A Broadband Transition Structure from Ridge-Gap Waveguide to Microstrip Line Based on Probe Current Coupling
A technology of gap waveguide and microstrip line, which is applied in the field of microwave/millimeter wave passive devices, can solve problems such as excessive loss, low assembly tolerance performance, and limited bandwidth, and achieve low insertion loss, high tolerance performance, The effect of high compactness and integration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
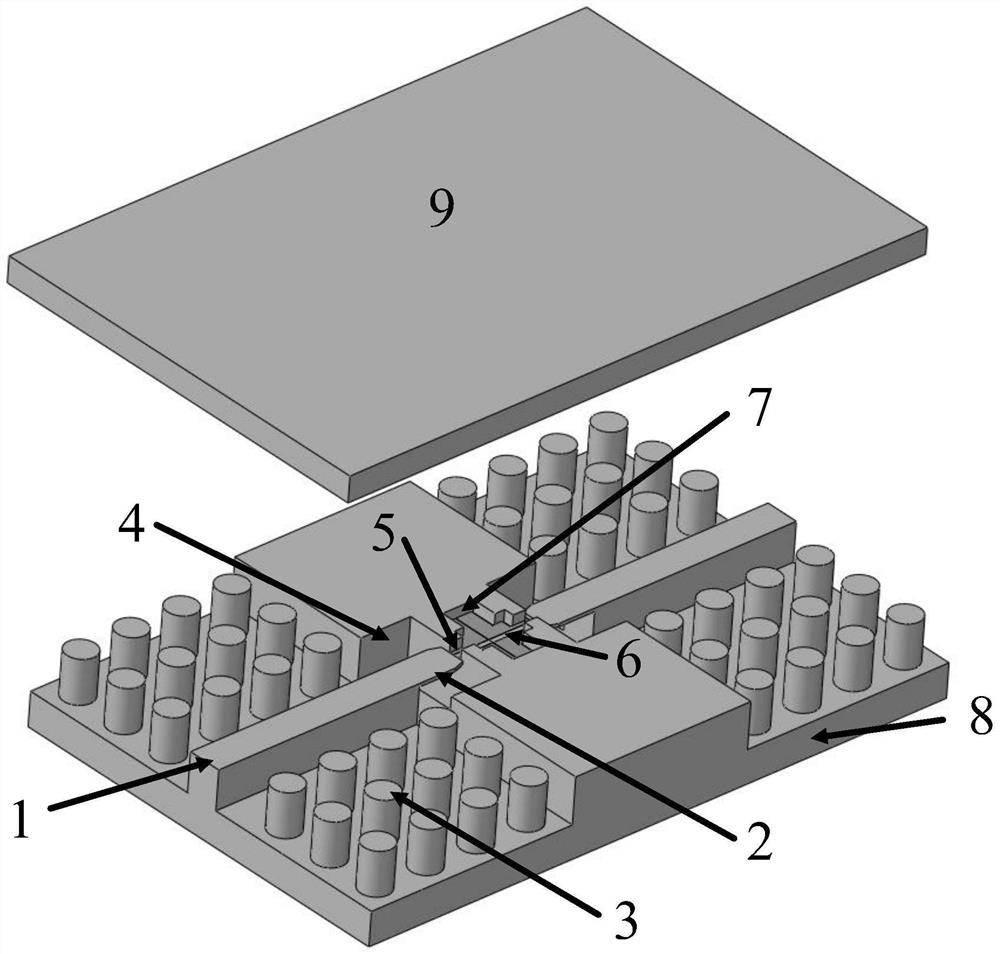
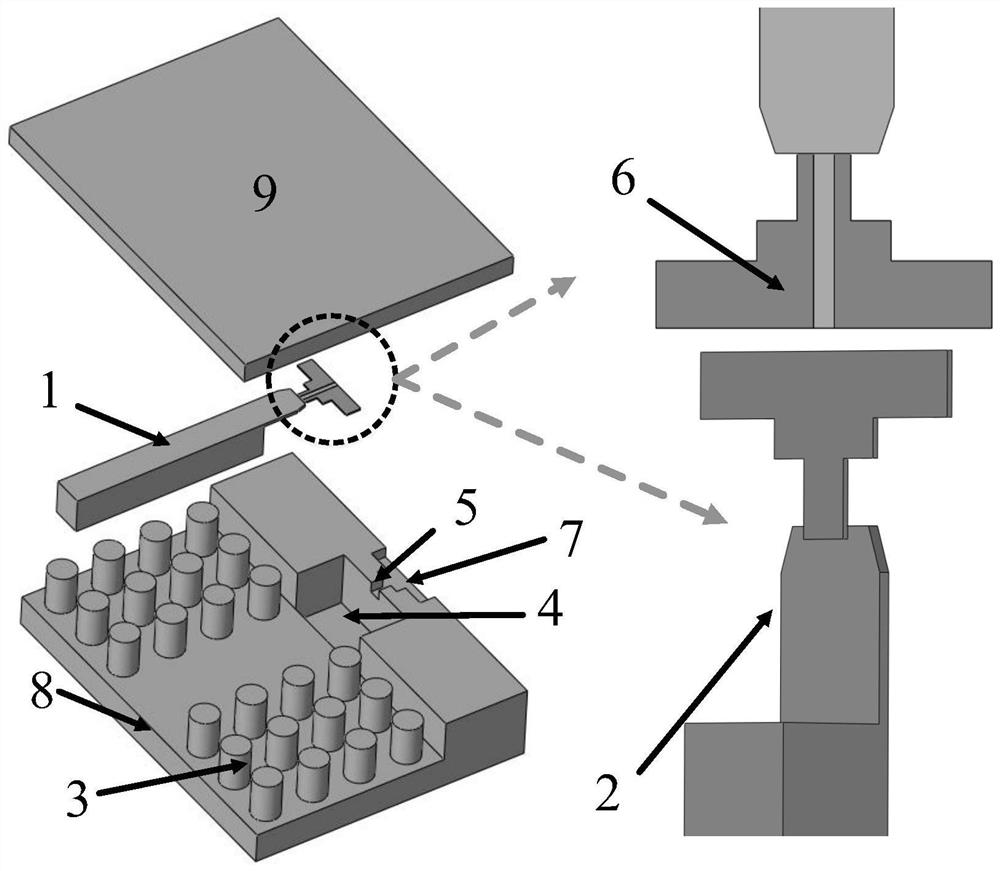
[0032] Taking a transition structure from a ridge-gap waveguide to a microstrip line working in the three bands of C, X, and Ku as an example, the technical solution proposed by the present invention will be further described in detail. The transition structure as a whole is as figure 1 , 2 shown. Includes: ridge-gap waveguide input 1, quarter-wavelength end-cut ridge probe 2, electromagnetic bandgap (EBG) structure 3, terminated short circuit cavity 4, probe and microstrip interconnect window 5, 50 ohm micro Strip line (Rogers 5880 substrate) 6, MMIC installation cavity 7, lower cavity 8 and upper cover 9.
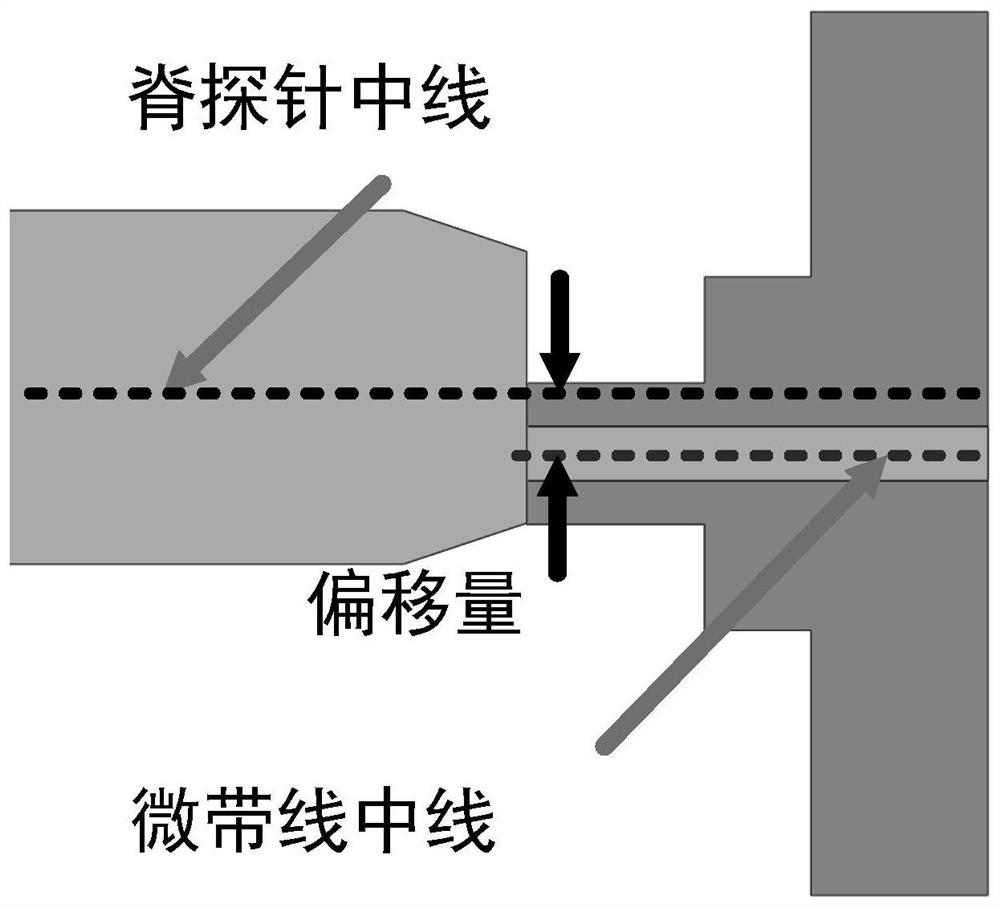
[0033] From the ridge-gap waveguide to the microstrip transition structure, the microwave signal is input from the ridge-gap waveguide in the form of a quasi-TEM mode, and the electromagnetic energy is transmitted to the terminal short-circuit cavity through the ridge probe, and the ridge-gap waveguide and 50 Impedance transformation between ohmic microstrip lines, fol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com