Analysis of exosomes and methods of diagnosing cancer
An exosome and cancer technology, applied in the field of exosome analysis and cancer diagnosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
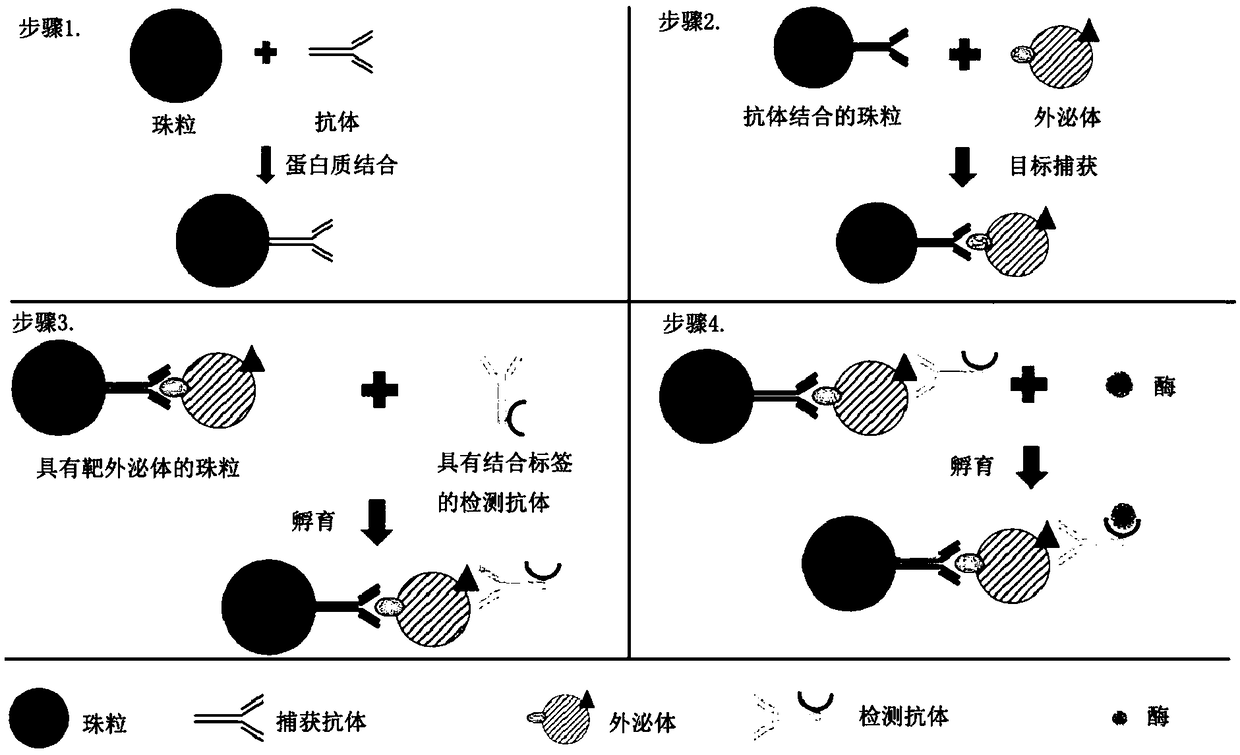
[0112] Example 1 - Construction of exosome immune complexes on beads
[0113] Digital ELISAs have been demonstrated in various microfluidic platforms. Exosome solutions are obtained from biological fluids and prepared by ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods. Since antigens are present on the surface of exosomes, they can be recognized by specific antibodies. A pair of antibodies that identify exosomes is built on the beads as an immune complex. Construction of immune complexes on beads as figure 1 shown. Antibodies that recognize biomarkers (such as CD63) on the surface of exosomes and beads (such as Dynabeads TM or agarose beads) binding. The beads were then incubated with the exosome solution. After incubation, collect the beads magnetically or by centrifugation. After thorough washing, the target exosomes bound to the beads were purified from the sample solution. Next, exosomes are detected using a sec...
Embodiment 2
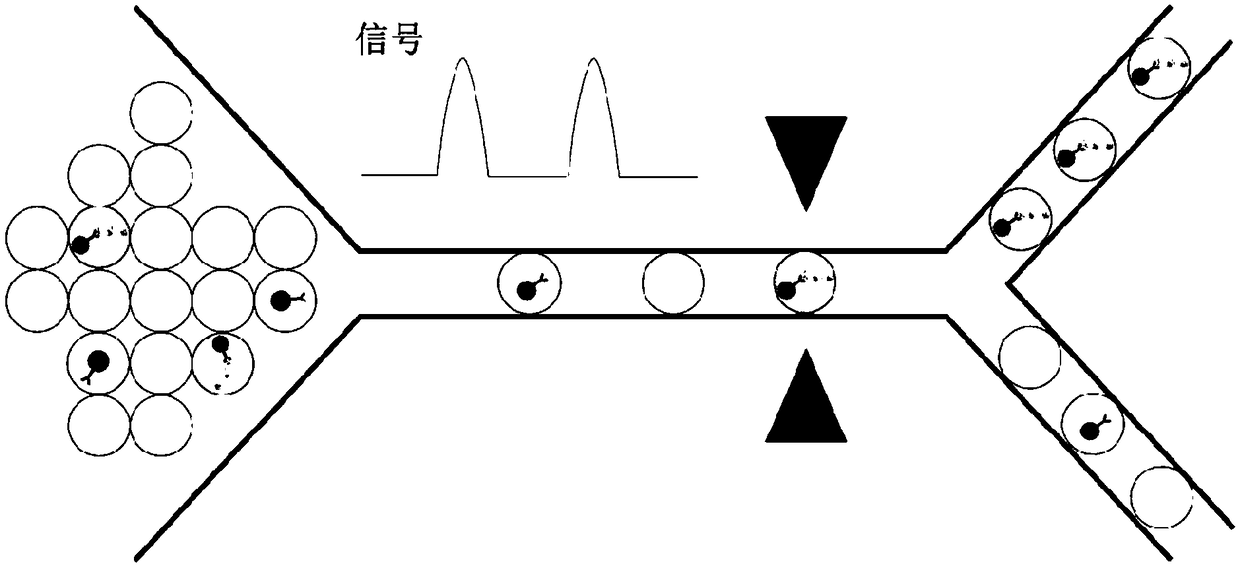
[0114] Example 2-digital quantification of target exosomes
[0115] Digital quantification of immune complex beads bound to target exosomes by specific protein biomarkers. The immune complex-constructed bead solution is flowed into the channel to mix the solution with the flow of another channel's matrix (eg, FDG) and form droplets of the mixture. Instead of using droplets as compartments, microwells fabricated on flat chips can also be used to divide the sample solution. A sample with beads can first be dropped onto the chip and scraped into the wells. Substrate (eg FDG) solution is then added to each compartment. The microwell chip is then sealed on top to isolate each individual space for reactions. Microfluidic workflows such as figure 2 shown. After incubation, the droplets / wells of beads with constructed immune complexes emit a color or a fluorescent or electrochemical signal for detection. Signals can be detected by fluorescence microscopy or electrochemical sens...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Example 3 - Exosome Isolation
[0119] By constructing immune complexes on beads and encapsulating them into droplets, signals from labeled fluoresceins or chemiluminescence can be used as triggers for droplet sorting. Droplets containing target exosomes can be isolated by droplet sorting techniques including electrical sorting, mechanical sorting, or acoustic sorting. image 3 Schematic illustration of the isolation of fluorescent exosomes with desired information.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com