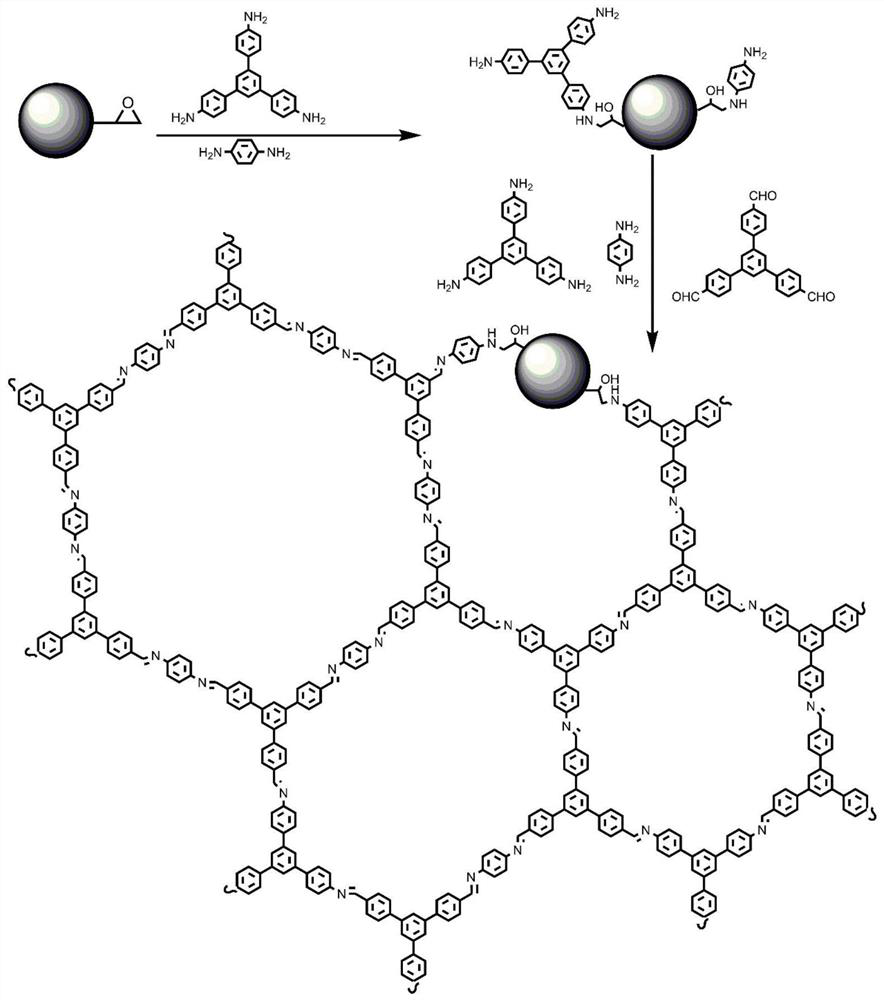
A composite material based on heteroporous covalent organic framework and its preparation method and application
A technology of covalent organic frameworks and composite materials, which is applied in the field of composite materials based on heteroporous covalent organic frameworks and its preparation, can solve the problems of low affinity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, easy aggregation of covalent organic framework materials, The adsorption capacity needs to be improved to achieve the effect of large adsorption capacity, fast adsorption speed and enhanced stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1 Preparation of covalent organic framework / polyglycidyl methacrylate-divinylbenzene composite material
[0031] (1) Preparation of polyglycidyl methacrylate-divinylbenzene microspheres
[0032] Polyglycidyl methacrylate-divinylbenzene microspheres are prepared by using existing conventional methods; the specific preparation process is as follows:
[0033]3 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone and 100 mL of a mixture of ethanol and water (volume ratio of ethanol to water 95:5, V / V) were added to a 250 mL four-neck round bottom flask and heated in a water bath at 70°C. Mix 18 g of styrene and 0.8 g of azobisisobutyronitrile and add dropwise to the above flask, control the dropping speed, and complete the dropwise addition in about 30 minutes. After reacting under nitrogen protection for 24 hours, the obtained solids (ie, polymer seeds) were washed with excess water and stored in a 1% aqueous solution of sodium dodecyl sulfonate (m / v). The polymer seeds were dispersed in 1...
Embodiment 2
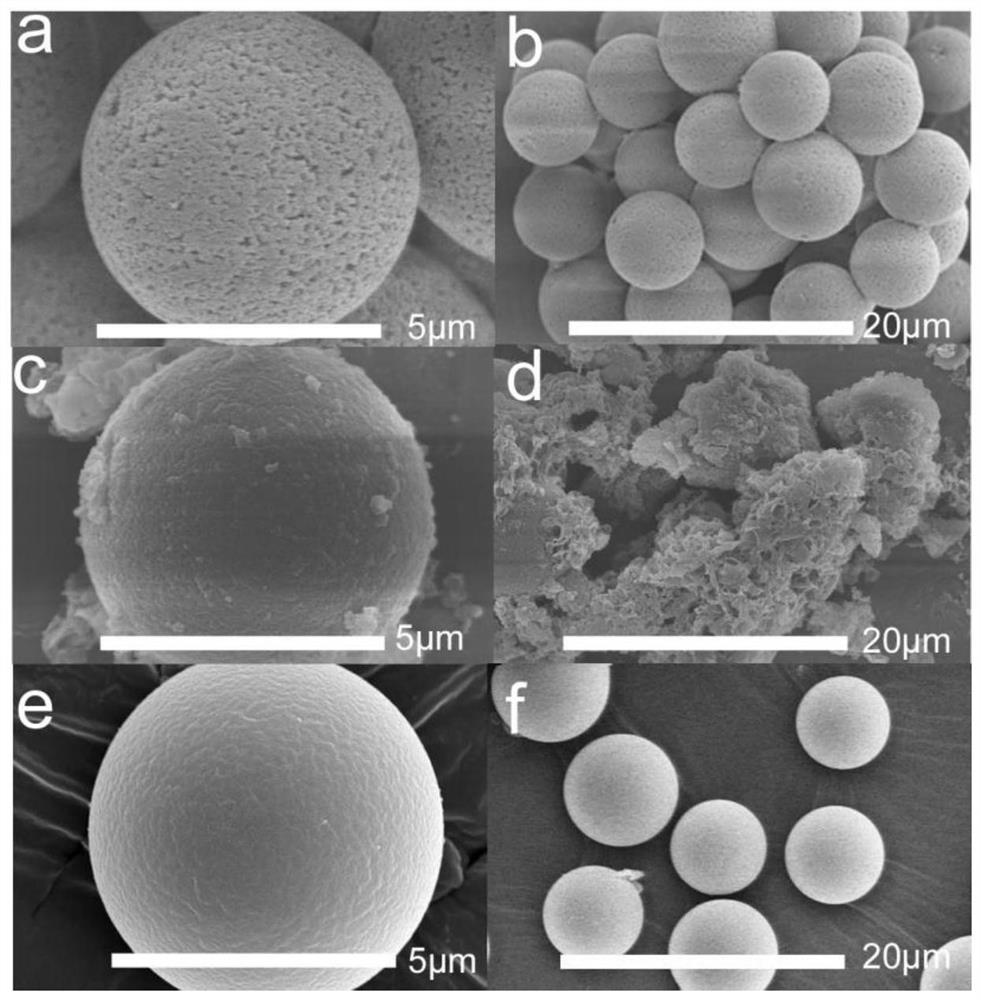
[0036] Example 2 Morphology study
[0037] like figure 2 As shown in a and 2b, the surface of polyglycidyl methacrylate-divinylbenzene microspheres has a porous structure. like figure 2 As shown in c and 2d, in the whole reaction, p-phenylenediamine, 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene, 1,3,5-tris(p-formylbenzene)benzene and polymethacrylic acid The mass ratio of glycidyl ester-divinylbenzene microspheres is 1:3:5:12; in the dehydration reaction stage, p-phenylenediamine, 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene and polymethyl The mass ratio of glycidyl acrylate-divinylbenzene microspheres was 9:20:300; the final reaction product was agglomerated spheres with uneven crystal growth on the surface of the spheres;
[0038] like figure 2 As shown in e and 2f, in the whole reaction, when p-phenylenediamine, 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene, 1,3,5-tris(p-formylbenzene)benzene and polymethyl The mass ratio of glycidyl acrylate-divinylbenzene microspheres is 1:2:4:12, in the dehydration ...
Embodiment 3
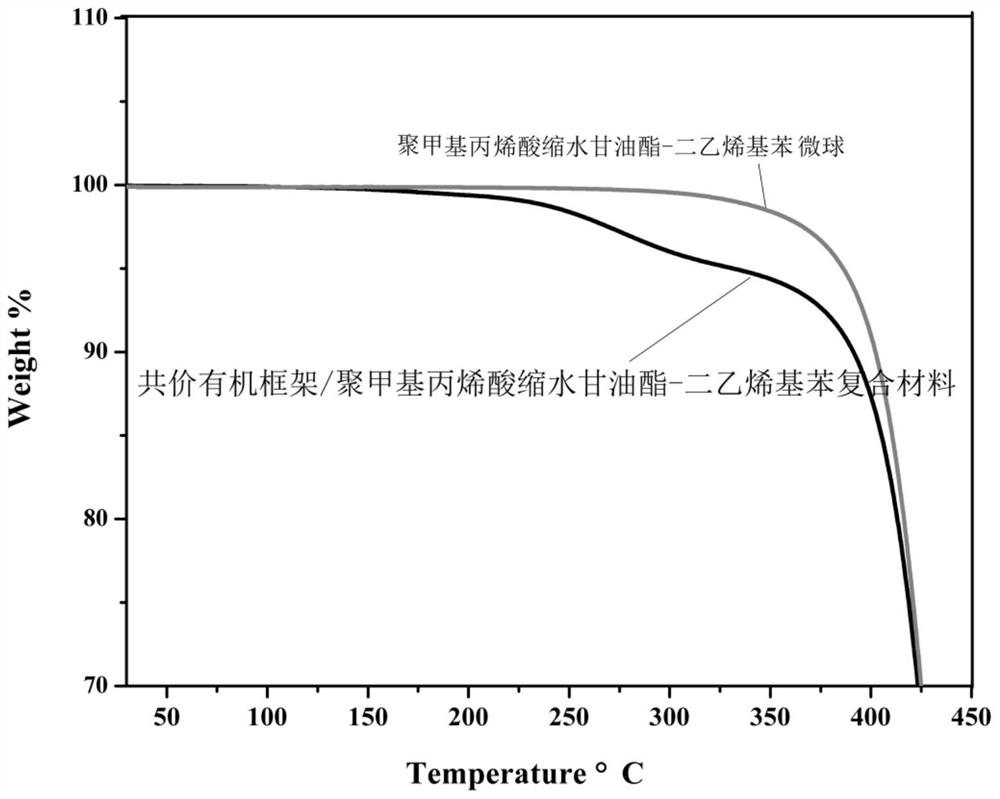
[0040] Example 3 Thermal Stability Study
[0041] Thermogravimetric analysis of polyglycidyl methacrylate-divinylbenzene microspheres and covalent organic framework / polyglycidyl methacrylate-divinylbenzene composites was performed using DSCQ1000 differential scanning calorimetry, respectively. The result is as image 3 As shown, according to the results, the covalent organic framework / polyglycidyl methacrylate-divinylbenzene composite material begins to thermally decompose at 150 degrees Celsius, indicating that it can meet the daily extraction needs.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com