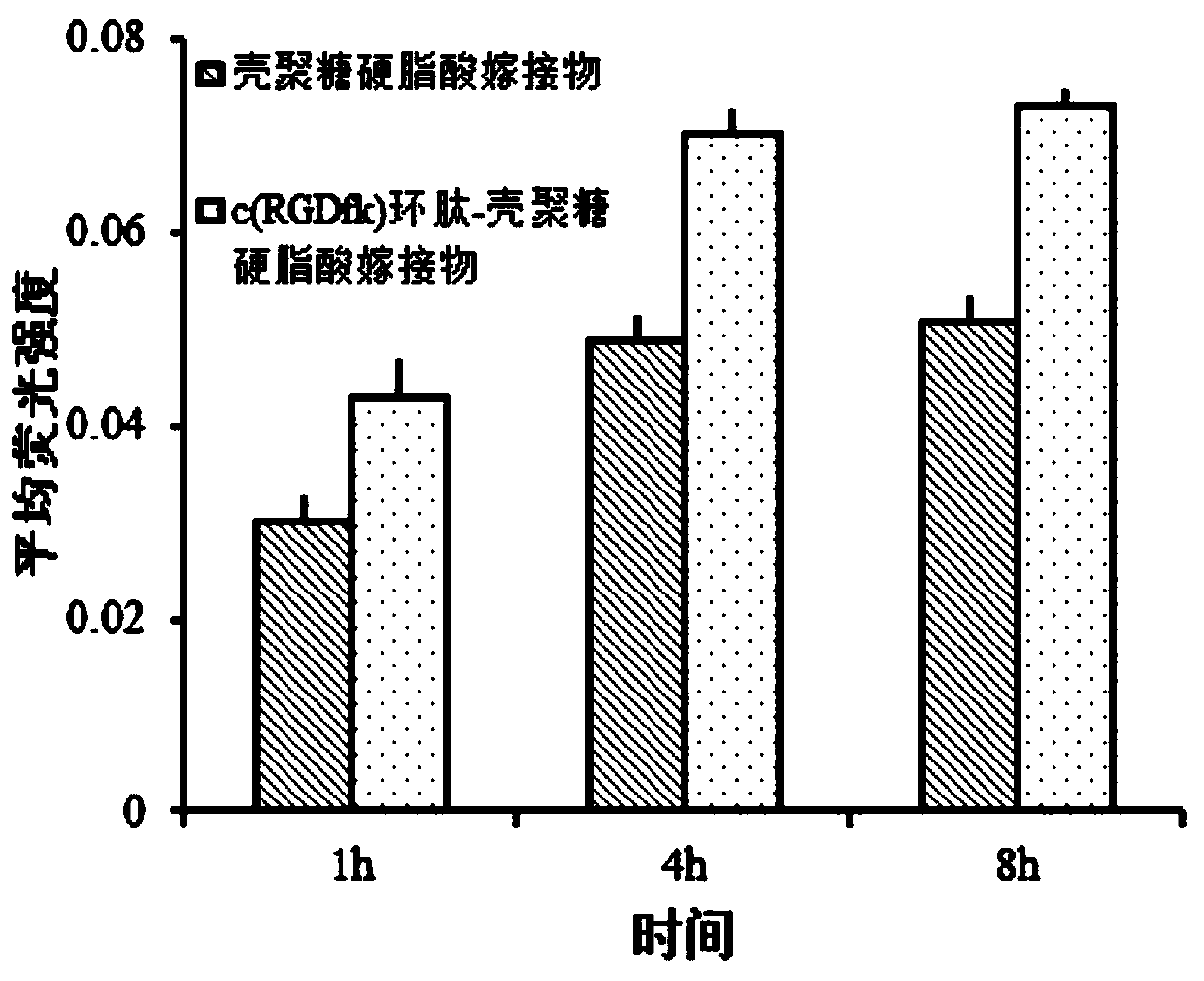
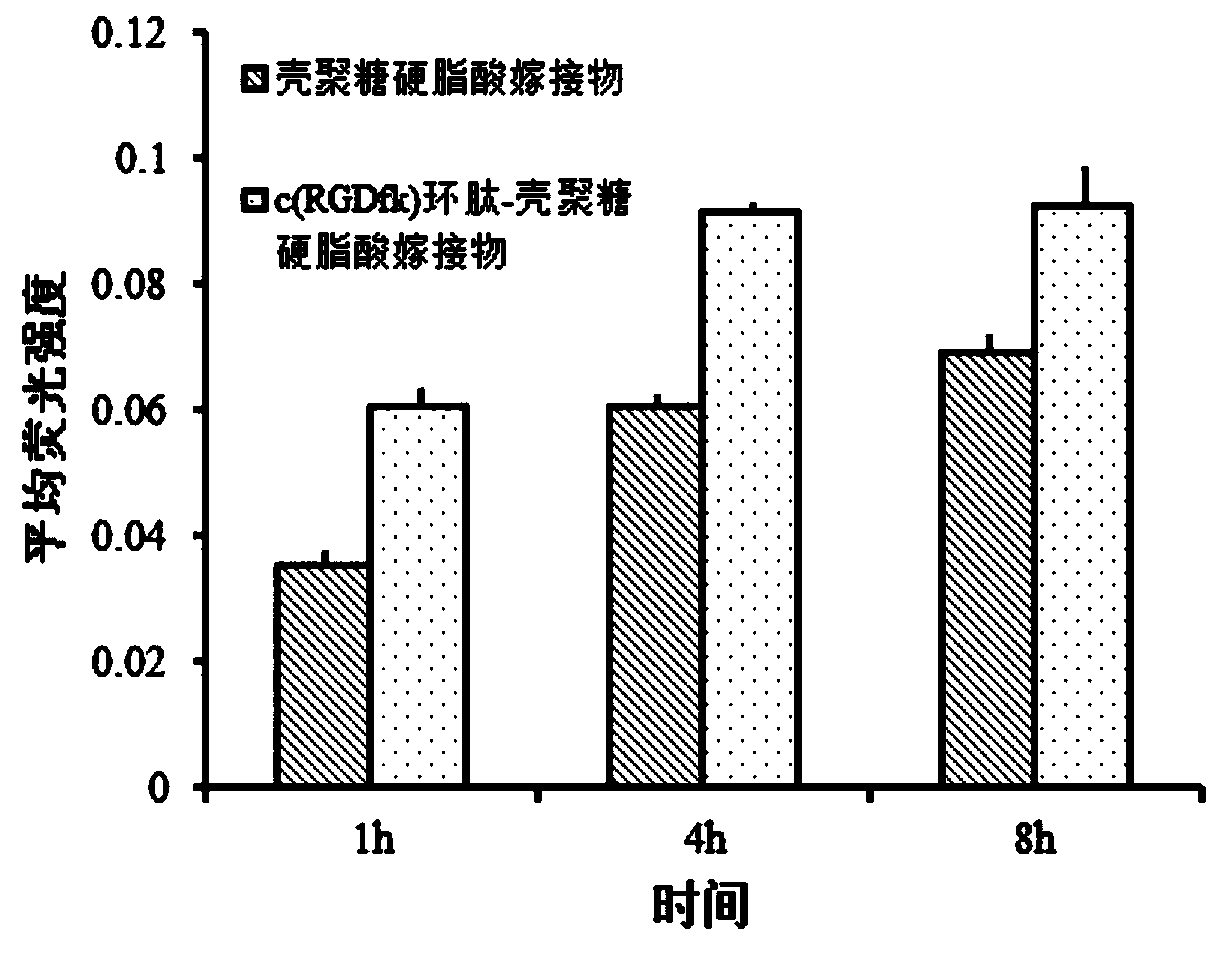
c(RGDfk) cyclic peptide-chitosan stearic acid graft drug-loaded micelles as well as preparation and application thereof
A technology of drug-loaded micelles and chitosan, which can be used in anti-tumor drugs, drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve problems such as serious toxic side effects, drug resistance, and unsatisfactory patient prognosis, and can inhibit the formation of new blood vessels and improve the The concentration of photosensitizer, the effect of high-efficiency photothermal conversion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] (1) Preparation of low molecular weight chitosan
[0038] Take 20 g of chitosan with a molecular weight of 450 kDa and a degree of deacetylation of 95%, disperse it in 1000 mL of hydrochloric acid solution with a volume ratio of 0.9%, stir in a water bath at 60°C for 12 hours, and fully swell. Slowly drop chitosanase with a weight ratio of 2% therein, and enzymolysis reaction occurs at a temperature of 60°C. Gel permeation chromatography was used to control the molecular weight of chitosan during the degradation process. After the degradation is complete, add activated carbon with a weight / volume ratio of 5% at 80°C, stir for 30 minutes, cool to room temperature, and gradually remove activated carbon with ordinary filter paper, 0.45 μm and 0.22 μm microporous membranes, and vacuum freeze-dry Low-molecular-weight chitosan is obtained, and the weight-average molecular weight of the obtained chitosan is 5-20 kDa.
[0039] (2) Synthesis of chitosan stearic acid graft
[...
Embodiment 2
[0045] (1) Preparation of low molecular weight chitosan
[0046] Take 20 g of chitosan with a molecular weight of 450 kDa and a degree of deacetylation of 95%, disperse it in 1000 mL of hydrochloric acid solution with a volume ratio of 0.9%, stir in a water bath at 60°C for 12 hours, and fully swell. Slowly drop chitosanase with a weight ratio of 2% therein, and enzymolysis reaction occurs at a temperature of 60°C. Gel permeation chromatography was used to control the molecular weight of chitosan during the degradation process. After the degradation is complete, add activated carbon with a weight / volume ratio of 5% at 80°C, stir for 30 minutes, cool to room temperature, and gradually remove activated carbon with ordinary filter paper, 0.45 μm and 0.22 μm microporous membranes, and vacuum freeze-dry Low-molecular-weight chitosan is obtained, and the weight-average molecular weight of the obtained chitosan is 5-20 kDa.
[0047] (2) Synthesis of chitosan stearic acid graft
[...
Embodiment 3
[0053] (1) Preparation of low molecular weight chitosan
[0054] Take 20 g of chitosan with a molecular weight of 450 kDa and a degree of deacetylation of 95%, disperse it in 1000 mL of hydrochloric acid solution with a volume ratio of 0.9%, stir in a water bath at 60°C for 12 hours, and fully swell. Slowly drop chitosanase with a weight ratio of 2% therein, and enzymolysis reaction occurs at a temperature of 60°C. Gel permeation chromatography was used to control the molecular weight of chitosan during the degradation process. After the degradation is complete, add activated carbon with a weight / volume ratio of 5% at 80°C, stir for 30 minutes, cool to room temperature, and gradually remove activated carbon with ordinary filter paper, 0.45 μm and 0.22 μm microporous membranes, and vacuum freeze-dry Low-molecular-weight chitosan is obtained, and the weight-average molecular weight of the obtained chitosan is 5-20 kDa.
[0055] (2) Synthesis of chitosan stearic acid graft
[...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com