Thin-beam laser melting deposition additive manufacturing method and laser processing head used therefor
A technology of laser melting deposition and laser processing head, which is applied in the direction of additive processing, metal material coating process, coating, etc. It is suitable for high-precision parts and other problems, so as to achieve high utilization rate of laser energy, improve the quality of additive manufacturing, and avoid the effect of powder oxidation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
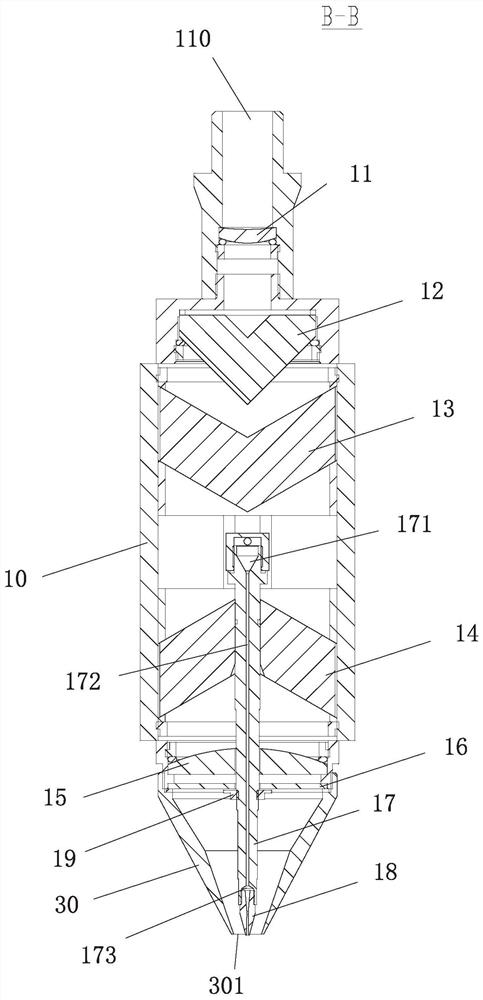
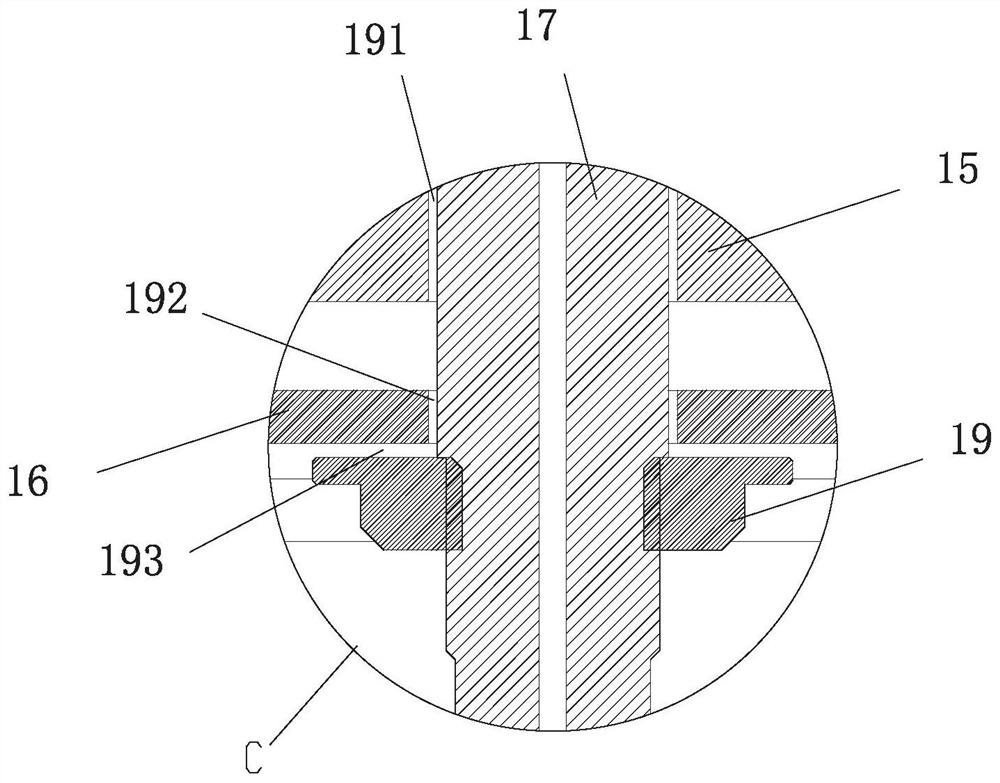
[0037] refer to Figure 10 to Figure 15 To understand, the present invention proposes a thin beam laser melting deposition additive manufacturing method, comprising the following steps:
[0038] 1) Transform an incident beam of parallel collimated laser light into an annular laser beam (such as Figure 11 );
[0039] 2) Through a pair of upper and lower refracting prisms 13 and 14 opposite to the roof ridge, the annular laser beam is first converted into two semicircular laser beams with a gap 120 between them and then restored back to the annular laser beam, wherein: Upper refraction prism 13 will circular ring laser beam (as Figure 11 ) is transformed into two semi-circular laser beams with a gap 120 between them (such as Figure 12 ), the lower refracting prism 14 restores the two semicircle ring laser beams back to the ring laser beam (as Figure 13 );
[0040] 3) by the focusing lens 15, the annular laser beam (such as Figure 13 ) converges into a fine focused spot ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Defocus amount | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com