Preparation method of pure phase nanocrystalline yttrium doped bismuth ferrite
A technology of yttrium doping and bismuth ferrite, applied in nanotechnology, chemical instruments and methods, iron compounds, etc., can solve the problems of weak magnetism at room temperature and achieve low firing temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1--doping amount 5% (doping amount refers to the amount of yttrium oxide instead of bismuth oxide)
[0022] A preparation method of pure-phase nanocrystalline yttrium-doped bismuth ferrite, the steps are as follows:
[0023] S1. Preparation of amorphous yttrium-doped bismuth ferrite by mechanical alloying method:
[0024] S1.1. In terms of molar ratio, according to iron oxide: bismuth oxide: yttrium oxide = 1: 0.855: 0.045, iron oxide, bismuth oxide and yttrium oxide were weighed and ground together to obtain a mixture;
[0025] S1.2. Put the above mixture into a planetary ball mill for high-energy ball milling according to the ball-to-material mass ratio of 20:1. Set the rotation speed of the main turntable at 350 rpm and the rotation speed of the planetary disk at 800 rpm. Control the ball milling time at 25 h, to obtain an intermediate product;
[0026] S2, high temperature heat treatment:
[0027] Under normal pressure and air atmosphere, the amorphous...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2--doping amount 10%
[0029] The difference from Example 1 is: iron oxide: bismuth oxide: yttrium oxide = 1:0.81:0.09, and the others are the same as in Example 1.
[0030] Comparative example 1--no doping
[0031] The difference from Example 1 is: iron oxide: bismuth oxide: yttrium oxide=1:0.9:0, and the others are the same as in Example 1.
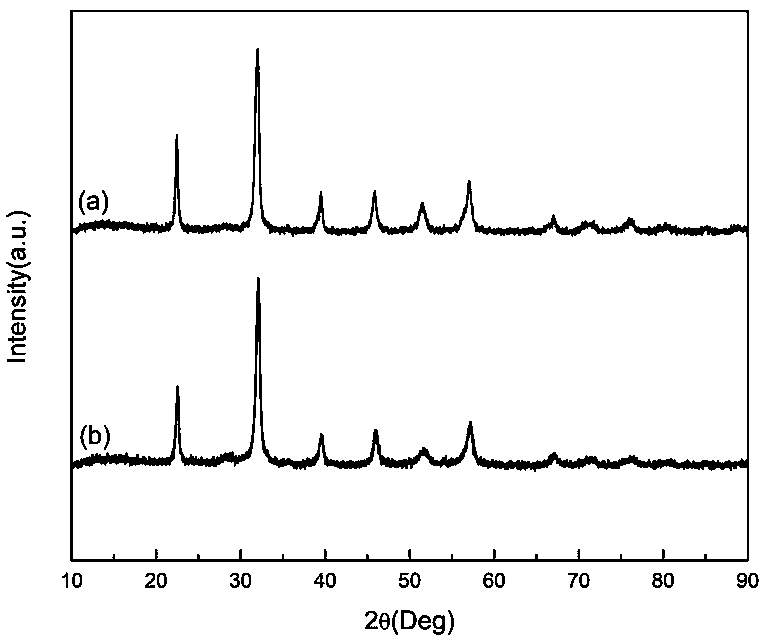
[0032] The XRD pattern of embodiment 1-2 and comparative example 1 gained intermediate product is shown in figure 1 ,specifically, figure 1 (a) is the XRD pattern of iron oxide: bismuth oxide: yttrium oxide = 1:0.9:0 mixed powder in Comparative Example 1 after mechanical alloying for 25 hours, figure 1 (b) is the XRD pattern of iron oxide: bismuth oxide: yttrium oxide = 1:0.855:0.045 mixed powder in Example 1 after mechanical alloying for 25 hours, figure 1 (c) is the XRD pattern of the iron oxide: bismuth oxide: yttrium oxide = 1:0.81:0.09 mixed powder in Example 2 after mechanical alloying for 25 hours. From fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com