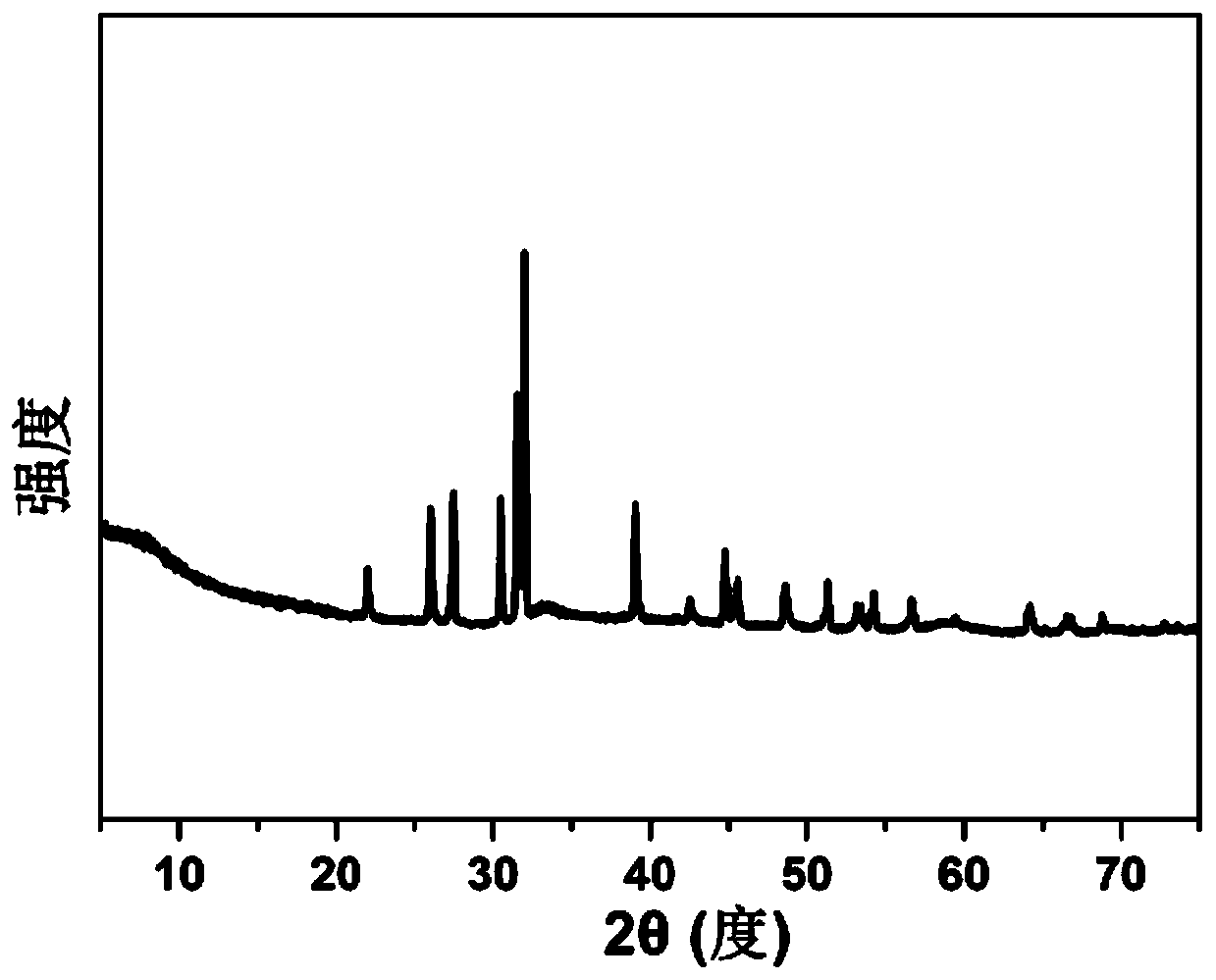
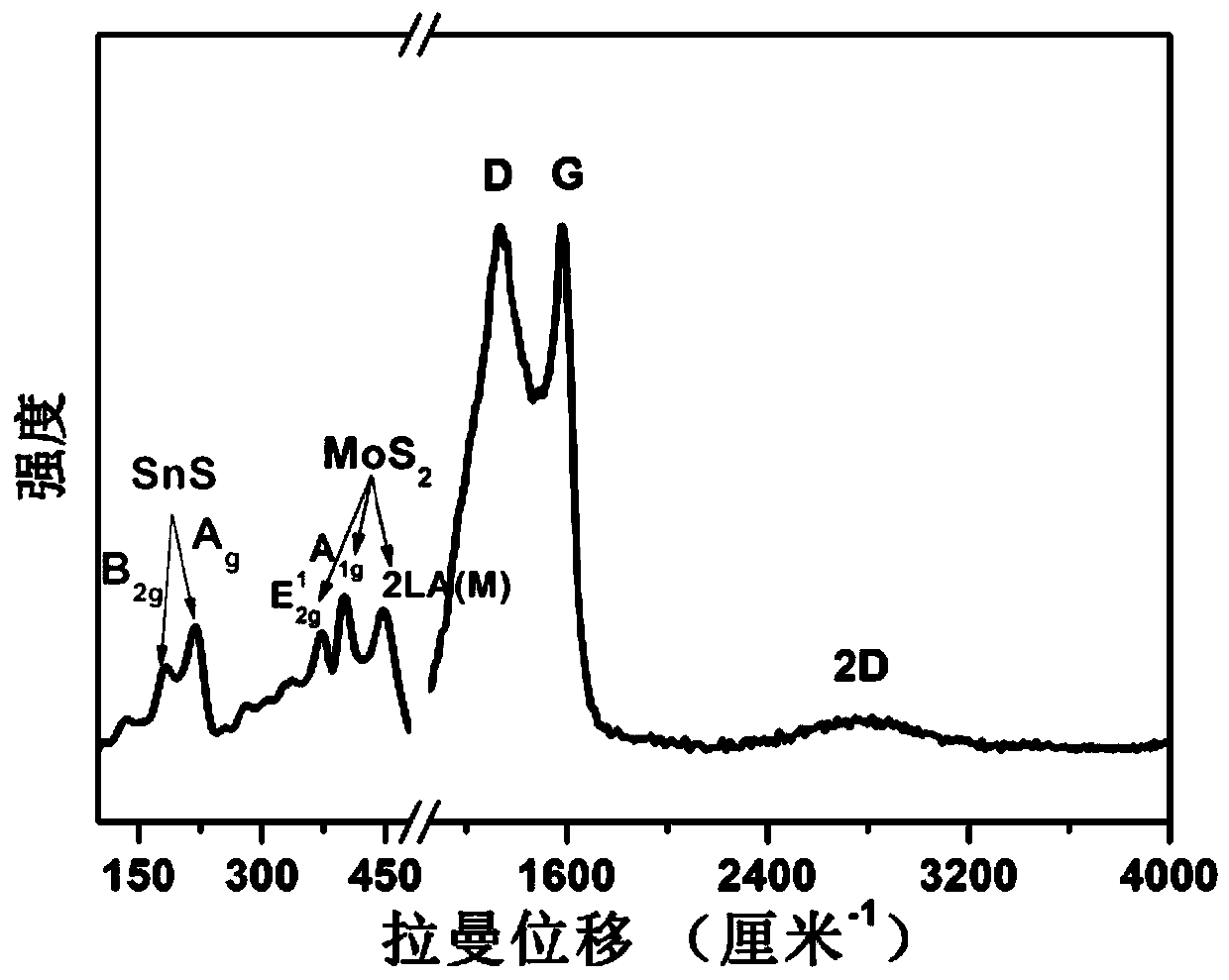
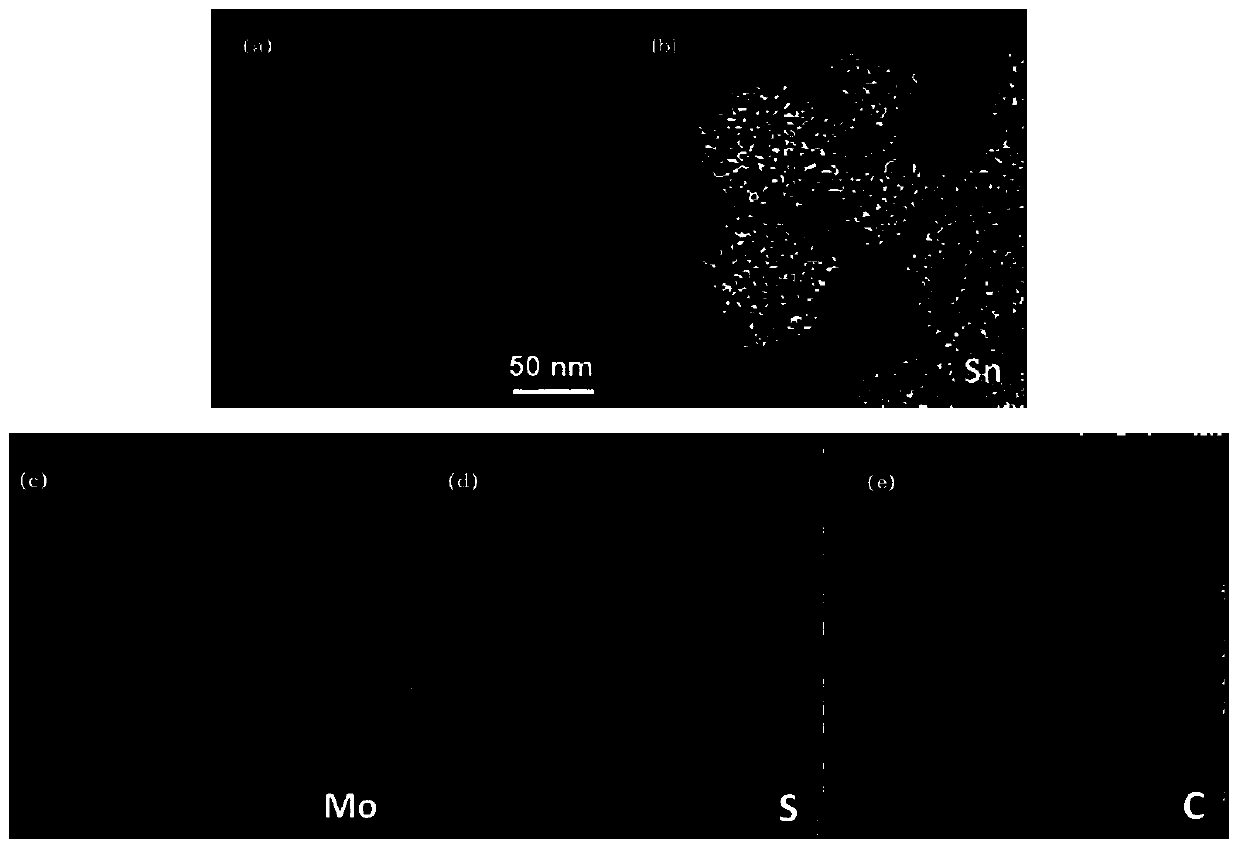
Molybdenum disulfide and double-carbon-layer co-modified stannous sulfide nanospheres and preparation method thereof
A technology of molybdenum disulfide and stannous sulfide, which is applied in the direction of secondary batteries, electrochemical generators, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of limiting sodium ion storage capacity, enhancing electronic conductivity, and limiting electron transmission, etc. The effect of large-scale production, good repeatability, and high cycle performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Weigh 4.0g of glucose and 1.2g of sodium stannate in a beaker of 30mL of deionized water, stir on a magnetic stirrer for 30min, completely dissolve the raw materials and mix them uniformly, then transfer them to a reaction kettle lined with polytetrafluoroethylene , and then put it in an oven at 170°C for 4 hours; wait for the reaction kettle to cool down to room temperature naturally, pour off the supernatant, then centrifuge, wash with water and ethanol three times in turn, and put it in an oven at 80°C to dry After 12 hours, brown tin dioxide nanosphere powder was obtained; the tin dioxide nanosphere powder of 0.2 g was weighed and put into 50 mL of deionized water, ultrasonicated for 30 minutes, and 300 μL of pyrrole and 1.0 g of phosphomolybdic acid were added to the solution. Stir continuously at room temperature for 24 hours; then centrifuge at 8,000 rpm for 10 minutes, then disperse with water and ethanol, centrifuge, and wash 3 times to obtain a black solid, whi...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Weigh 4.5g of glucose and 1.5g of sodium stannate in a beaker of 30mL of deionized water, stir on a magnetic stirrer for 30min, completely dissolve the raw materials and mix them evenly, then transfer them to a reaction kettle lined with polytetrafluoroethylene , and then put it in an oven at 180°C for 6 hours; wait for the reaction kettle to cool down to room temperature naturally, pour off the supernatant, then centrifuge, wash with water and ethanol three times in turn, and put it in an oven at 70°C to dry After 11 hours, brown tin dioxide nanosphere powder was obtained; the tin dioxide nanosphere powder of 0.2 g was weighed and put into 50 mL of deionized water, ultrasonicated for 30 minutes, and 400 μL of pyrrole and 1.2 g of phosphomolybdic acid were added to the solution. Continue to stir at room temperature for 23 hours; then centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes, then disperse with water and ethanol, centrifuge, and wash 3 times to obtain a black solid, which is...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Weigh 3.0 g of glucose and 1.8 g of sodium stannate in a beaker of 30 mL of deionized water, stir on a magnetic stirrer for 30 min, completely dissolve the raw materials and mix them uniformly, then transfer them to a reaction kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner , and then put it in an oven at 160°C for 7 hours; wait for the reaction kettle to cool down to room temperature naturally, pour off the supernatant, then centrifuge, wash with water and ethanol three times in turn, and put it in an oven at 90°C to dry After 13 hours, brown tin dioxide nanosphere powder was obtained; the tin dioxide nanosphere powder of 0.2 g was weighed and put into 50 mL of deionized water, ultrasonicated for 30 minutes, and 200 μL of pyrrole and 0.8 g of phosphomolybdic acid were added to the solution. Stir continuously at room temperature for 25 hours; then centrifuge at 8,000 rpm for 10 minutes, then disperse with water and ethanol, centrifuge, and wash 3 times to obtain a black soli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com