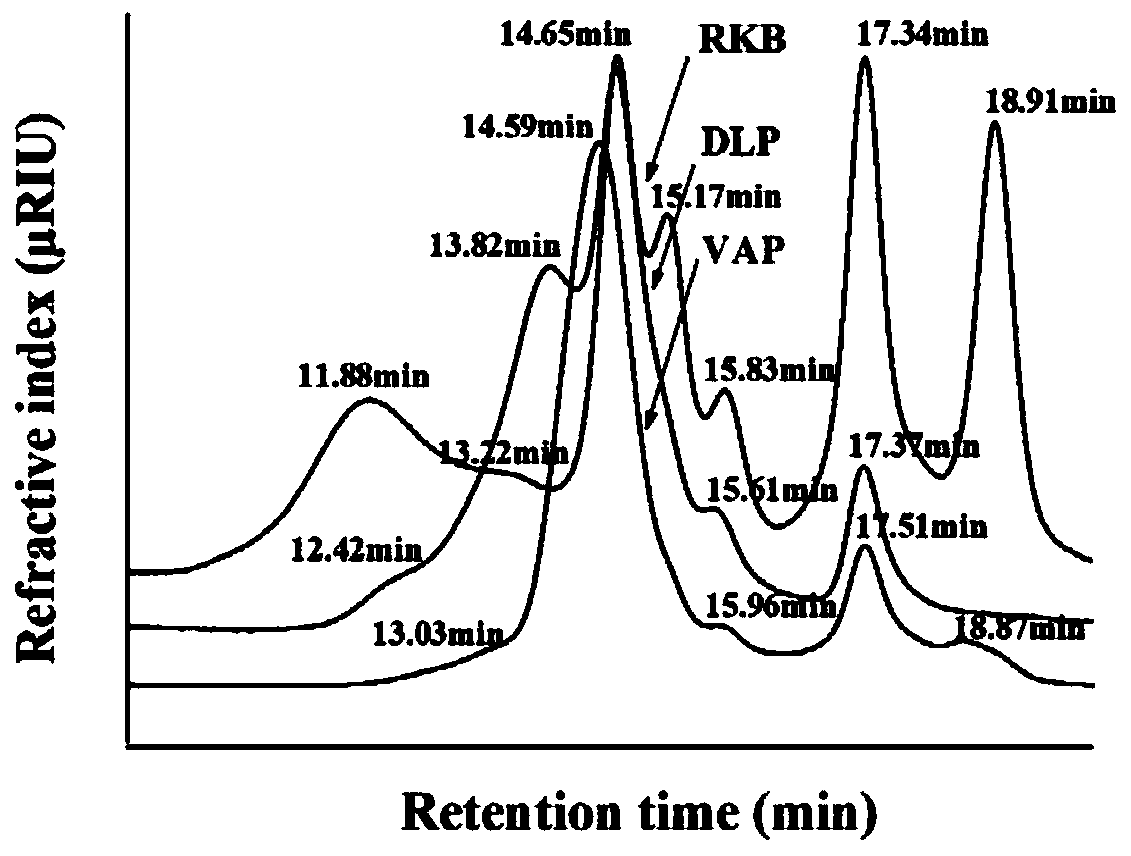
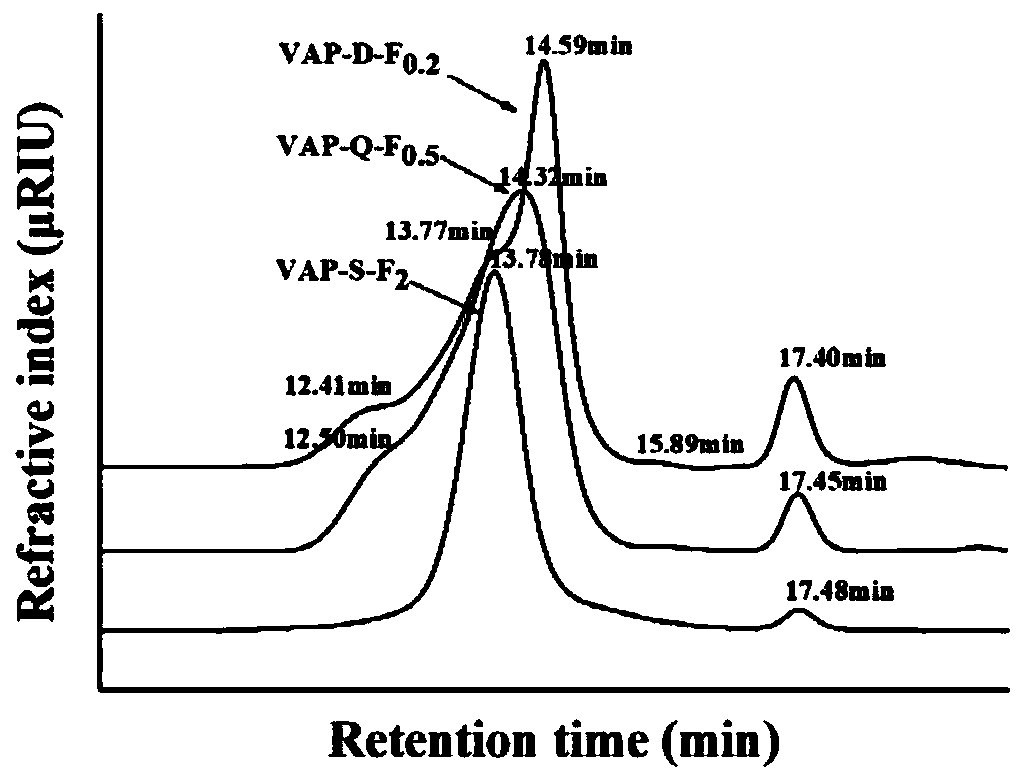
Method for separating and purifying mixed-bean pectic polysaccharides
A pectin polysaccharide, separation and purification technology can solve the problems of low separation efficiency, low extraction efficiency, low efficiency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] (1) Red bean polysaccharide extraction:
[0040] Process 1000g red bean raw material by ultrafine grinding, collect the fine powder passed through a 250 mesh sieve, add 10L volume concentration ratio of 95% ethanol to soak for 24 hours to degrease, filter and dry, and extract the dried red bean powder with hot water at 95°C for 2 hours twice , combine the extracts, add α-amylase, protease, and glucoamylase in turn for enzymolysis, the enzymolysis conditions are α-amylase at a temperature of 95°C, time 1.5h, protease at a temperature of 60°C, time 0.5h, pH 4.5 , glucoamylase at 60°C, time 0.5h, amylase hydrolyzes starch into dextrin, glucoamylase hydrolyzes dextrin into glucose, protease hydrolyzes protein into polypeptide, inactivates the enzyme at 100°C for 10 minutes, and then Centrifuge at a speed of 8000r / min for 10min, take the supernatant and concentrate it in vacuum, then add 95% ethanol 5.33 times the volume of the concentrated solution, let it stand at 4°C, red...
Embodiment 2
[0050] (1) White lentil polysaccharide extraction:
[0051] Process 1000g of white lentil raw material by ultrafine grinding, collect the fine powder passed through a 250-mesh sieve, add 10 L of ethanol with a volume concentration ratio of 95% to soak for 24 hours to degrease, filter and dry, and extract the dried white lentil powder with hot water at 95°C for 2 hours twice , combine the extracts, add α-amylase, protease, and glucoamylase in turn for enzymolysis, the enzymolysis conditions are α-amylase at a temperature of 95°C, time 1.5h, protease at a temperature of 60°C, time 0.5h, pH 4.5 , glucoamylase at 60°C, time 0.5h, amylase hydrolyzes starch into dextrin, glucoamylase hydrolyzes dextrin into glucose, protease hydrolyzes protein into polypeptide, inactivates the enzyme at 100°C for 10 minutes, and then Centrifuge at a speed of 8000r / min for 10min, take the supernatant and concentrate it in a vacuum, then add 95% ethanol 5.33 times the volume of the concentrated soluti...
Embodiment 3
[0061] (1) Red kidney bean polysaccharide extraction:
[0062] Process 1000g of red kidney bean raw material by ultrafine grinding, collect the fine powder passed through a 250-mesh sieve, add 10 L of ethanol with a volume concentration ratio of 95% to soak for 24 hours to degrease, filter and dry, and extract the dried red kidney bean powder with hot water at 95°C for 2 hours twice , combine the extracts, add α-amylase, protease, and glucoamylase in turn for enzymolysis, the enzymolysis conditions are α-amylase at a temperature of 95°C, time 1.5h, protease at a temperature of 60°C, time 0.5h, pH 4.5 , glucoamylase at 60°C, time 0.5h, amylase hydrolyzes starch into dextrin, glucoamylase hydrolyzes dextrin into glucose, protease hydrolyzes protein into polypeptide, inactivates the enzyme at 100°C for 10 minutes, and then Centrifuge at 8000r / min for 10min, take the supernatant and concentrate it in vacuum, then add 95% ethanol 5.33 times the volume of the concentrated solution, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com