Exopolysaccharide and application thereof
An extracellular polysaccharide and mannose technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of generating and eliminating balance damage, attacking cell components, damaging cell integrity, etc., to prevent direct damage, high application value, and high free radical scavenging ability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Embodiment 1: the identification of bacterial strain of the present invention
[0059] Specific steps are as follows:
[0060] (1) After the contents of chicken cecum were heat-treated at 85°C, they were enriched and cultured with Clostridium-enriched medium, and then 53 isolates were isolated after anaerobic culture on solid medium for bacteria screening;
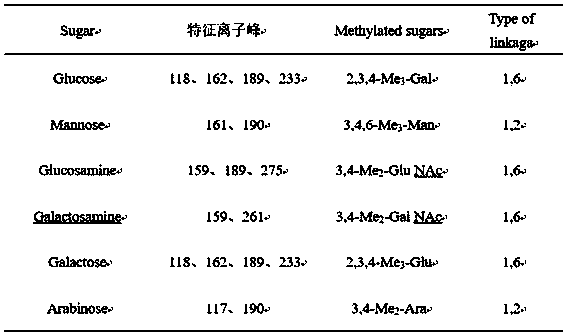
[0061] (2) After the isolates undergo colony morphology, growth characteristics, Gram staining, and colony drawing experiments, a strain that can grow well on an anaerobic plate, has a smooth surface, is Gram-positive, produces acid, produces gas, and can produce Strains that utilize starch, cannot hydrolyze gelatin, and produce higher polysaccharides;
[0062] (3) The genomic DNA of the strain was extracted, and the 16S rRNA gene of the strain was amplified, recovered and sequenced, and the obtained 16S rRNA nucleotide sequence was submitted to NCBI for BLAST analysis. %above;
[0063] (4) Select a sequence with...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2: Preparation of exopolysaccharide of the present invention
[0065] (1) Clostridium butyricum (Clostridium butyricum) RO-07 in Example 1 is activated and expanded;
[0066] (2) Inoculate the expanded strain obtained in step (1) into the fermentation medium, and perform anaerobic culture at 30° C. for 48 to 72 hours to obtain a fermentation broth containing the exopolysaccharide of Clostridium butyricum;
[0067] (3) centrifuging the liquid fermentation broth prepared in step (2), and collecting the supernatant;
[0068] (4) Concentrate the supernatant obtained in step (3) by ultrafiltration to 1 / 5 of the original volume to obtain a concentrated solution, then add three times the volume of absolute ethanol to the concentrated solution, and after alcohol precipitation, centrifuge, collect sediment;
[0069] (5) Dissolve the precipitate collected in step (4) with water, add 1 / 4 volume of Seveage reagent to remove protein, and prepare a crude sugar solution; ...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3: Identification of exopolysaccharides of the present invention
[0074] 1. Determination of molecular weight
[0075] Specific steps are as follows:
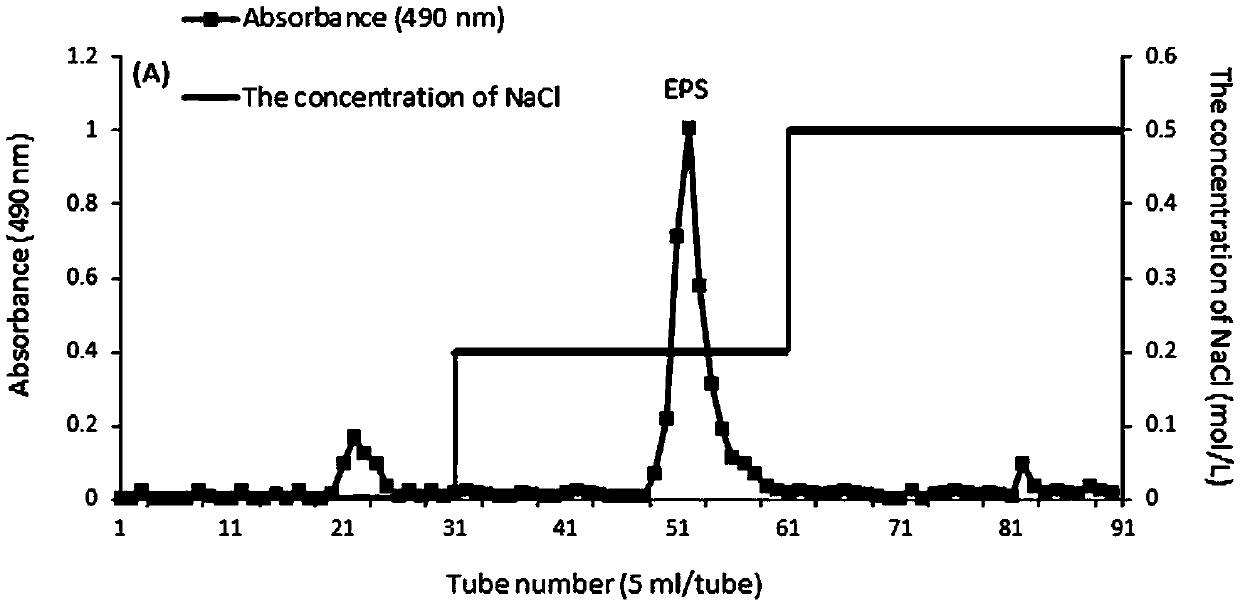
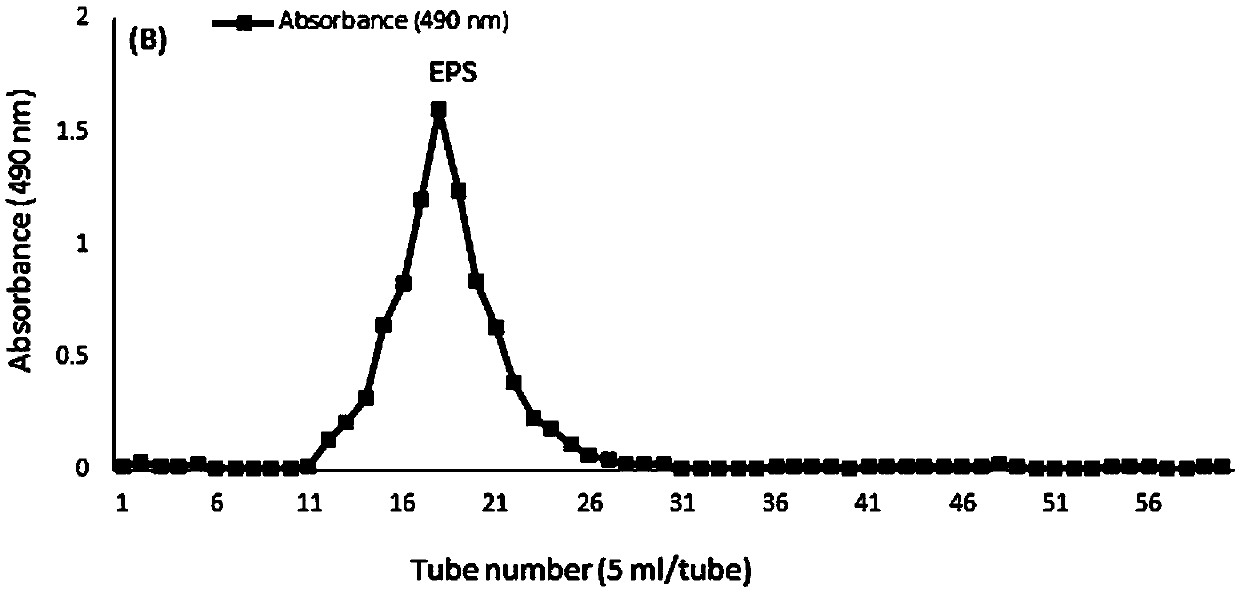
[0076] (1) Filter the EPS sample (5 mg / mL, 200 μL) obtained in Example 2 with a syringe filter (pore size 0.22 μm);
[0077] (2) Inject the filtered EPS sample into two Ultrahydrogel TM linear series columns (ID 7.8mm×300mm), and use NaNO 3 The solution (0.1M) was eluted at a flow rate of 0.9mL / min to obtain the response value data;
[0078] (3) The obtained data was collected and processed with Empower (Waters, USA), and the molecular weight (Mw) was directly calculated according to the molecular weight of each elution volume and the defined Mw of the RI signal value.
[0079] The measurement result is: the average molecular weight of EPS is 1.23×10 4 The chromatogram of Da; EPS showed a single symmetrical narrow peak, indicating that EPS is a homogeneous material; meanwhile, no peaks were detected from the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com