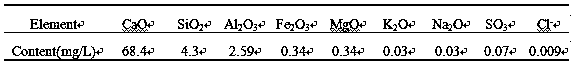Method for treating arsenic in nonferrous smelting waste acid by jarosite slag collaborated by carbide slag
A technology of jarosite slag and carbide slag, which is applied in the fields of filtration treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of toxic elements polluting the environment, large amount of secondary hazardous waste slag, and high water hardness , to achieve the effect of broad market prospect, simple process operation and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
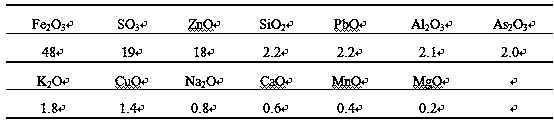
[0019] Example 1: The components of jarosite slag in this example are shown in Table 1, and the components of carbide slag are shown in Table 2. The dirty acid comes from the sulfuric acid workshop of a zinc smelter in Southwest China, which contains a large amount of The dirty acid with impurities such as arsenic, the main components are shown in Table 3;
[0020] Table 1 Jarosite slag components
[0021]
[0022] Table 2 Composition of carbide slag
[0023]
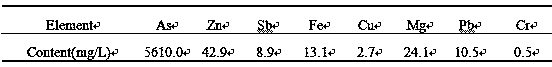
[0024] Table 3 Sewage Acid Components
[0025]
[0026] A method for treating arsenic in non-ferrous smelting sewage acid with jarosite slag and calcium carbide slag, the specific steps are as follows:
[0027] (1) Mix jarosite slag and calcium carbide slag evenly, and ball mill after drying until the particle size of the mixture is not higher than 0.56 μm to obtain mixed slag powder; the mass ratio of jarosite slag to calcium carbide slag is 10:1, and the ball mill The rotating speed is 760r / min, and the gr...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: The components of jarosite slag in this example are shown in Table 6, and the components of carbide slag are shown in Table 7. The dirty acid comes from the sulfuric acid workshop of a zinc smelter in Southwest China, which contains a large amount of Sewage acid with impurities such as arsenic, the main components are shown in Table 8;
[0038] Table 6 jarosite slag components
[0039]
[0040] Table 7 Composition of carbide slag
[0041]
[0042] Table 8 Sewage Acid Components
[0043]
[0044] A method for treating arsenic in non-ferrous smelting sewage acid with jarosite slag and calcium carbide slag, the specific steps are as follows:
[0045] (1) Mix jarosite slag and carbide slag evenly, and ball mill after drying until the particle size of the mixture is not higher than 0.47 μm to obtain mixed slag powder; the mass ratio of jarosite slag to carbide slag is 13:4, and the ball mill The rotating speed is 910r / min, and the grinding time is 11mi...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3: The components of jarosite slag in this example are shown in Table 11, and the components of carbide slag are shown in Table 12. The dirty acid comes from the sulfuric acid workshop of a zinc smelter in Southwest China, which contains a large amount of Sewage acid with impurities such as arsenic, the main components are shown in Table 13;
[0056] Table 11 Jarosite slag components
[0057]
[0058] Table 12 Composition of carbide slag
[0059]
[0060] Table 13 Sewage Acid Components
[0061]
[0062] A method for treating arsenic in non-ferrous smelting sewage acid with jarosite slag and calcium carbide slag, the specific steps are as follows:
[0063] (1) Mix jarosite slag and carbide slag evenly, and ball mill after drying until the particle size of the mixture is not higher than 0.42 μm to obtain mixed slag powder; the mass ratio of jarosite slag to calcium carbide slag is 11:2, and the ball mill The rotating speed is 835r / min, and the grinding ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com