Carbide blade and preparation method thereof
A cemented carbide blade and cemented carbide technology, applied in the field of cemented carbide blades, can solve the problems of low versatility of cutting blades, achieve excellent edge strength and impact resistance, improve precise control, and improve mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
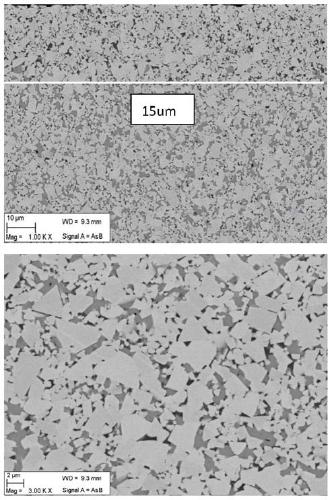
[0046] A cemented carbide blade of the present invention, the blade model is WNMG080408. The composition of the cemented carbide insert matrix in this embodiment is shown in Table 1. 5.6wt.% Co metal is used as the binder phase, and WC and titanium-containing cubic phase compounds are used as the hard phase. The cemented carbide insert substrate has a surface structure lacking titanium-containing cubic phase compounds whose average binder phase content is 1.5 times the nominal Co binder phase content, and the thickness of the surface structure is 15 μm. The average particle size of the titanium-containing cubic phase compound in the alloy is 2.0 μm, the atomic ratio of Ti / (Ti+Ta+Nb) is 0.6, and the atomic ratio of N / Ti is 0.17. The average grain size of the titanium-containing cubic phase is 0.90 μm. Tungsten carbide (WC) grain distribution has a bimodal structure, one of which is 0.5 μm and the other is 2.0 μm. The C / W atomic ratio of the binder phase in the surface gradie...
Embodiment 2
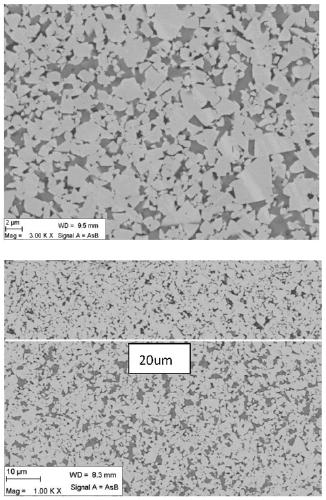
[0064] A cemented carbide blade of the present invention, the blade model is WNMG080408. The matrix composition of the cemented carbide insert in this example is shown in Table 1, 6.8wt.% Co metal is used as the binder phase, and substances including WC and titanium-containing cubic phase compounds are used as the hard phase. The cemented carbide insert substrate has a surface structure lacking titanium-containing cubic phase compounds whose average binder phase content is 1.7 times the nominal Co binder phase content, and the thickness of the surface structure is 20 μm. The C / W atomic ratio of the binder phase in the surface gradient structure is 0.95, and the C / W atomic ratio of the core binder phase is 0.83. The average particle size of the titanium-containing cubic phase compound in the alloy is 2.2 μm, the atomic ratio of Ti / (Ti+Ta+Nb) is 0.58, and the atomic ratio of N / Ti is 0.18. The average grain size of the titanium-containing cubic phase is 1.1 μm. The grain distri...
Embodiment 3
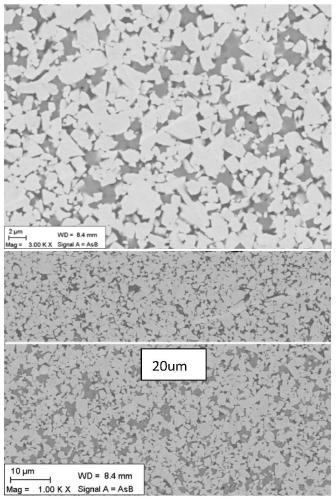
[0071] A cemented carbide blade of the present invention, the blade model is WNMG080408. The matrix composition of the cemented carbide insert in this example is shown in Table 1, 8.4wt.% Co metal is used as the binder phase, and substances including WC and titanium-containing cubic phase compounds are used as the hard phase. The cemented carbide insert substrate has a surface structure lacking titanium-containing cubic phase compounds with an average binder phase content of 1.8 times the nominal Co binder phase content, with a thickness of 20 μm. The C / W atomic ratio of the binder phase in the surface gradient structure is 0.94, and the C / W atomic ratio of the core binder phase is 0.81. The average particle size of the titanium-containing cubic phase compound in the alloy is 1.5 μm, the atomic ratio of Ti / (Ti+Ta+Nb) is 0.65, and the atomic ratio of N / Ti is 0.17. The average grain size of the titanium-containing cubic phase is 1.2 μm. The grain distribution of tungsten carbi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com