Method for extracting and enriching phage in soil
A bacteriophage and enrichment technology, applied in the field of soil biology, can solve the problems of low phage acquisition rate, time-consuming and labor-intensive operation, difficulty in passing through the membrane, etc., and achieves the effect of good operation prospect, simple operation, and simple operation method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
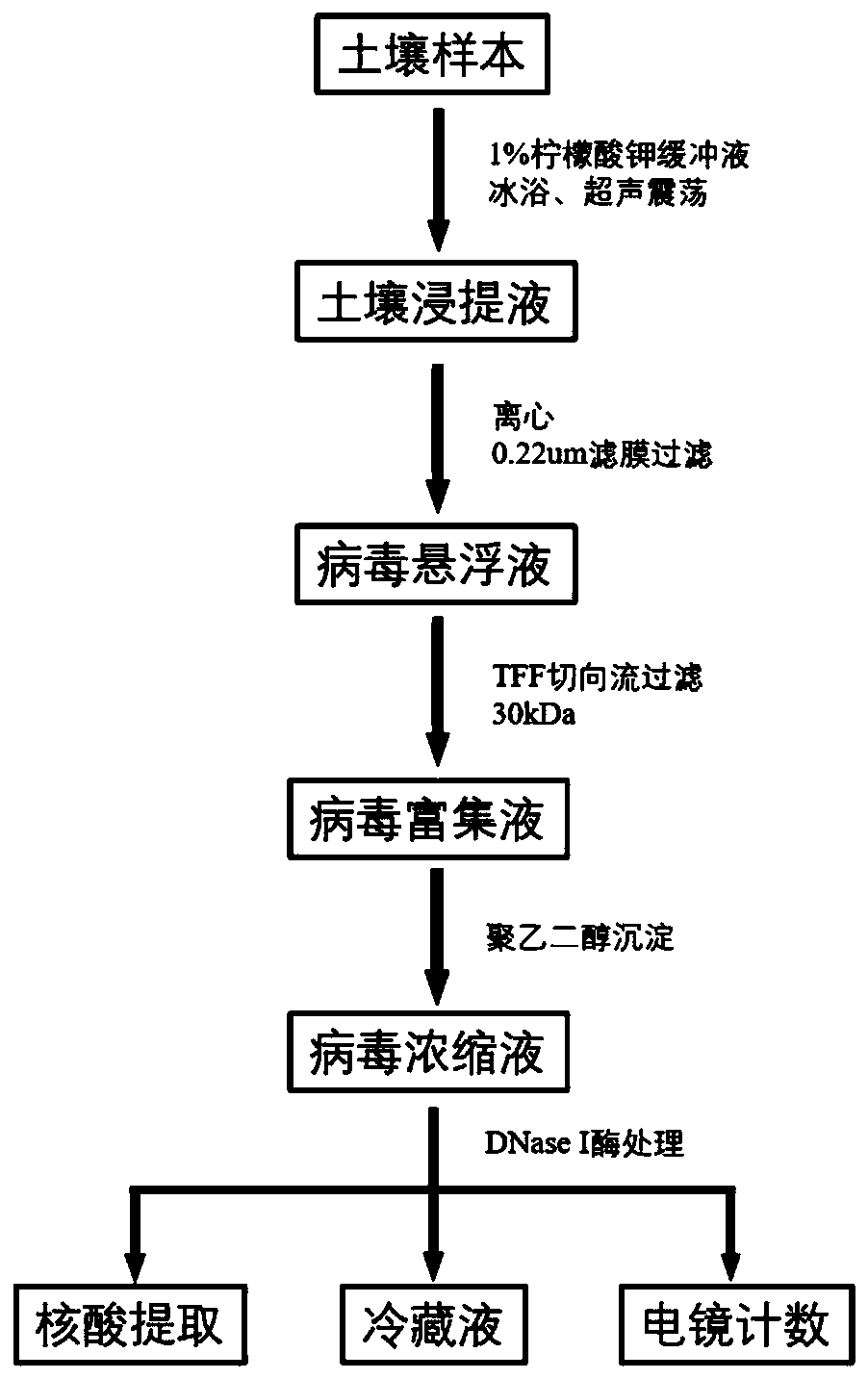
[0023] Example 1 Method for Soil Phage Extraction and Enrichment in Grassland Soil
[0024] Grassland soil (a total of three samples, numbered Grassland-1, Grassland-2, and Grassland-3) was collected in Nanjing Agricultural University, and transported back to the laboratory at 4 °C. After removing impurities such as plant roots and stones in the soil, mix 300g of soil samples with 1L of 1% potassium citrate buffer solution. Each liter of potassium citrate buffer solution contains: 10g C 6 h 5 K 3 o 7 , 1.92 g Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O, 0.24g KH 2 PO 4 , pH=7, placed at 4°C for low-temperature incubation for 15 minutes to disperse the soil sample, and subjected it to short-term ultrasonic treatment in an ice-bath environment. shaken manually for 30 s; the total time of ultrasound was 3 minutes, and the ultrasound conditions were 100 W, 47 kHz. Since the soil texture is fine and difficult to centrifuge, centrifuge at 8000rpm for 10 minutes to obtain the supernatant, transfer the...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2 The method for extracting and enriching soil phages from chromium-contaminated soil
[0026] The formulations of each reagent are the same as in Example 1. In a chromium slag contaminated site in Luzhou City, Sichuan Province (two samples in total, numbered Luzhou-1, Luzhou-2) and a chromium slag contaminated site in Zhangye City, Gansu Province (one sample in total, numbered Zhangye -1) Obtain chromium-contaminated soil, remove impurities from the contaminated soil, mix 300g of soil sample with 1L of 1% potassium citrate buffer, and place it at 4°C for 15 minutes to incubate the soil sample to disperse the soil sample, and place it in an ice bath Ultrasonic treatment in the environment, the ultrasonic process is as follows: after every 1 minute of ultrasonication, the extract was taken out of the ice bath and shaken manually for 30 s; the total ultrasonic time was 3 minutes, and the ultrasonic conditions were 100 W and 47 kHz. Centrifuge at 7000rpm for 10 min...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3 Method for Extracting and Enriching Soil Phage from Pesticide Contaminated Soil
[0028] The formulations of the reagents are the same as in Example 1. Samples were collected at a pesticide-contaminated site in Qingyang Town, Nantong City, Jiangsu Province. The site was formerly a pesticide factory, and the soil in the site had varying degrees of pesticide pollution due to years of production. Collect the soil of plots with different degrees of pollution with less pollution (a total of six samples, numbered: Nantong-1, Nantong-2, Nantong-3, Nantong-4, Nantong-5, Nantong-6) at 4 °C Send back to lab. After removing impurities from the soil, mix 300g of the soil sample with 1L of 1% potassium citrate buffer, and incubate at 4°C for 15 minutes to disperse the soil sample, and then ultrasonicate it in an ice bath environment. The ultrasonic process is as follows: : After every 1 minute of ultrasonication, the extract should be taken out of the ice bath and shaken ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com