Method for simply preparing placenta mesenchymal stem cell exosome
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes, applied in the acquisition of membrane vesicles involved in cell biological activities, isolation and acquisition of exosomes from human placental mesenchymal stem cells, application in cell repair, isolation of human placental mesenchymal stem cells In the field of exosomes, it can solve the problems of complex process and low yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
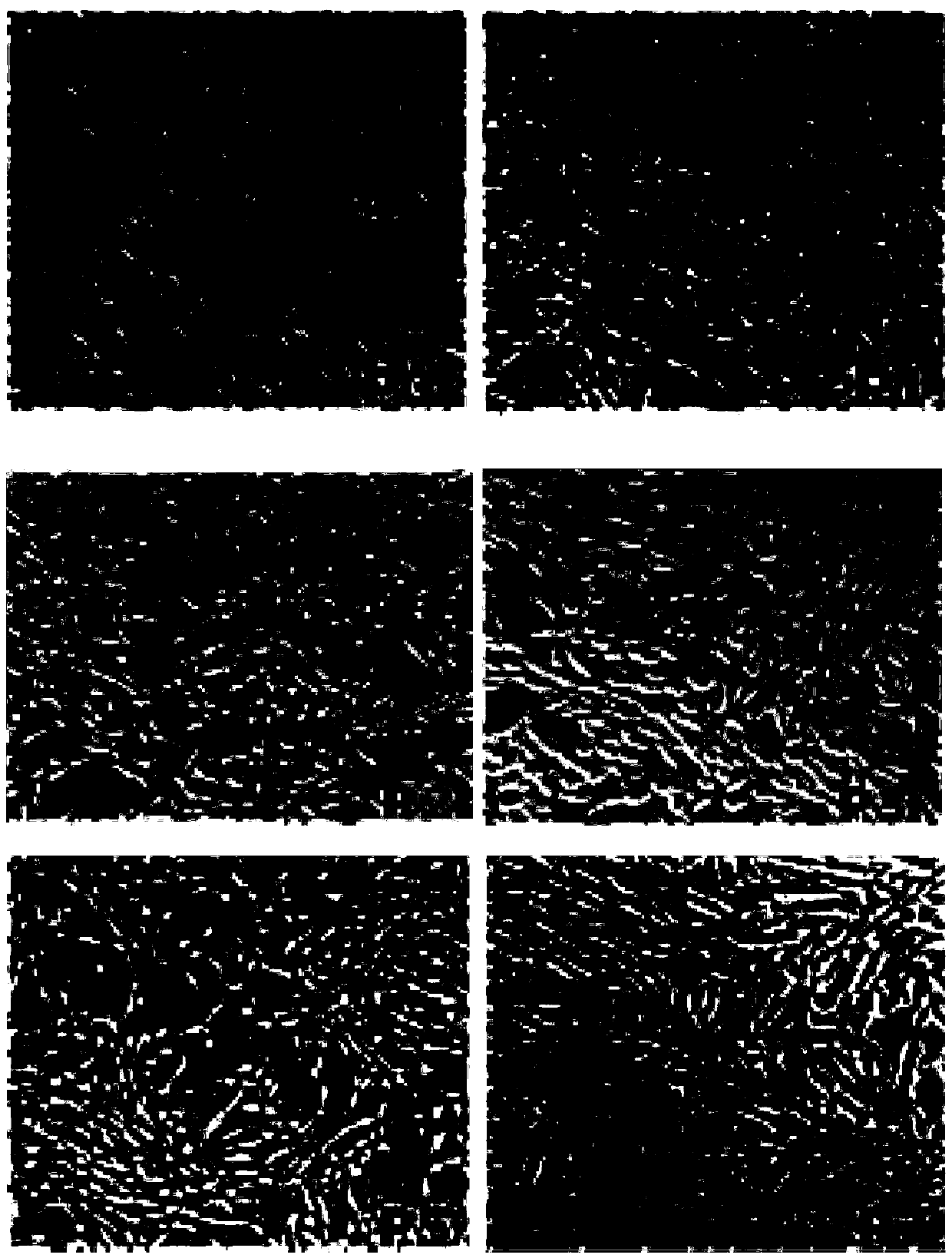
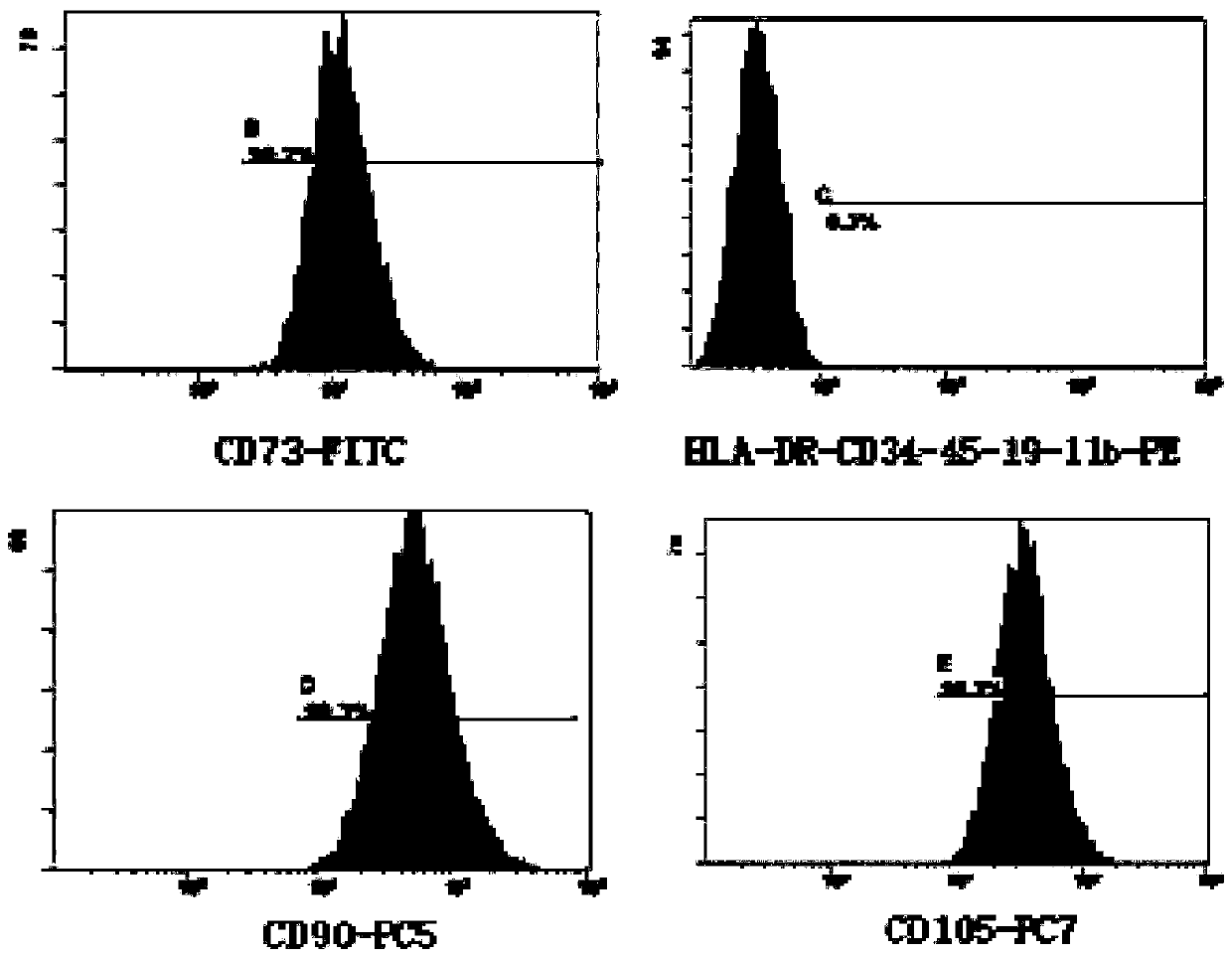
[0065] Example 1: Preparation of placental mesenchymal stem cells
[0066] (1) Processing placental tissue
[0067] Remove the amniotic membrane from a fresh human placenta, cut the membranous tissue on the surface of the placenta leaflet, and wash it with normal saline;
[0068] Shred the membranous tissue on the surface of the placental lobules into tissue fragments with a volume of about 0.2 cm3;
[0069] Put the tissue fragments into a centrifuge tube, add an appropriate amount of 0.9% normal saline (100ml), filter through a 300-mesh filter, and wash twice with an appropriate amount of 0.9% normal saline (100ml) until the filtrate is clear;
[0070] Add the cleaned tissue to the HBSS digestion solution (100ml) containing 0.005% Liberase MNP-S enzyme and 0.05% DNA type I enzyme, mix thoroughly, and shake and digest in a shaker for 30min (37°C, 100rpm) ;
[0071] (2) Obtaining placental blast cells
[0072] After the digestion, add fetal bovine serum (2ml) to the centr...
Embodiment 2
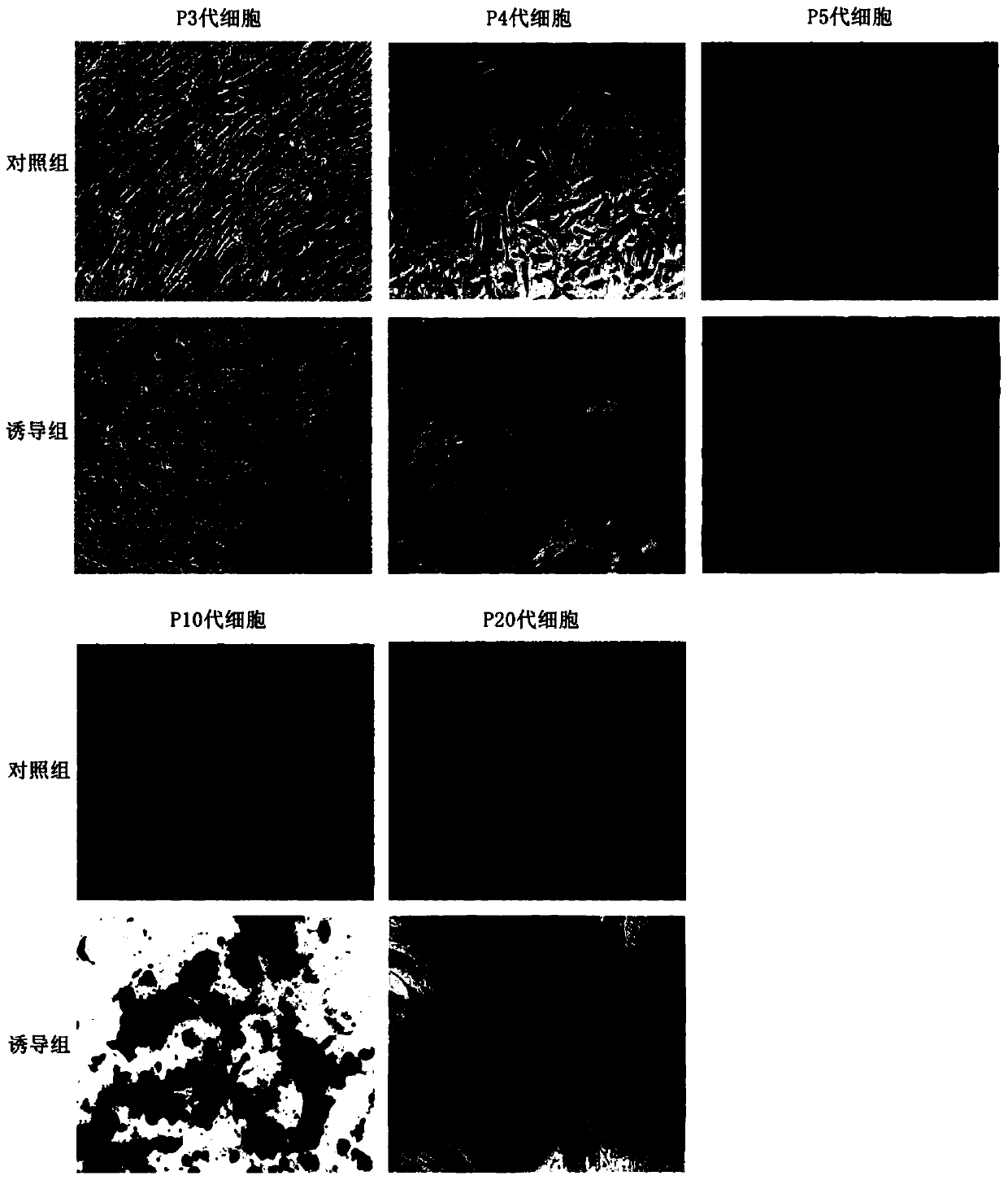
[0085] Example 2: Isolation and extraction of exosomes from placental mesenchymal stem cells
[0086] 1) Provide human placental mesenchymal stem cells of the 2nd to 5th passages in the logarithmic growth phase (this example takes the 3rd passage obtained in Example 1 as an example), at a rate of 5,000 to 15,000 / cm 2 The density inoculation (inoculation density of this embodiment: 10000 / cm2) is cultured in the DMEM / F12 medium that contains the L-glutamine of 2mM, after cultivating 3-4 days (this embodiment cultivates 4 days), collects Clear, remove cells and debris with 20000g centrifugal force for 20min, then filter through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, add mannose phosphate sodium to dissolve it, and obtain the culture supernatant; [in this embodiment, the amount of mannose phosphate sodium added accounts for The mass / volume percent concentration of filtrate is 0.08%]
[0087] 2) Drain the Pudex G-25 dextran gel filtration medium with a glass rod into the chromatographic col...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3: Isolation and extraction of exosomes from placental mesenchymal stem cells
[0106] Carry out with reference to Example 2.
[0107] 1) Provide the second generation human placental mesenchymal stem cells in the logarithmic growth phase at 5000 / cm 2 The density was inoculated into DMEM / F12 medium containing 2mM L-glutamine for culture. After 3 days of culture, the supernatant was collected, centrifuged at 20000g for 20min to remove cells and debris, and then filtered through a 0.22μm filter membrane, and added 0.1% sodium mannose phosphate was dissolved to obtain the culture supernatant;
[0108] 2) Drain the Pudex G-25 dextran gel filtration medium with a glass rod into the chromatography column (Sephadex G-25 column), and stir with a glass rod while loading;
[0109] 3) After installing the column, use a pipette gun to suck out the water above the column, and then load the culture supernatant collected in step 1) into the chromatography column;
[0110]...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com