Application of 2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinoline 4-modified derivatives in prevention and treatment of plant diseases
A trifluoromethyl, quinoline-based technology, applied in the field of natural medicinal chemistry, can solve the problems of increasing chemical resistance of pathogens, human health and environmental pollution, adverse effects of non-target organisms, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
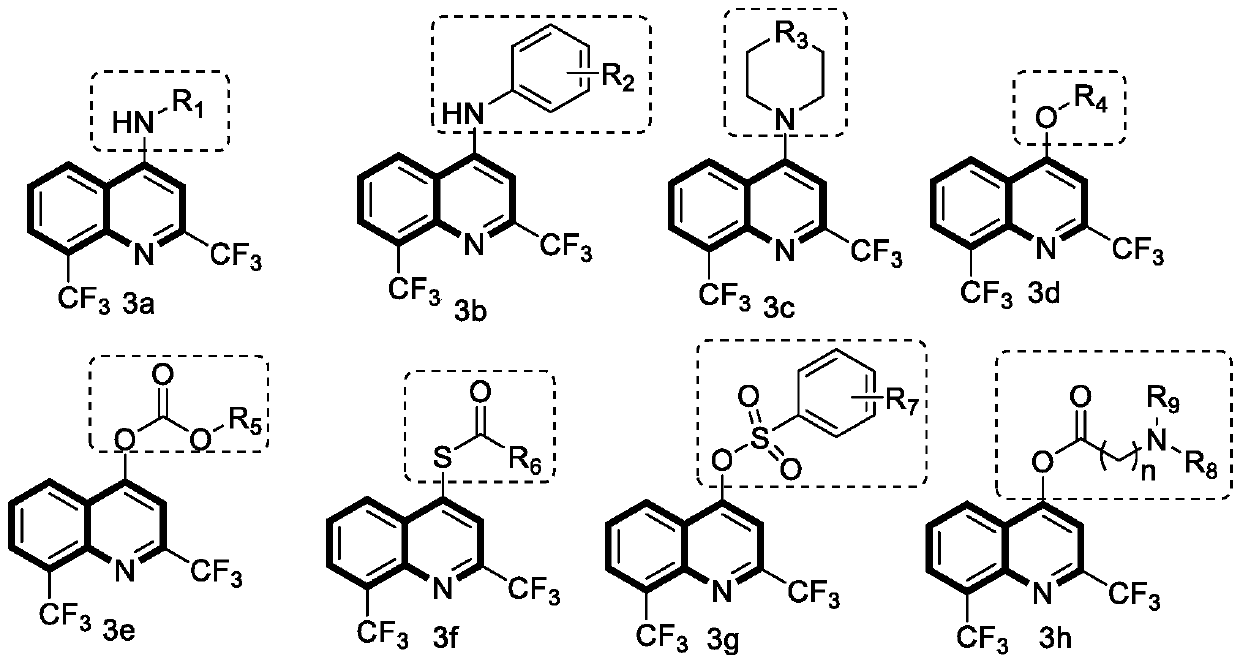
[0022] Embodiment 1: Synthetic method and chemical structure of 3a series compound
[0023]
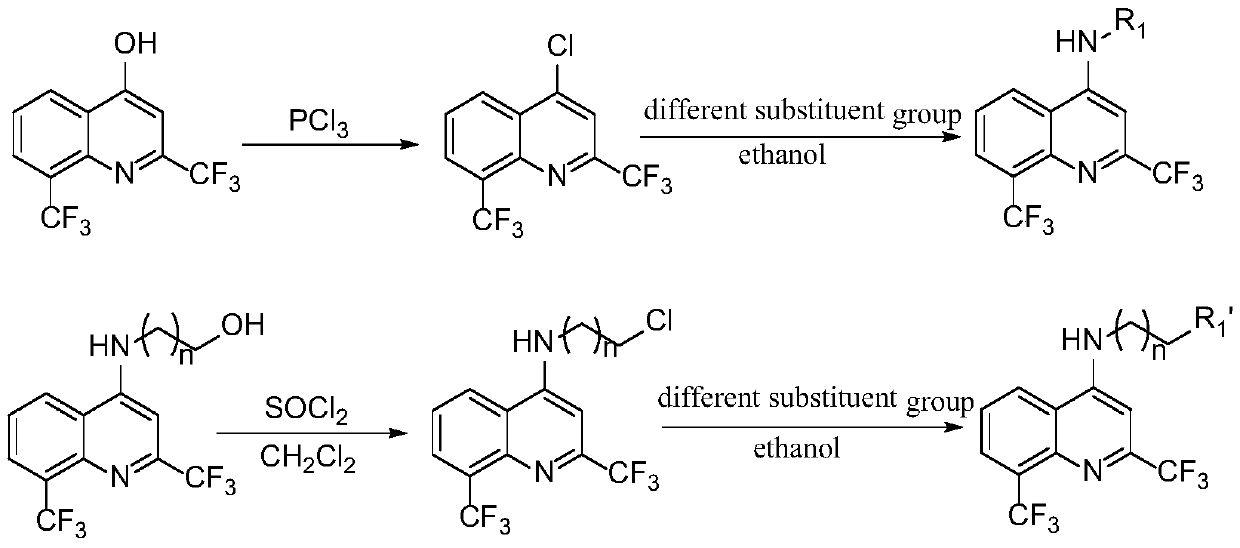
[0024] In a dry 100mL round-bottomed flask, add 2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)-4-hydroxyquinoline, then add an appropriate amount of phosphorus trichloride, stir at room temperature for 3 hours, and then remove it by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure. Phosphorus trichloride. Ice water was slowly dropped into the round bottom flask, and the resulting compound was extracted several times with dichloromethane. Collect the organic phase, dry it with anhydrous magnesium sulfate to remove the water in the solvent, hang it dry, and proceed to the next experiment directly.
[0025] The reactants obtained in the previous step and different substituent compounds were dissolved in ethanol and refluxed in a 100mL round-bottomed flask, and a small amount of triethylamine was added as a catalyst to react for about 3 hours, and the reaction was monitored by TLC. After the reaction was complet...
Embodiment 2
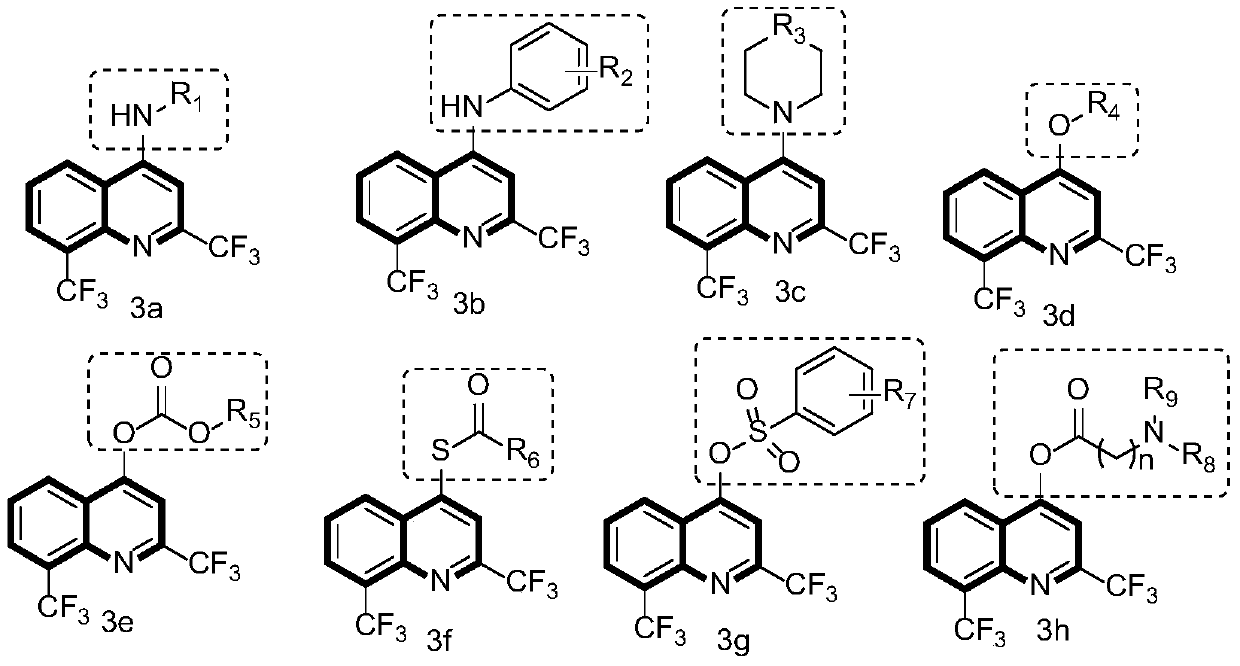
[0068] Embodiment 2: Synthetic method and chemical structure of 3b series compound
[0069]
[0070] In a dry 100mL round-bottom flask, add 2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)-4-hydroxyquinoline, then add an appropriate amount of phosphorus trichloride, stir at room temperature for 3 hours, and then rotary evaporate under reduced pressure to remove three Phosphorus chloride. Ice water was slowly dropped into the round bottom flask, and the resulting compound was extracted several times with dichloromethane. The organic phase was collected, dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate to remove the water in the solvent, spin-dried and directly proceeded to the next experiment.
[0071] First dissolve sodium hydride in anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (if the reaction yield is very low, then change the solvent to DMF), then slowly add different amines under ice bath conditions, activate for a period of time, finally add the compound obtained in the previous step, and The reaction was stirred at ro...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Embodiment 3: Synthetic method and chemical structure of 3c series compound
[0092]
[0093] In a dry 100mL round-bottomed flask, add 2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)-4-hydroxyquinoline, then add an appropriate amount of phosphorus trichloride, stir at room temperature for 3 hours, and then remove it by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure. Phosphorus trichloride. Ice water was slowly dropped into the round bottom flask, and the resulting compound was extracted several times with dichloromethane. The organic phase was collected, dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate to remove the water in the solvent, spin-dried and directly proceeded to the next experiment.
[0094] The reactants obtained in the previous step and different amines were dissolved in ethanol and refluxed in a 100mL round-bottomed flask, and a small amount of triethylamine was added as a catalyst to react for about 3 hours, and the reaction was monitored by TLC. After the reaction was completed, it was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com