Method for rapidly detecting food-borne salmonella based on PagN genes
A Salmonella, food-borne technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological measurement/inspection, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc., can solve the problems of low detection limit, long time, etc., to ensure the effectiveness and Accuracy, intuitive result judgment, and easy promotion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: the establishment of detection method
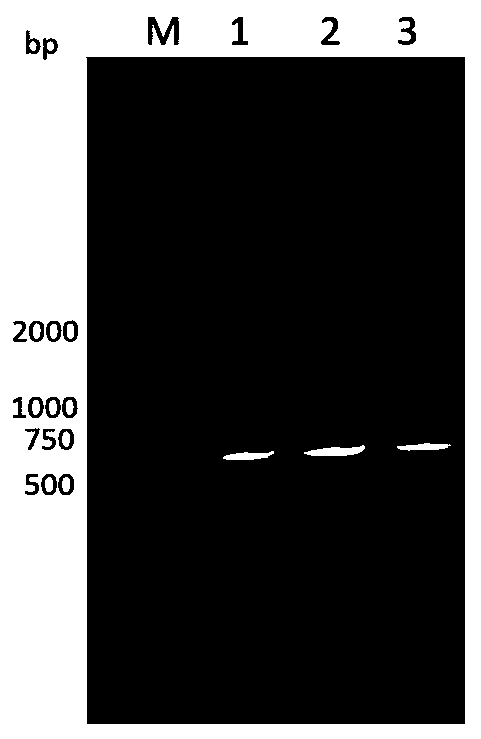
[0032] Step 1, search Salmonella PagN virulence gene according to Genbank, remove its transmembrane domain and design primers, the upstream primer is: 5'-AAAGAAGGGGCCTATATCACCG-3' (SEQ ID No.1), the downstream primer is: 5'-TTAAAATGCGTAAGTGATGCC-3' (SEQ ID No.2), the genomic DNA of different serotypes of Salmonella was extracted, and the results of PCR amplification showed that the virulence gene exists in most of the Salmonella, with a broad spectrum and a single amplified band, which is 657bp in length of DNA fragments.
[0033] PCR amplification reaction conditions: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min, denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 52°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 1 min, 30 cycles of amplification, and finally extension at 72°C for 10 min.
[0034]Step 2: Construct the pET-28a-PagN prokaryotic expression vector, express and purify the prokaryotic recombinant protein, immunize rabbits with 1 m...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2; Immunomagnetic beads capture efficiency and parameter optimization
[0044] To explore the optimal parameters of the experiment of capturing Salmonella with immunomagnetic beads in order to improve the capture efficiency. Multiple conditions such as the amount of antibody coating, coupling time, and the amount of immunomagnetic beads during capture were optimized by controlling variables. First, different volumes of PagN polyclonal antibodies were coupled with 1 mg of magnetic beads to determine the optimal antibody amount. Measure the amount of antibody coupled to the magnetic beads at different time points to explore the optimal coupling time. After the preparation of the immunomagnetic beads, different concentration gradients were set for 10 5 CFU / mL Salmonella bacteria liquid was captured, and after obtaining the optimal amount of immunomagnetic beads, Salmonella with different concentration gradients were captured, and the optimal capture parameters ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3: Scanning electron microscope observes and captures the situation
[0046] In order to visually determine whether the constructed PagN immunomagnetic beads can capture Salmonella, observation was carried out under the scanning electron microscope. A single colony of Salmonella CMCC 619 was picked and inoculated in 5mL LB liquid medium by streaking on the plate, and cultured overnight on a shaker at 37°C. Centrifuge at 4000rpm for 5min, wash with 1mL sterile double distilled water and dilute to 10 4 -10 5 CFU / mL, according to the method described in Example 1, 0.2 mg of immunomagnetic beads were added for capture. After capture, the magnetic frame adsorbed the immunomagnetic beads-bacteria complex, and washed 3 times with 1 mL of sterile double distilled water. The washed complex was resuspended in 200 μL sterile double-distilled water, the glass slide was cut into 1 cm squares, 20 μL of the complex was dropped onto the coverslip, fixed, and air-dried in an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com