Inverter current sharing method, device, inverter system and wireless charging system
A technology of inverters and multi-inverters, which is applied in the current sharing method of inverters, wireless charging systems, and devices, and can solve problems such as reduced reliability, reduced system power density, and small output current.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
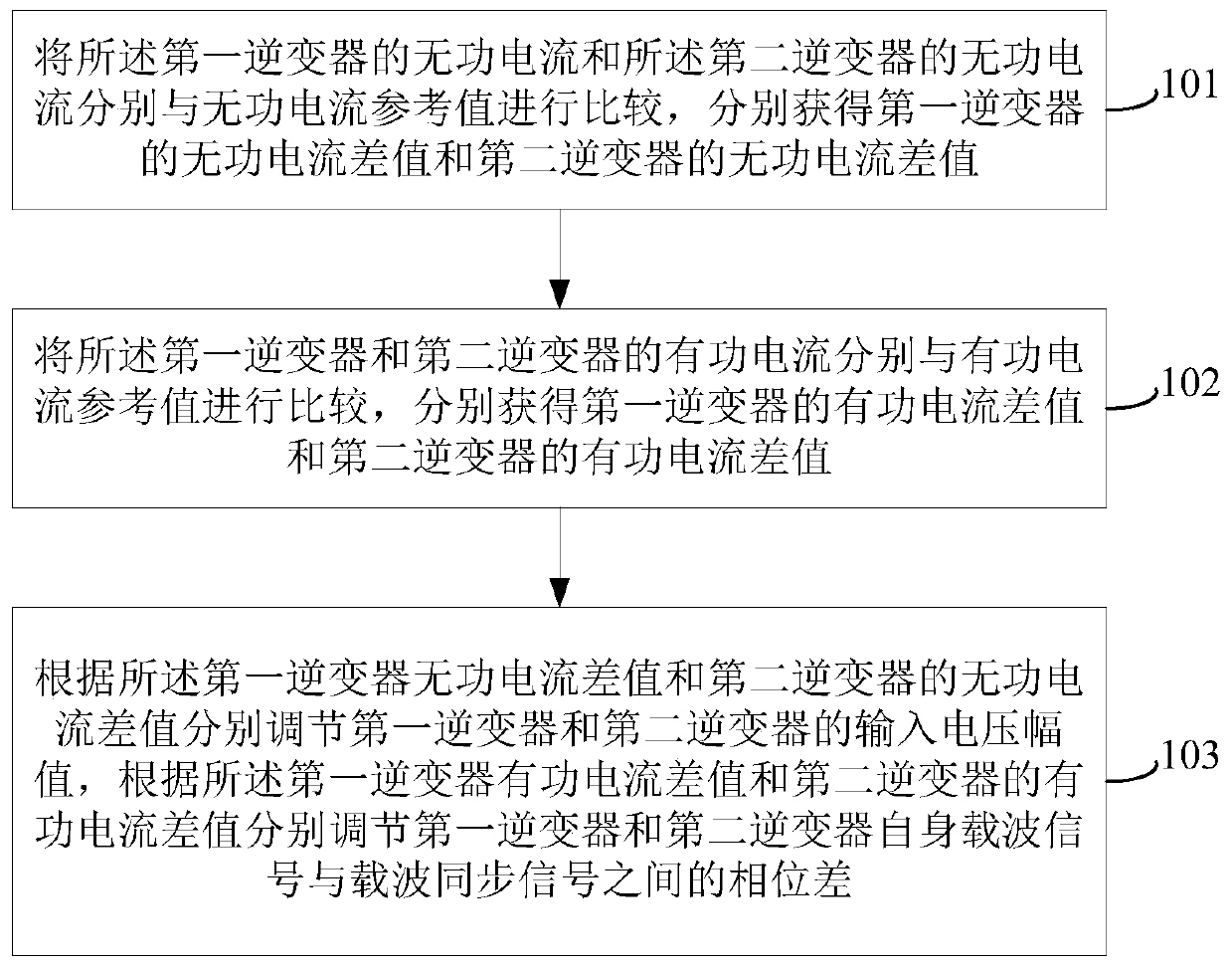
[0111] see figure 1 , is a flow chart of a current sharing method when inverters are connected in high-frequency parallel connection provided in this embodiment.
[0112] This method is applied to achieve current sharing when the output terminals of multiple inverters are connected in parallel at high frequency. The multiple inverters include at least the following two inverters: the first inverter and the second inverter, and the first inverter The output ends of the inverter and the second inverter are connected in parallel and are inductive.
[0113] The method provided in the embodiment of this application is suitable for high-frequency parallel connection of inverters. High-frequency parallel connection means that the frequency of the output voltage of each inverter connected in parallel is the same as the switching frequency of the inverter, generally hundreds of Hz to hundreds of Hz kHz. The high frequency output voltage of the inverter is different from the power fre...
Embodiment 2
[0148] see Figure 4 , is a flow chart of the reactive current regulation method of the inverter provided in this embodiment.
[0149] This reactive current regulation method is applicable to inverters with two or more high-frequency output terminals connected in parallel. For the convenience of description, this embodiment takes the parallel connection of the output terminals of two inverters as an example for introduction. . This current sharing method includes:
[0150] Step 401: Obtain a first voltage trimming amount according to the reactive current difference of the first inverter; obtain a second voltage trimming amount according to the reactive current difference of the second inverter.
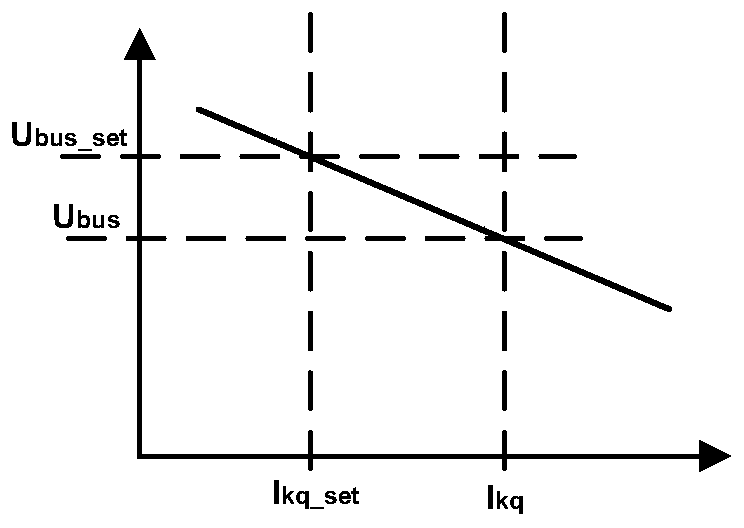
[0151] After the reactive current difference of each inverter is obtained, the reactive current difference of each inverter is input into the reactive current regulator accordingly, and after compensation processing by the reactive current regulator, corresponding to different inver...
Embodiment 3
[0165] see Image 6 , is the flow chart of the active current regulation method of the inverter provided in this embodiment. The current sharing method is suitable for inverters with two or more high-frequency output terminals connected in parallel. For the convenience of description, this embodiment In this paper, the parallel connection of the output ends of two inverters is taken as an example for introduction. This current sharing method includes:
[0166] Step 601: Obtain a first angle trimming amount according to the active current difference of the first inverter; obtain a second angle trimming amount according to the active current difference of the second inverter.
[0167] After the active current difference of each inverter is obtained, the active current difference of each inverter is input into the active current regulator accordingly, and after compensation processing by the active current regulator, the angle fine-tuning corresponding to different inverters is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com