Method for preparing medical porous tantalum parts based on selective laser melting technology
A technology of selective laser melting and porous tantalum, which is applied in the fields of additive manufacturing, medical science, and process efficiency improvement, and can solve the problems of small environmental pollution, cracks in parts, and limited application of parts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
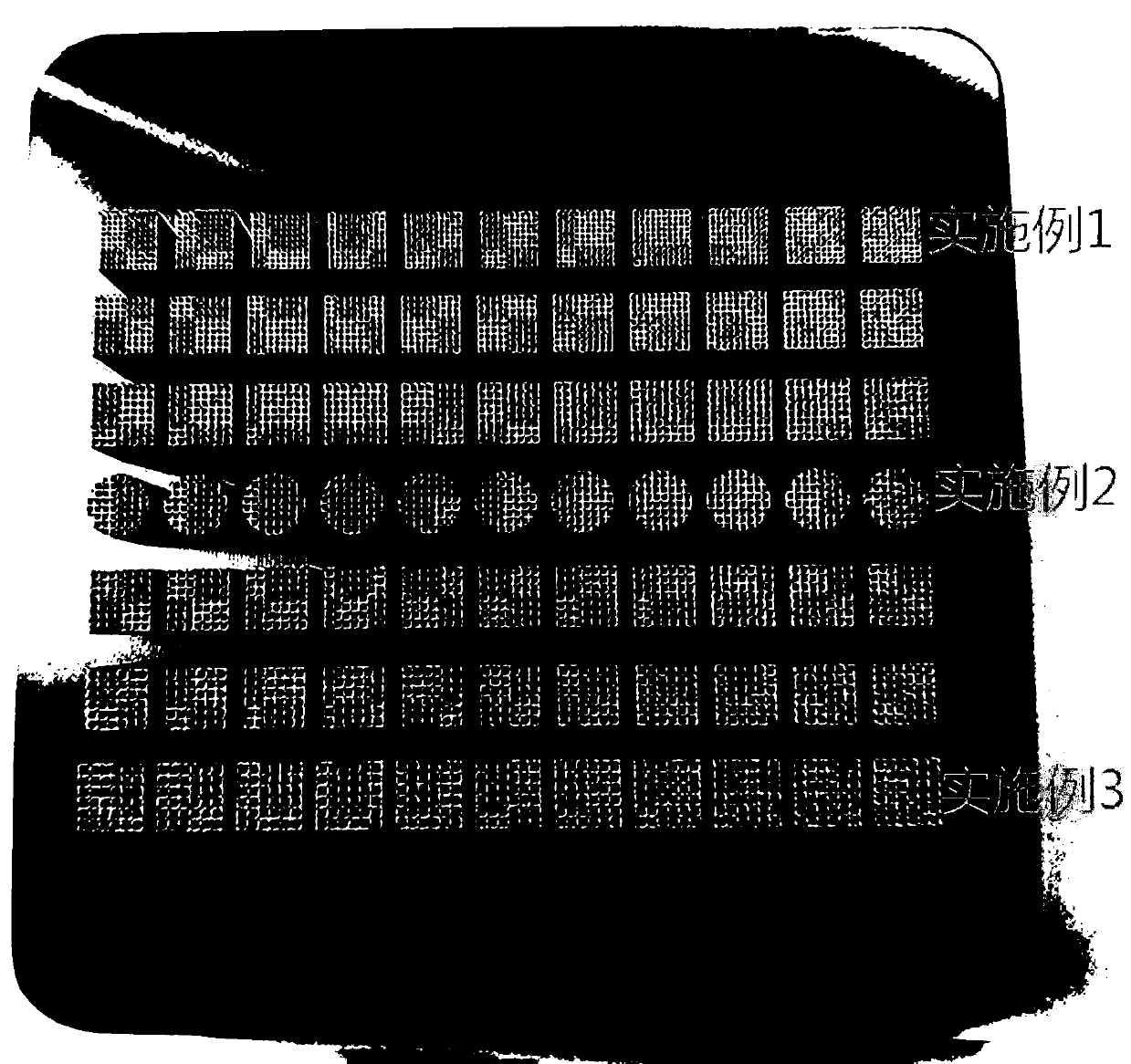
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: A method for preparing medical porous tantalum parts based on selective laser melting technology, comprising the following steps:
[0030] Step 1: Spherical pure Ta powder prepared by ultra-high-speed plasma rotating electrode method is selected as the raw material for selective laser melting and forming, and the particle size range is between 15 and 53 μm; fluidity ≤ 10s, tap density ≥ 10g / cm 3 ;The composition of pure Ta powder is: C: ≤0.08%, N: ≤0.05%, H: ≤0.012%, O: ≤0.08%, Ta: balance;
[0031] Step 2: Design the pore size to be 200 μm and the pore-strut size to be 200 μm, use 3D software to build a cubic porous structure model, add support, slice the model into 2D, and import the sliced files into the selected area laser melting molding equipment;
[0032] Step 3: Preheat the substrate before printing, and set the substrate preheating temperature to 100°C. Then pass argon gas into the forming cavity as a protective gas to ensure that the oxygen co...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: A method for preparing medical porous tantalum parts based on selective laser melting technology, comprising the following steps:
[0037] Step 1: Spherical pure Ta powder prepared by ultra-high-speed plasma rotating electrode method is selected as the raw material for selective laser melting and forming, and the particle size range is between 15 and 53 μm; fluidity ≤ 10s, tap density ≥ 10g / cm 3 ;The composition of pure Ta powder is: C: ≤0.08%, N: ≤0.05%, H: ≤0.012%, O: ≤0.08%, Ta: balance;
[0038] Step 2: Design the pore size to be 500 μm and the pore-strut size to be 200 μm, use 3D software to build a cubic porous structure model, add supports, slice the model into 2D slices, and import the sliced files into the selected area laser melting molding equipment;
[0039] Step 3: Preheat the substrate before printing, and set the substrate preheating temperature to 90°C. Then pass argon gas into the forming cavity as a protective gas to ensure that the ox...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: A method for preparing medical porous tantalum parts based on selective laser melting technology, comprising the following steps:
[0044] Step 1: Select the ultra-high-speed plasma rotating electrode method to prepare spherical Ta powder as the raw material for selective laser melting and forming, with a particle size range of 15-53 μm; fluidity ≤ 10s, tap density ≥ 10g / cm 3 ;Pure Ta powder composition: C: ≤0.08%, N: ≤0.05%, H: ≤0.012%, O: ≤0.08%, Ta: balance;
[0045] Step 2: Design the pore size to be 700 μm and the pore-strut size to be 200 μm, use 3D software to build a cubic porous structure model, add supports, slice the model into 2D, and import the sliced files into the selected area laser melting molding equipment;
[0046] Step 3: Preheat the substrate before printing, and set the substrate preheating temperature to 80°C. Then pass argon gas into the forming cavity as a protective gas to ensure that the oxygen content in the forming cavity is n...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fluidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com