×10 6 indivual. Place the plate in an incubator for a period of time (37°C, 5% CO). 2 ). Add 10 μl of CCK solution to each well (be careful not to generate air bubbles in the wells, they will affect the OD reading). Incubate the plate in the incubator for 1-4 hours. The absorbance at 450 nm was measured with a microplate reader. The results of the toxicity of granules on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and fibroblasts were as follows: Figure 4 a and Figure 4 b, it shows that the magnetic nanoparticle material of this example has good biocompatibility and no cytotoxicity.
Embodiment 3
[0051] Ordinary magnetic particles (as a control) and PHBV-coated magnetic nanoparticles prepared in this example were added to a 6-well plate, inoculated with rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), and the cell suspension (100 μl / well) was inoculated into each well. ) to make the amount of cells about 1×10 6 indivual. Incubate the plate in an incubator (37°C, 5% CO) for 12 hours. 2 ). Trypsinize, collect the suspension, use a magnet to collect the cells that have phagocytosed the magnetic particles, wash with medium every hour, and count the cells. like Figure 5 shown, the verification results show that Fe 3 O 4 @PHBV nanoparticles are better than ordinary Fe 3 O 4 Magnetic nanoparticles labeled stem cells with a longer labeling time.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com