A pathogenicity-related gene of rice sheath blight and its application
A technology of Rhizoctonia solani and disease-related genes, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problems of difficult inoculation identification operation, few varieties, lack of resistance sources, etc., and achieves important popularization and application value. Wide application prospects, significant disease resistance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 Cloning of rice sheath blight pathogenicity-related genes and their silencing target gene fragment Rstpp
[0040] 1. Experimental method
[0041] S1. Extraction of rice sheath blight RNA
[0042] Rice sheath blight RNA was extracted using TaKaRa Total RNA Extraction Kit (Product No. 9769), and the specific experimental steps were as follows:
[0043]Weigh 0.1g of rice sheath blight mycelia and quickly grind it into powder in liquid nitrogen, add it into a 1.5mL sterilized centrifuge tube containing BufferRL lysis solution, and centrifuge the lysis solution at 12,000rpm at 4°C for 5min. Carefully pipette the supernatant into a new 1.5 mL sterile centrifuge tube. Add 1 / 2 volume of absolute ethanol to the supernatant in the sample lysis step, and immediately transfer all the mixed solution (including the precipitate) to the RNA Spin Column (containing 2mLCollection Tube). Centrifuge at 12,000rpm for 1min and discard the filtrate. Add 500 μL of BufferRWA, 600 ...
Embodiment 2
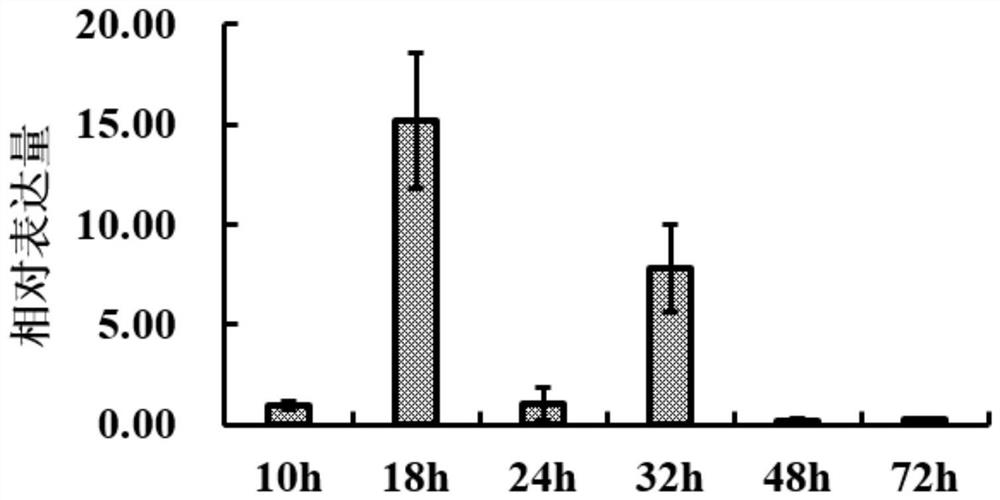
[0055] Example 2 Expression analysis of the silencing target gene fragment Rstpp of rice sheath blight pathogenicity-related genes during rice sheath blight infection in rice
[0056] S1. Preparation of rice sheath blight inoculum
[0057] First, the rice sheath blight strain GD118 preserved in our laboratory was activated using a PDA plate, and cultured at 28° C. for 2 days under dark conditions. At the same time, the rice grains were soaked for 24 hours and put into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, sterilized by high-pressure steam at 121° C. for 30 minutes. Spread the sterilized grains evenly on the PDA plate after 2 days of cultivation, and culture them at 28°C for 7 days in the dark until the surface of the grains is covered with hyphae and sclerotia, then they can be used for inoculation.
[0058] S2. Planting of rice and inoculation of rice sheath blight
[0059] Use 10% sodium hypochlorite and 30% hydrogen peroxide to sterilize the rice seeds (intermediate resistant variet...
Embodiment 3
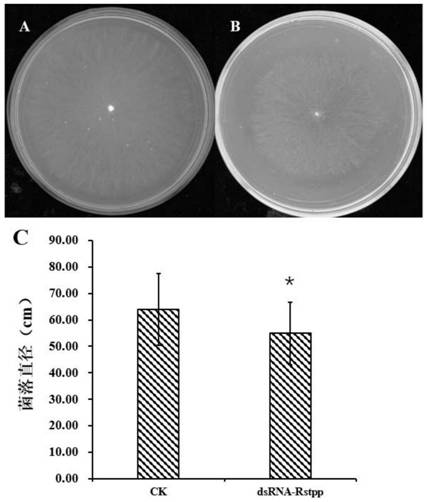
[0070] Example 3 Synthesis and antibacterial experiment of the silencing target gene fragment Rstpp double-stranded RNA of rice sheath blight pathogenicity-related genes
[0071] 1. Experimental method
[0072] S1. In vitro synthesis of Rstpp double-stranded RNA for silencing target gene fragment
[0073] T7RNA Polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Catalog number: EP011) was used to synthesize the target gene Rstpp to obtain double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). The T7 RNA polymerase promoter can be added to any DNA sequence using PCR by adding the T7 promoter sequence to the 5' end of either amplification primer. The minimal T7 RNA polymerase promoter sequence is: 5'-TAATACGACTCACTATAGG-3'. T7 promoter sequences were added to the 5' ends of the upstream and downstream primers respectively to obtain primers T7-4214F / T7-4214R (shown in SEQ ID NO: 13-14).
[0074] Primer T7-4214F (SEQ ID NO: 13): TAATACGACTCACTATAGGACGCTGCTGATGACGGAA;
[0075] Primer T7-4214R (SEQ ID NO: 14): TAATACG...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com