Angelicae sinensis extracts useful for treatment of cancers
a technology of angelicae sinensis and extracts, which is applied in the direction of biocide, plant/algae/fungi/lichens, drug compositions, etc., to achieve the effect of inhibiting telomerase activity and inducing apoptosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Analysis of Cell Cytotoxicity
[0060] The effects on cell viability after the treatments with different concentrations of the Angelicae sinensis extracts or the active components purified therefrom were evaluated by modified MTT assay in triplicate. Briefly, the cells (5×103) were incubated into 96-well plates containing 100 μl of a growth medium. The cells were permitted to adhere for 24 hours, then treated with 100 μl of the herbal extracts or the active components dissolved in the medium. The control contained DMSO of ≦0.02% (v / v). After 24, 48 and 72 h incubation, the drug-containing medium was replaced by 50 μl of fresh medium, and cells in each well were incubated in 50 μl of 400 μg / ml MTT for 6-8 h. The medium and MTT were removed later and 100 μl of DMSO was added to each well and to the control, to dissolve the soluble components. Absorbance at 550 nm of the solutions was measured with MRX Microtiter Plate Luminometer (DYNEX, USA). The absorbance of untreated cells was consi...
example 2
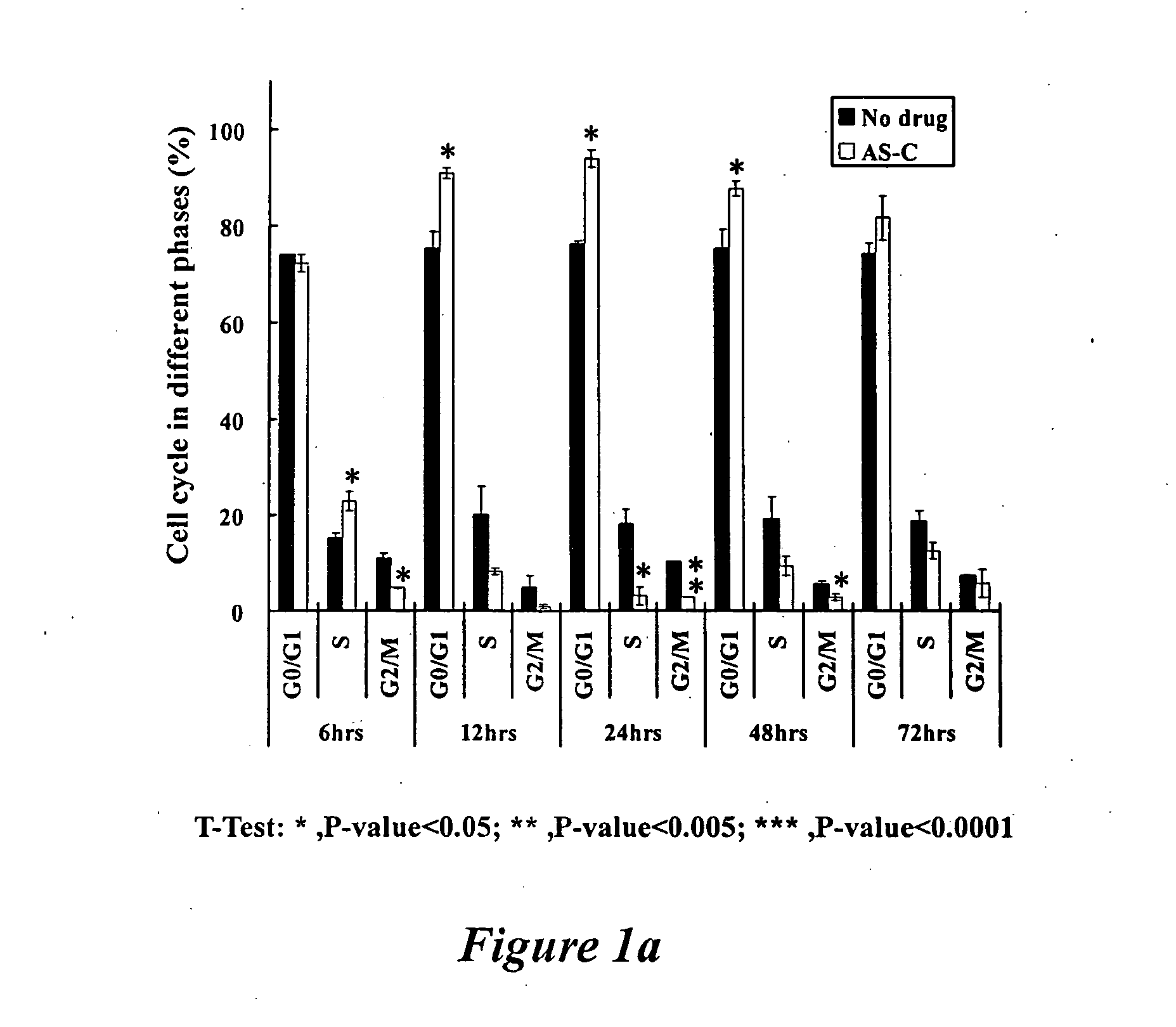
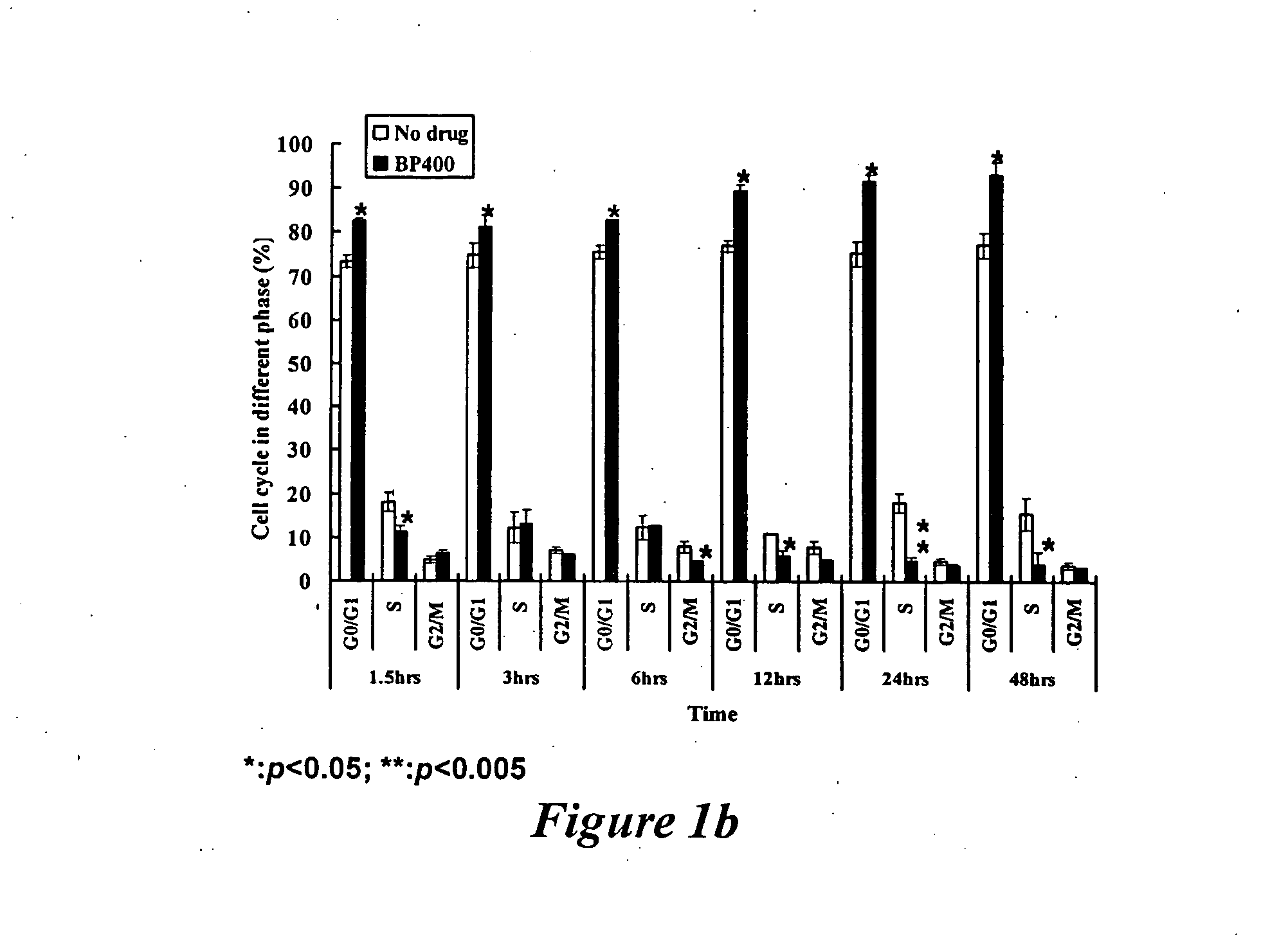
AS-C and BP Enhance the Cell Cycle Arrest at G0 / G1 Phase in GBM Cells
[0068] Brain tumor cell lines DBTRG-05MG and G5T / VGH were cultured in the growth medium with a diluent. For each test and control, DMSO was added, and the content is less than 0.02% (v / v). For the AS-C and BP treatment, 70 μg / ml of AS-C and 400 μM of BP were added, respectively. All were cultured for 48 hours. The analysis of cell cycle distribution was performed by DNA staining with propidium iodide (PI). Briefly, 2×106 adherent cells were detached by trypsinization. The detached cells and the floating dead cells were centrifuged and washed twice with 10 ml of cold 1×PBS (Life Technologies, Inc.). Supernatant was aspirated, cells were re-suspended in 0.8 ml of 1×PBS, and then 200 μl of PI solution (50 μg / ml PI+0.05 mg / ml RNase A; Sigma Chemical Co.) was added, and the cells were refrigerated at 4° C. overnight. The cells were incubated while protected from light at room temperature for at least 2 h before DNA ana...
example 3
AS-C and BP Induce GBM Cells Apoptosis
[0070] Apoptotic cell death was analyzed using In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit, POD (Roche, Germany). Changes in DNA chromatin morphologic features were used for quantification. The procedures were performed in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, cells were cultured on culture dish and analyzed 72 hours after treatment with AS-C (70 μg / ml) and BP (5˜800 μg / ml), respectively. In AS-C and BP-treated groups, the suspended cells were collected. In the control group, adherent and floating cells were collected. Then, the cells were fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde at room temperature for 15 min. on saline coated slides, washed once in 1×PBS, and incubated in cold permeabilization solution (0.1% Triton X-100+0.1% sodium citrate) after reducing activity of endogenous peroxidase with 3% H2O2. The cells were washed with 1×PBS again, and incubated with terminal deoxynucleiotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nicks labeling (TUNEL) rea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| blood pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| MRI imaging | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com