Application of short n import fragments in tobacco and its screening and estimation methods
A tobacco and fragment technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in estimating the number of gene components, inability to quickly evaluate plant yield, yellowing and drying of short N-introduced fragments. Problems such as improving the condition of roasting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The preparation of embodiment 1 plant material and DNA extraction
[0048] 1. Backcrossing of N import fragments
[0049] Coker176 (genotype NN) and 5F (genotype nn) were planted, Coker176 pollen was collected to pollinate emasculated 5F flowers during flowering, and F1 seeds (genotype Nn) were harvested. Plant F1 plants, collect F1 pollen to pollinate emasculated 5F flowers during flowering, and harvest BC1F1 seeds (genotype Nn:nn=1:1). Sow BC1F1, inoculate TMV at the seedling stage, and screen out TMV-resistant plants. When flowering, collect pollen and backcross with 5F to obtain backcross seeds. Through continuous backcrossing, the seeds of the fifth generation of backcrossing (BC5F1) were obtained.
[0050] 2. Screening of TMV-resistant plants
[0051] 4-5 sheets of tobacco seedlings from BC5F1 backcross populations planted in 32-hole trays, 1 plant per hole, were artificially inoculated with TMV, and 5-7 days after inoculation, it was investigated whether the in...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 Chromosomal Plant Screening of Short N Imported Fragments
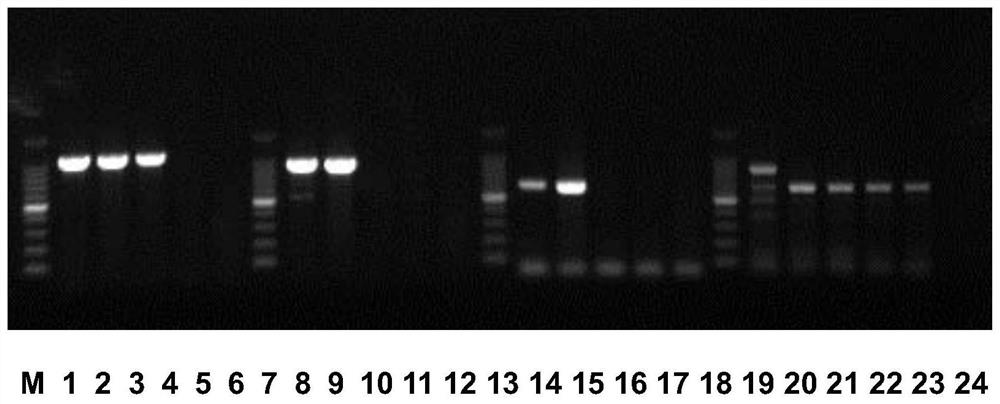
[0061] Tobacco germplasm 5F susceptible to TMV was used as a disease-resistant control, and the tobacco variety Coker176 known to contain the N gene resistant to TMV was used as a disease-resistant control; the primer pair of TN5. Genomic DNA and the tobacco genomic DNA of the disease-resistant control were used as templates for PCR amplification, and the amplified products were detected by electrophoresis;
[0062] The PCR reaction system is as follows:
[0063]
[0064] The primer pair is TN5.51 primer pair.
[0065] All reagents used were purchased from Treasure Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0066] The PCR reaction program was as follows: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes; denaturation at 94°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 55°C for 30 seconds, extension at 72°C for 30 seconds, and 35 cycles; final extension at 72°C for 10 minutes. PCR amplification products can be stored at 4°C.
[0067] Ele...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3 Detection of the reduction in the number of non-target gene components linked to the N gene
[0072] Tobacco germplasm 5F that is sensitive to TMV is a disease-resistant control, and the tobacco variety Coker176 that is known to contain N gene resistance to TMV is a disease-resistant control; N1N2 positive and 3 plant DNAs without 845bp amplification products obtained in Example 2, The tobacco genomic DNA of the susceptible control and the tobacco genomic DNA of the disease-resistant control are used as templates for PCR amplification, and the amplified products are detected by electrophoresis;
[0073] The PCR reaction system is as follows:
[0074]
[0075]
[0076] The primer pair is TN5.51 primer pair, TN5.34 primer pair, TN5.20 primer pair and TN4.99 primer pair.
[0077] All reagents used were purchased from Treasure Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0078] The PCR reaction program was as follows: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes; denaturation at 9...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com