Transforming bacterium strain and method for catalytically synthesizing miglitol intermediate
A technology for miglitol and intermediates, which is applied in the field of transforming bacterial strains that catalyze the synthesis of miglitol intermediates, can solve the problem of poor tolerance of N-hydroxyethylglucosamine, no significant increase in specific enzyme activity, wild strain N - Problems such as weak activity of hydroxyethylglucosamine dehydrogenase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Construction of Gluconobacter oxydans recombinant strain Gluconobacter oxydans pBBR-sldAB (CCTCC No.M2019033).
[0026] (1) Molecular construction of recombinant expression plasmid pBBR-sldAB:
[0027] The coding sequence (GenBank number is EF493853.1) of the large and small subunits SldA (protein sequence accession number ABP65281.1) and SldB (protein sequence accession number ABP65282.1) of the sorbitol dehydrogenase localized to the cell membrane of Gluconobacter oxidans, The substitution of one or several nucleotides will cause the substitution of corresponding amino acid residues, thereby affecting the function of N-hydroxyethylglucosamine dehydrogenase. The coding sequence was inserted into the middle of SEQ ID No.1 (promoter sequence) and SEQ ID No.2 (terminator sequence), and inserted into the broad host expression vector pBBR1MCS-5 using restriction endonuclease sites XhoI and EcoRI to construct Obtain pBBR-sldAB recombinant expression plasmid.
[0028] (2) P...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Comparison of N-hydroxyethylglucosamine dehydrogenase activity between Gluconobacter oxydans pBBR-sldAB (CCTCC No.M 2019033) and the mutant strain ZJB16009 (CCTCC No.M201703).
[0049] (1) Preparation of resting cells of Gluconobacter oxydans: the starting strain Gluconobacter oxydans mutagenic strain ZJB16009 and the recombinant strain Gluconobacter oxydans pBBR-sldAB constructed by the present invention were respectively inoculated into 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing 40 mL of seed culture solution Among them, the composition of the seed culture solution is D-sorbitol 50g / L, yeast extract powder 25g / L, KH 2 PO 4 5g / L, K 2 HPO 4 5g / L, the solvent is water, and the pH value is natural (referring to no need to adjust the pH). Cultivate at 28°C and 235rpm for 48 hours to obtain seed liquid, centrifuge at 10,000rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant, wash with water once, centrifuge and discard the supernatant, and precipitate into resting cells for subsequent tra...
Embodiment 3
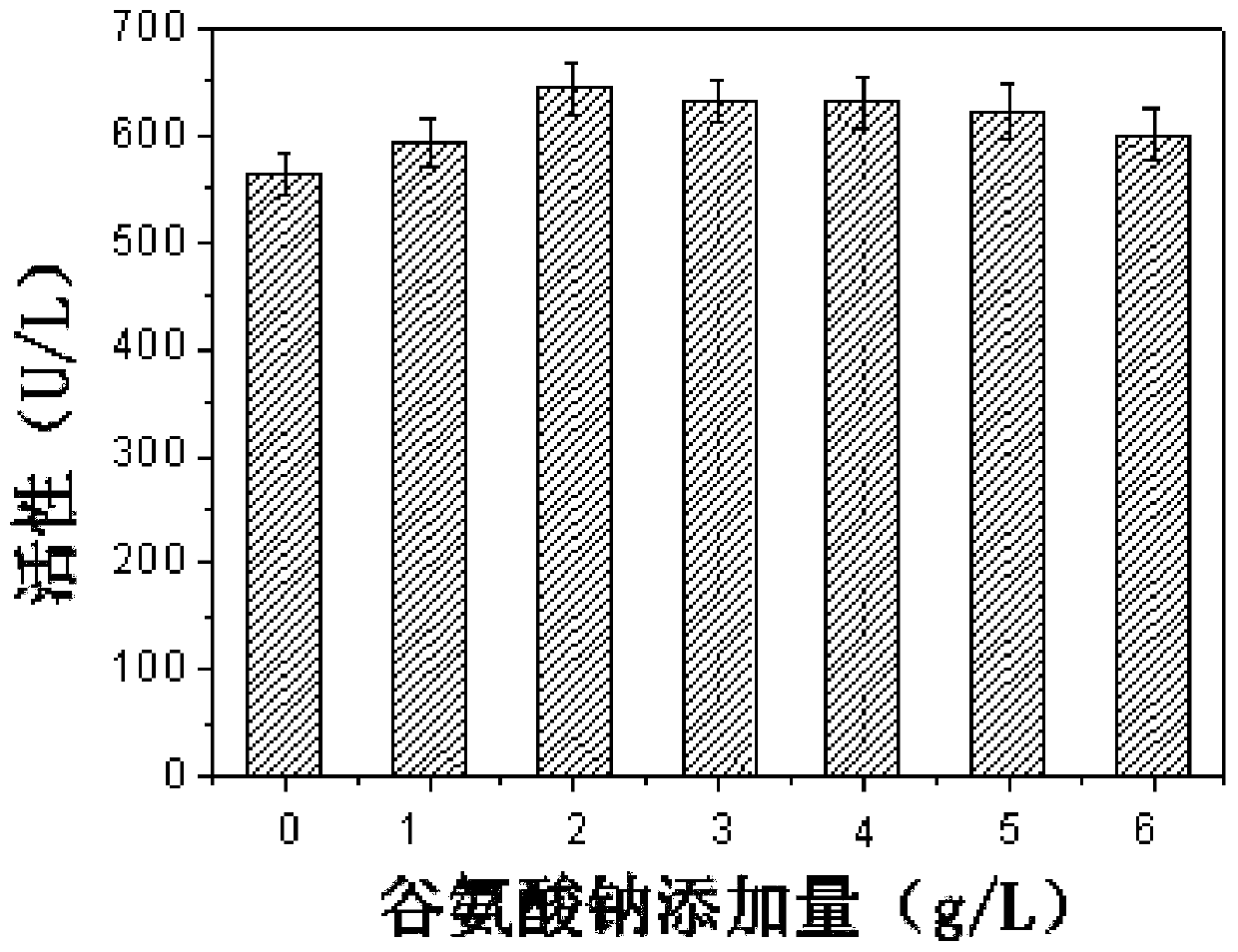
[0061] The effect of different amino acids on the synthesis of sorbitol dehydrogenase by fermentation cultured Gluconobacter oxydans was investigated.
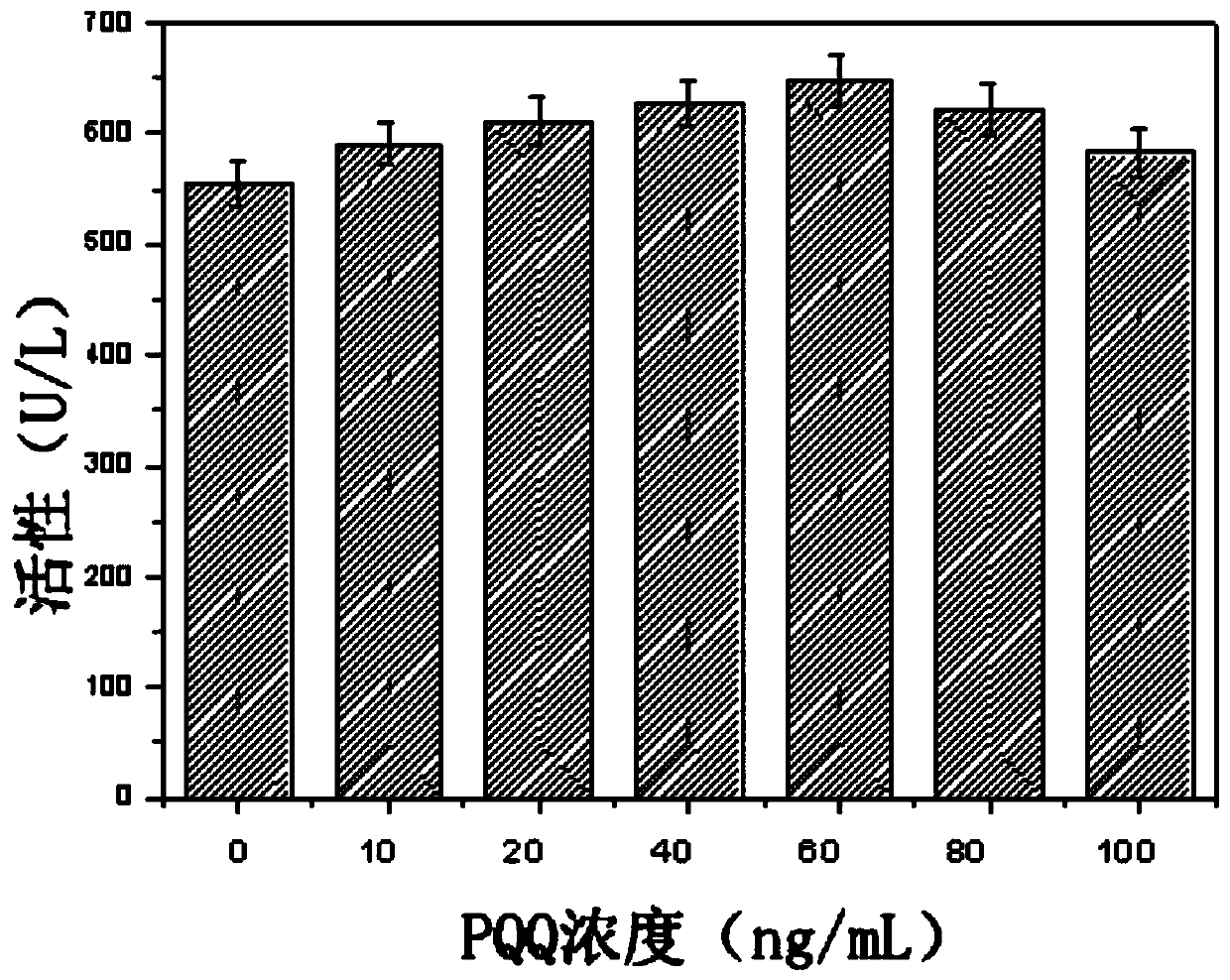
[0062] As can be seen from Example 2, although the N-hydroxyethylglucosamine dehydrogenase activity of the recombinant bacteria has been significantly improved, the content of the extracellular coenzyme PQQ is significantly lower than that of the starting strain (23.32vs.39.93mg / L) , suggesting that limited PQQ content may inhibit the improvement of N-hydroxyethylglucosamine dehydrogenase activity in cells. In order to verify this hypothesis, the corresponding dehydrogenase activity was determined by adding different concentrations of PQQ to the culture supernatant of the recombinant bacteria. From figure 1 It can be seen that with the increase of the exogenous PQQ content, the corresponding N-hydroxyethylglucosamine dehydrogenase activity is also significantly improved, confirming that the synthesis of PQQ in the recombinant...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com