Quantitative method for judging influence of meteorological and source emission change on air quality
A technology of air quality and meteorology, applied in meteorology, measuring devices, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve the problems of rising ozone concentration, complex relationship, inability to qualitative and quantitative analysis, etc., and achieve the effect of reasonable design and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
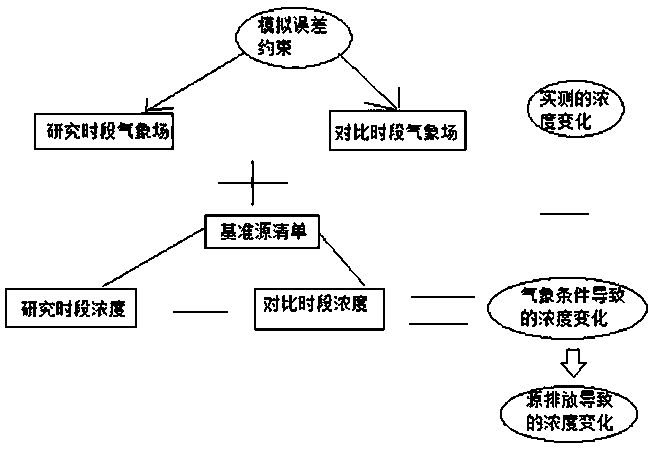
[0022] A quantitative method for judging the impact of meteorological and source emission changes on air quality, the technical scheme is as follows: select A and B years (or months) as the research period, take A year as the benchmark, and compare the same period of each month of B year with the determined concentration Changes, by using mesoscale meteorological models (such as WRF model) and three-dimensional air quality models (such as CAMx model, etc.) under different meteorological conditions to simulate the concentration of pollutants (such as PM2.5, etc.) The source inventory of year A is used for two years (or months) to compare the influence of different meteorological conditions on the concentration under the same emission scenario, and the estimated results of the model's favorable weather conditions in different periods are verified with measured data. Then use the measured data to determine the actual concentration change, and then compare the concentration change ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com