Preparation method of nano-porous carbon material
A technology of nanoporous carbon and waste liquid, which is applied in the field of preparation of nanoporous carbon materials, and can solve the problems of high preparation cost, complicated preparation methods, and the need for activators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] The present invention provides a kind of preparation method of nanoporous carbon material, comprises the following steps:
[0033] A) mixing the alkaline waste liquid with water and freeze-drying to obtain a solid mixture;
[0034] The alkaline waste liquid is the alkaline waste liquid produced in the coal chemical deashing process;
[0035] B) subjecting the solid mixture to medium temperature treatment to obtain a pretreated product;
[0036] C) activating the pretreated product at high temperature to obtain a nanoporous carbon material.
[0037] A large amount of alkaline waste liquid will be produced in the process of chemical deashing of coal. The alkaline waste liquid contains a large amount of organic matter. As the reaction proceeds, the organic matter will continue to accumulate, which will eventually affect the reaction. Under normal circumstances, the treatment of alkaline waste liquid is difficult, and direct discharge into the sewage treatment plant will ...
Embodiment 1
[0052] (1) Mix the prepared coal powder (particle size less than 1mm) with 13wt% KOH solution, the ratio of coal powder to KOH solution is 1:3.45 (coal powder content 22.5wt%). Move the coal-alkali mixture into the autoclave. According to different coal types, adjust the temperature and pressure to appropriate values. The general temperature is 200℃~240℃, and the pressure is 40bar (4MPa). After the alkali solution is digested, the coal-alkali mixture is filtered through a vacuum filter to obtain an alkali leaching solution of the coal.
[0053] The alkali leaching solution of coal was mixed with deionized water at a ratio of 2:1. After mixing, it was ultrasonically treated for 30 minutes, and 50 mL of the mixed solution was pipetted and placed in a freeze dryer at -40°C for 48 hours at low temperature to obtain a solid mixture.
[0054] (2) Put the solid mixture obtained in step (1) into a nickel oxide crucible and put it into a high-temperature furnace. Under the protection...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Using the preparation method provided in Example 1, the difference is that: the target temperature of the activation treatment in step (3) is 600° C.; and a nanoporous carbon material is obtained.
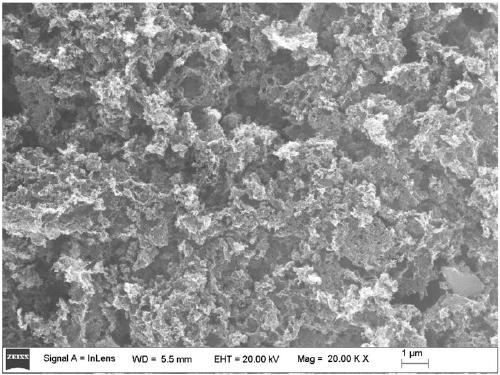
[0059] as attached figure 2 The material shown by the scanning electron microscope also has a loose and porous nanostructure; after testing, the specific surface area of the nanoporous carbon material provided by Example 2 is 1730m 2 / g; if Figure 6 As shown, using this material as an electrode material, the capacity after 1000 cycles at a current density of 0.5A / g is 297F / g, and the capacity after 1000 cycles at a current density of 1A / g is 163F / g, which has a good cycle stability.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com