Method for manufacturing water-permeable bricks with gradient holes from ceramic solid waste materials
A technology of ceramic waste and solid waste, which is applied in the production and application of ceramic products and ceramic materials, and can solve the problems of environmental pollution, high cost, and inability to filter water.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A method for manufacturing gradient hole permeable bricks from ceramic solid waste, comprising the steps of:
[0029] 1. Weigh each component according to the following mass percentages: 80% ceramic solid waste, 8% kaolin, and 12% feldspar;
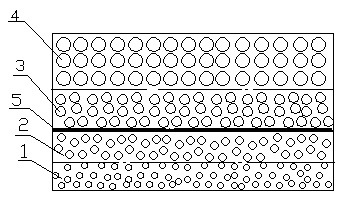
[0030] 2. Perform external force crushing, ball milling, and sieving of the weighed ceramic solid waste to obtain waste particles and powders with different particle sizes and meshes, and divide the particle size meshes into 10-14 meshes into one level (including 12 meshes) 16-24 mesh is divided into two grades (including 20 mesh), 30-70 mesh is divided into three grades (including 50 mesh), 100-200 mesh (including 150 mesh) is divided into four grades of powder,
[0031] 3, in step 2 gained different mesh size ranges are divided into all levels of powder and grain, add kaolin, feldspar in proportion by the actual weight of each level of powder and grain;
[0032] 4. Add the materials of all levels obtained in step 3 into the mold...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2, embodiment 2 is on the basis of embodiment 1, in order to further improve the various technical indicators of permeable bricks, the technical measures taken, the specific manufacturing method steps are:
[0036] 1. Weigh each component according to the following mass percentage: ceramic solid waste 75%, kaolin 3%, water glass 2%, feldspar 17%, sugar filter mud 3%,
[0037] 2. Perform external force crushing, ball milling, and sieving of the weighed ceramic solid waste to obtain waste particles and powders with different particle sizes and meshes, and divide the particle size meshes into 10-14 meshes into one level (including 12 meshes) 16-24 mesh is divided into two grades (including 20 mesh), 30-70 mesh is divided into three grades (including 50 mesh), 100-200 mesh (including 150 mesh) is divided into four grades of powder,
[0038] 3, in step 2 gained all levels of powder granules, add kaolin, water glass, dolomite and sugar filter mud in proportion by the...
Embodiment 3
[0043] 1. Weigh each component according to the following mass percentage: 80% ceramic solid waste, 5% kaolin, 5% feldspar, 5% dolomite, 3% sugar mud and 2% calcium carbonate;
[0044] 2. Perform external force crushing, ball milling, and sieving of the weighed ceramic solid waste to obtain waste particles and powders with different particle sizes and meshes, and divide the particle size meshes into 10-14 meshes into one level (including 12 meshes) 16-24 mesh is divided into two grades (including 20 mesh), 30-70 mesh is divided into three grades (including 50 mesh), 100-200 mesh (including 150 mesh) is divided into four grades of powder,
[0045] 3, in step 2 gained all levels of granules, add kaolin, feldspar, dolomite and calcium carbonate in proportion by the actual weight of granules of all levels;
[0046] 4. Put the materials of all levels obtained in step 3 into the mold in turn, and apply pre-pressure to push the indenter into the mold to flatten it, and then spray a l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com