A kind of immobilized starter system and its preparation and application
An immobilized fermentation and system technology, applied in the directions of immobilization on or in inorganic carriers, immobilization on/in organic carriers, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of slow fermentation speed and incomplete degradation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
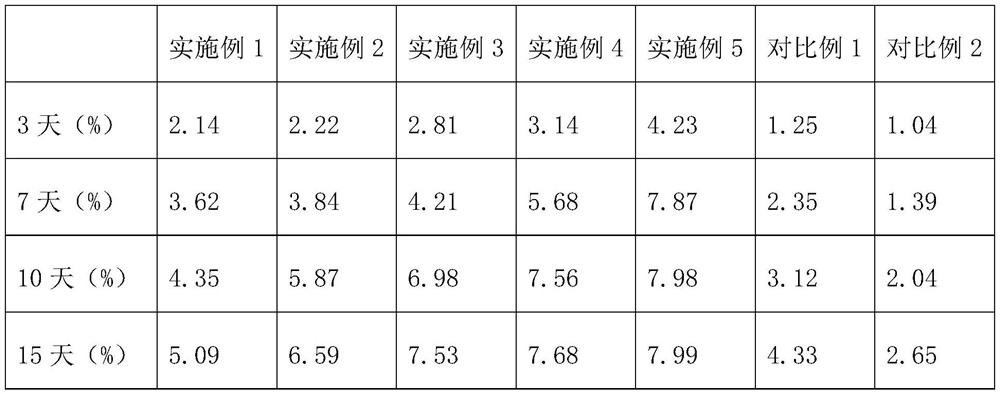
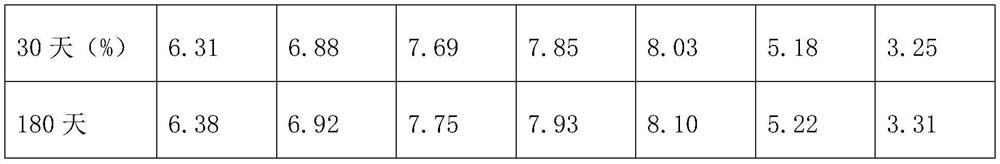
[0029] This embodiment provides a specific implementation of an immobilized fermentation system, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0030] Mix 8g of sodium alginate with 200ml of distilled water, heat and stir to dissolve, and cool to 30°C to make a carrier reagent;
[0031] In a ratio of 400g: 100g: 4000ml glucose, calcium chloride and water were mixed and stirred and dissolved to make a fixation reagent;
[0032] Take the yeast agent and mix it with distilled water to make a live bacteria solution. The concentration of the viable bacteria in the solution is 1.8×10 10 1 / ml, mix 400ml of bacterial liquid with 100ml of carrier reagent, drop the mixed solution in 2L of fixative reagent, soak for 20min, and form sclerotia with a diameter of 2-3mm;
[0033] Take α-amylase, glucoamylase, acid protease, endoglucanase, exoglucanase and β-glucosidase, dissolve them in pure water to make enzyme liquid, and the concentration of each enzyme in the enzyme liquid is 8×10 ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] This embodiment provides a specific implementation of an immobilized fermentation system, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0036] Mix 8g of sodium alginate with 200ml of distilled water, heat and stir to dissolve, cool to 30°C, then add 1.5g of gluconic acid-modified Fe with a diameter of 300-500nm 3 o 4 Stir the magnetic particles evenly to make a carrier reagent;
[0037] In a ratio of 400g: 100g: 4000ml glucose, calcium chloride and water were mixed and stirred and dissolved to make a fixation reagent;
[0038] Take the yeast agent and mix it with distilled water to make a live bacteria solution. The concentration of the viable bacteria in the solution is 1.8×10 10 1 / ml, mix 400ml of bacterial liquid with 100ml of carrier reagent, drop the mixed solution in 2L of fixative reagent, soak for 20min, and form sclerotia with a diameter of 2-3mm;
[0039] Take α-amylase, glucoamylase, acid protease, endoglucanase, exoglucanase and β-glucosidase, dissol...
Embodiment 3
[0041] This embodiment provides a specific implementation of an immobilized fermentation system, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0042]Mix 8g of sodium alginate with 200ml of distilled water, heat and stir to dissolve, cool to 30°C, then add 0.5g of amino acid-modified Fe with a diameter of 500-800nm 3 o 4 Stir the magnetic particles evenly to make a carrier reagent;
[0043] In a ratio of 400g: 100g: 4000ml glucose, calcium chloride and water were mixed and stirred and dissolved to make a fixation reagent;
[0044] Take the yeast agent and mix it with distilled water to make a live bacteria solution. The concentration of the viable bacteria in the solution is 1.8×10 10 1 / ml, mix 400ml of bacterial liquid with 100ml of carrier reagent, drop the mixed solution in 2L of fixative reagent, soak for 20min, and form sclerotia with a diameter of 2-3mm;
[0045] Take α-amylase, glucoamylase, acid protease, endoglucanase, exoglucanase, β-glucosidase, and Aspergill...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com