Drug conjugate of nucleic acid aptamer in targeted combination with CD133 protein and application of drug conjugate
A nucleic acid aptamer and drug conjugate technology, which can be used in drug combinations, medical preparations without active ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc. It can solve the problem of less cytotoxic conjugates and achieve easy Long-term storage, no immune response, strong affinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
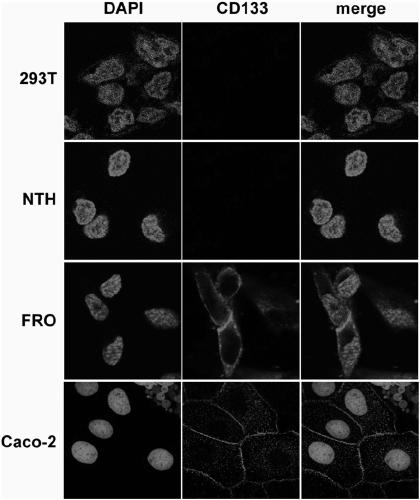
[0030] Example 1: Expression and localization of CD133 protein in different cell lines
[0031] Such as figure 1 Shown, Caco-2: colon adenocarcinoma cell; FRO: undifferentiated thyroid cancer cell; NTH: normal thyroid cell; 293T: human embryonic kidney cell line.
[0032] Confocal Microscopy was used to observe the expression of CD133 protein in different cell lines ( figure 1 ), red fluorescence (ie figure 1 The membrane-like distribution of bright spots in the four photomicrographs in the lower left corner of the center) represents the expression distribution of the membrane protein CD133 protein, and the blue fluorescence (ie figure 1 Nucleated bright spots) in each micrograph represent DAPI, indicating cell nuclei. The results showed that CD133 protein was expressed on the cell membrane in undifferentiated thyroid cancer FRO cells and colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells as a positive control group, while HEK-293T cells as a negative control group and normal thyroid cells ...
Embodiment 2
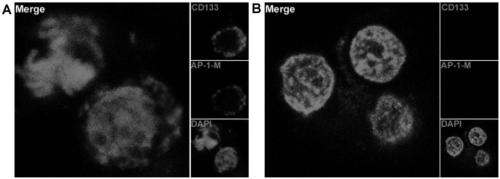
[0033] Example 2: Aptamer AP-1-M binds to CD133 positive cells and negative cells.
[0034] Such as figure 2 As shown, by using FITC to label the AP-1-M nucleic acid aptamer, HEK-293T cells overexpressing CD133 protein were regarded as positive cells, and wild-type HEK-293T cells were regarded as negative cells. The 1-M nucleic acid aptamer was incubated with positive cells and negative cells, and then observed under a laser confocal microscope to find that AP-1-M was combined with positive cells and located on the cell membrane ( figure 2 -A), while not binding to negative cells ( figure 2 -B), which also shows that AP-1-M is a targeting nucleic acid aptamer for CD133 protein.
[0035] The results show that AP-1-M is a nucleic acid aptamer that specifically binds to CD133 protein, and the affinity curve of the nucleic acid aptamer is measured by flow cytometry, and the Kd value of AP-1-M is 101.4nM .
Embodiment 3
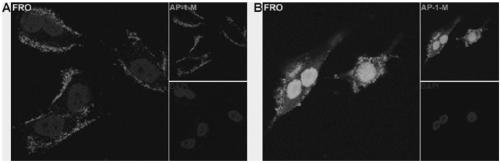
[0036] Example 3: Binding of aptamer CD133 and undifferentiated thyroid cancer cell FRO.
[0037] Such as image 3 As shown, AP-1-M and FRO cells were incubated at 4°C and 37°C for 30 minutes, respectively, and it was found that at 4°C, because the endocytosis of cells was inhibited, AP-1-M and FRO cells bound to and localized on the cell membrane ( image 3 -A); and at 37°C due to the endocytosis of the cells, AP-1-M was endocytosed into the cells by the FRO cells ( image 3 -B).
[0038] The results indicated that AP-1-M can be combined with FRO cells and located on the cell membrane and can be endocytosed into the cells to achieve the purpose of targeted delivery.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com